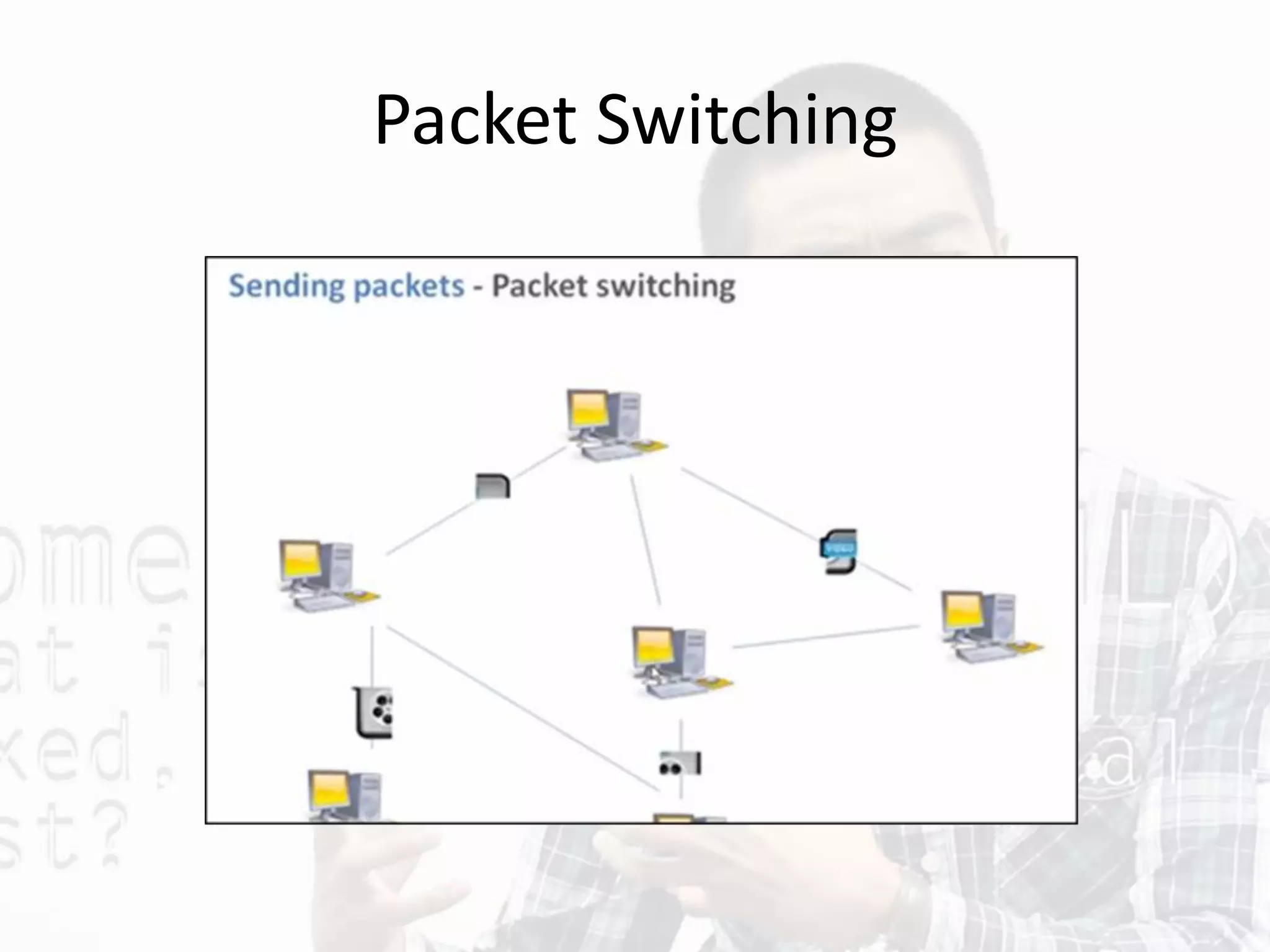
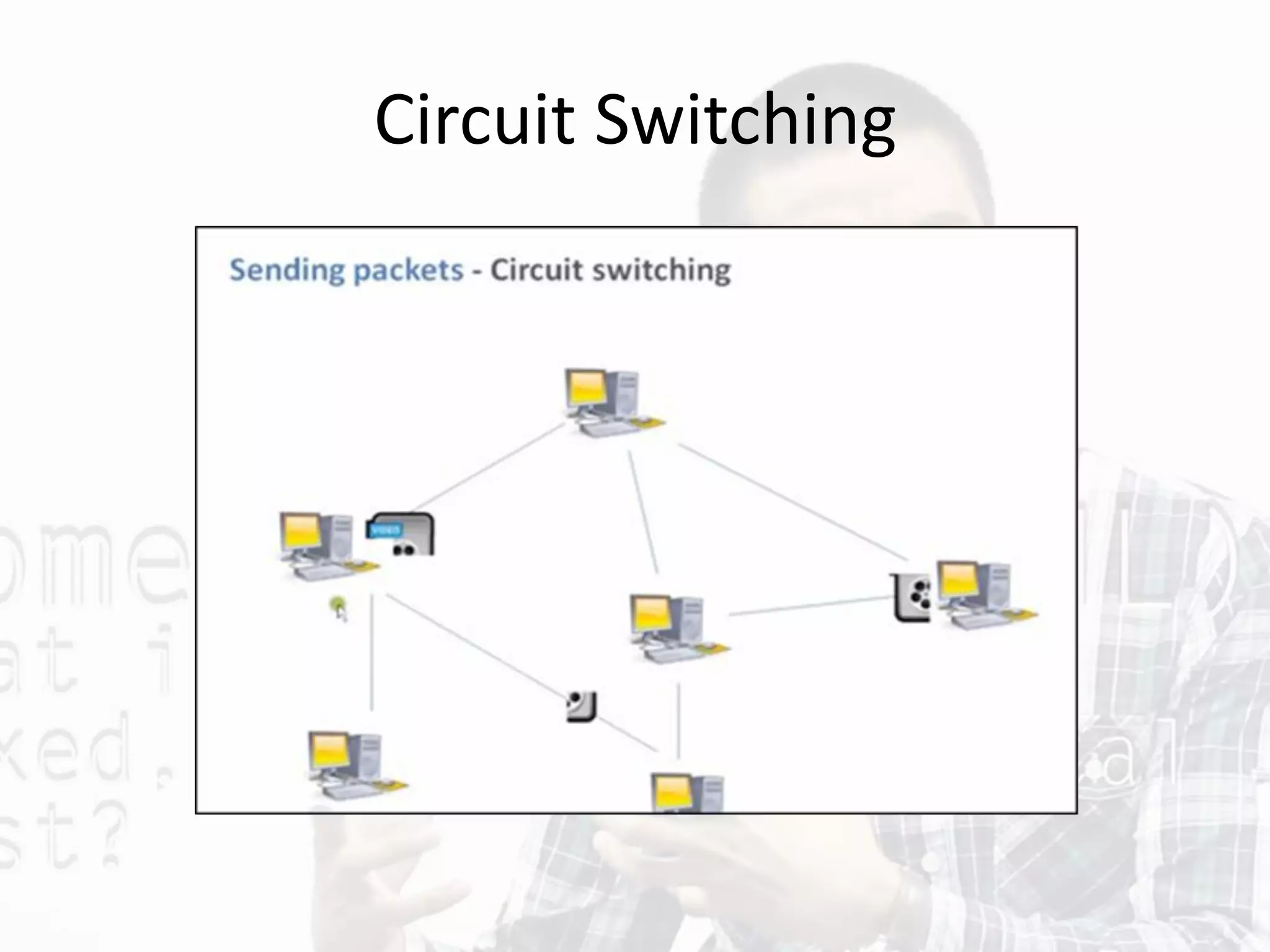
This document discusses different types of internet connections and technologies. It describes how ISPs (Internet service providers) provide access to individuals and companies. It also explains WAP (Wireless Application Protocol) which standardizes how wireless devices can access the internet. Finally, it summarizes various types of internet connections including dial-up, wireless, cable, leased lines, and hotspots.