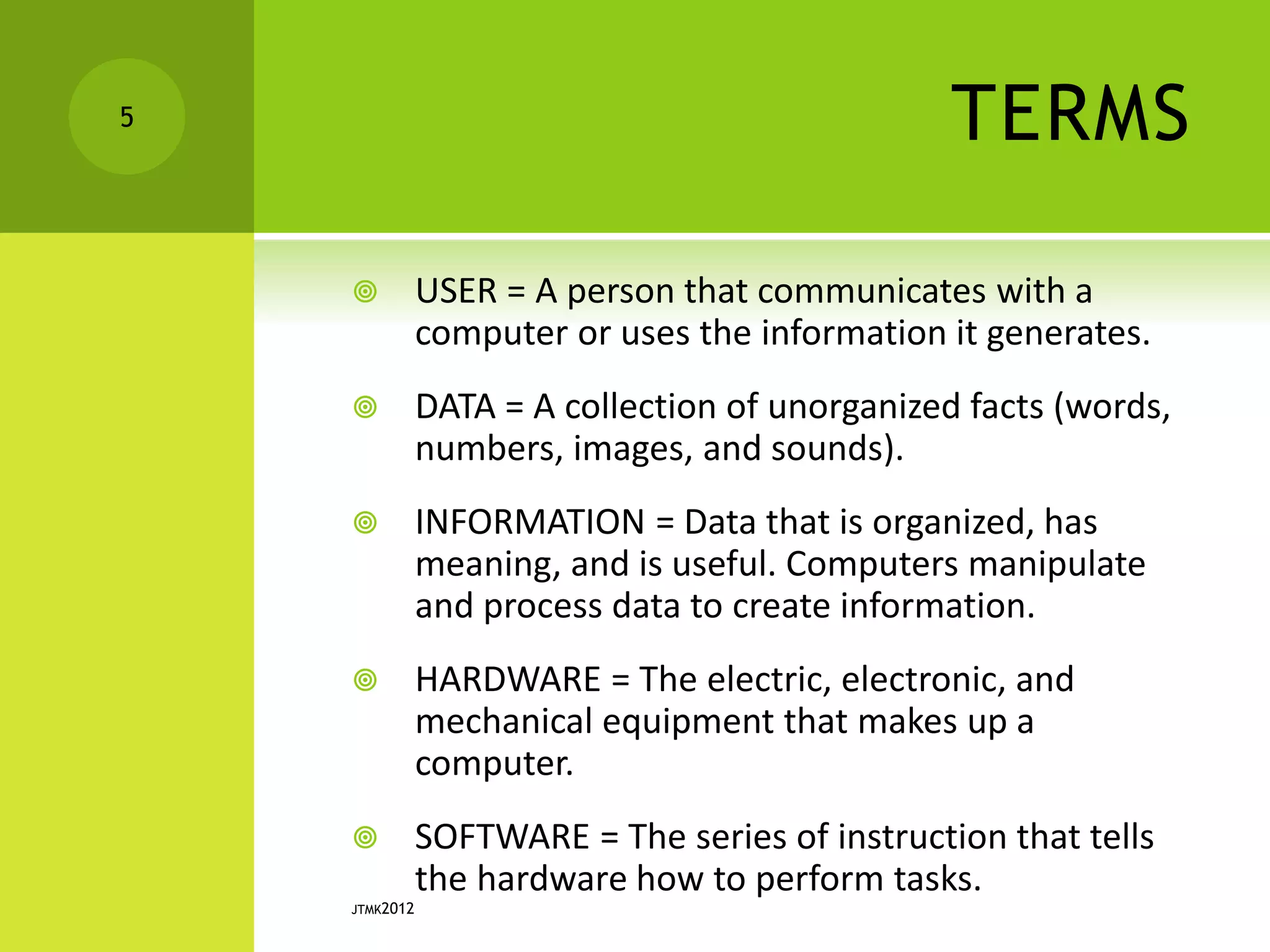
