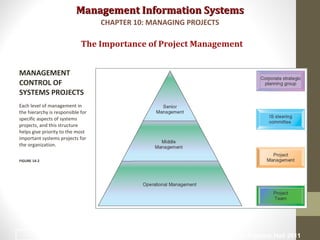
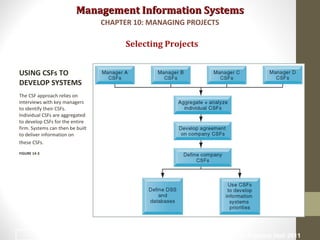
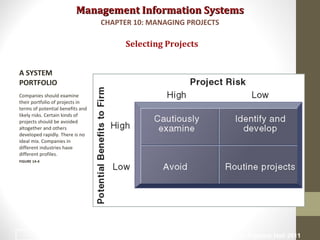
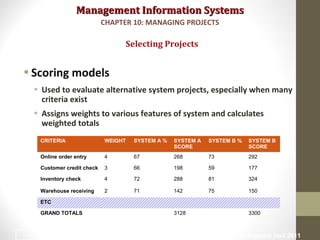
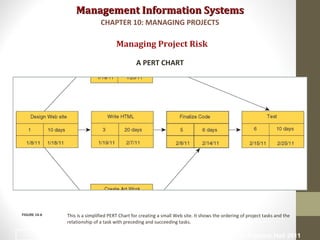
Project management is essential for developing information systems. Firms use various methods to select projects that align with business goals like portfolio analysis and scoring models. It is important to establish the business value of projects using methods like capital budgeting that measure costs and benefits. Managing project risk is also key, and risk is influenced by factors like project size, structure, and experience with technology. Effective change management is needed to help users adapt to new systems.