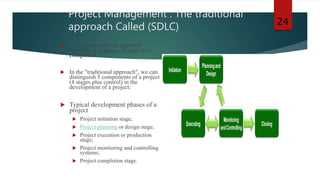
This document discusses project management for information systems. It begins with an introduction to project management and why learning it is important. It then lists the objectives of the document, which are to explain the main tasks of project managers, introduce software project management, discuss project planning and risk management, and show how schedules are represented graphically. The document also defines what a project and project management are, and discusses the traditional approach to project management called the System Development Life Cycle (SDLC).