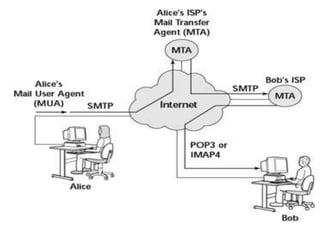
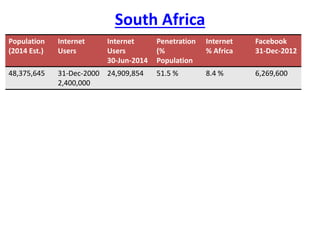
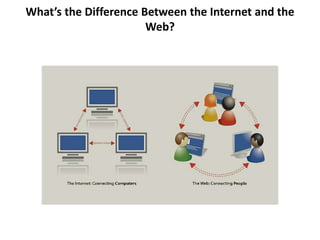
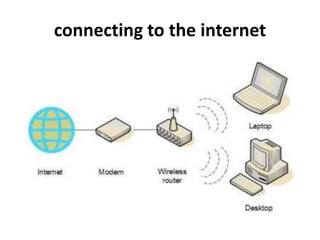
The document provides information about connecting to and using the internet. It defines key terms like internet, world wide web, IP address, domain name, and email. It discusses different types of internet connections like dial-up, DSL, cable, satellite, and wireless. It also explains the hardware needed like modems, routers, and network cards. It provides an overview of how to choose an internet service provider and types of internet access. It discusses communication protocols, web browsers, and challenges for learning more.















![Host name
In computer networking, a hostname (archaically nodename[1]) is a label that
is assigned to a device connected to a computer network and that is used to
identify the device in various forms of electronic communication such as
the World Wide Web, e-mail or Usenet.
Hostnames may be simple names consisting of a single word or phrase, or
they may be structured.
c-61-123-45-67.hsd1.co.comcast.net](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter1html-150417062458-conversion-gate02/85/Chapter-1-html-20-320.jpg)