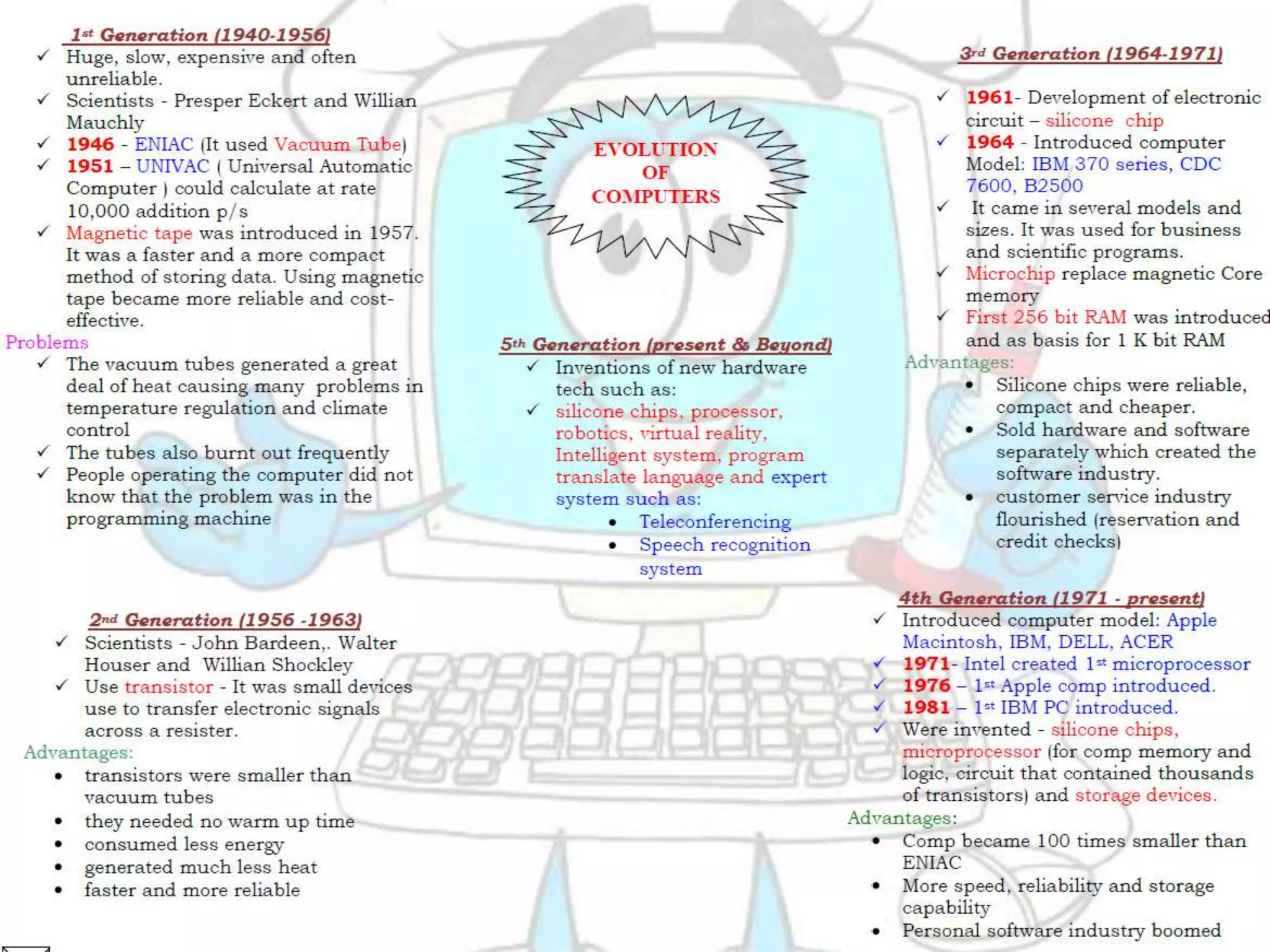
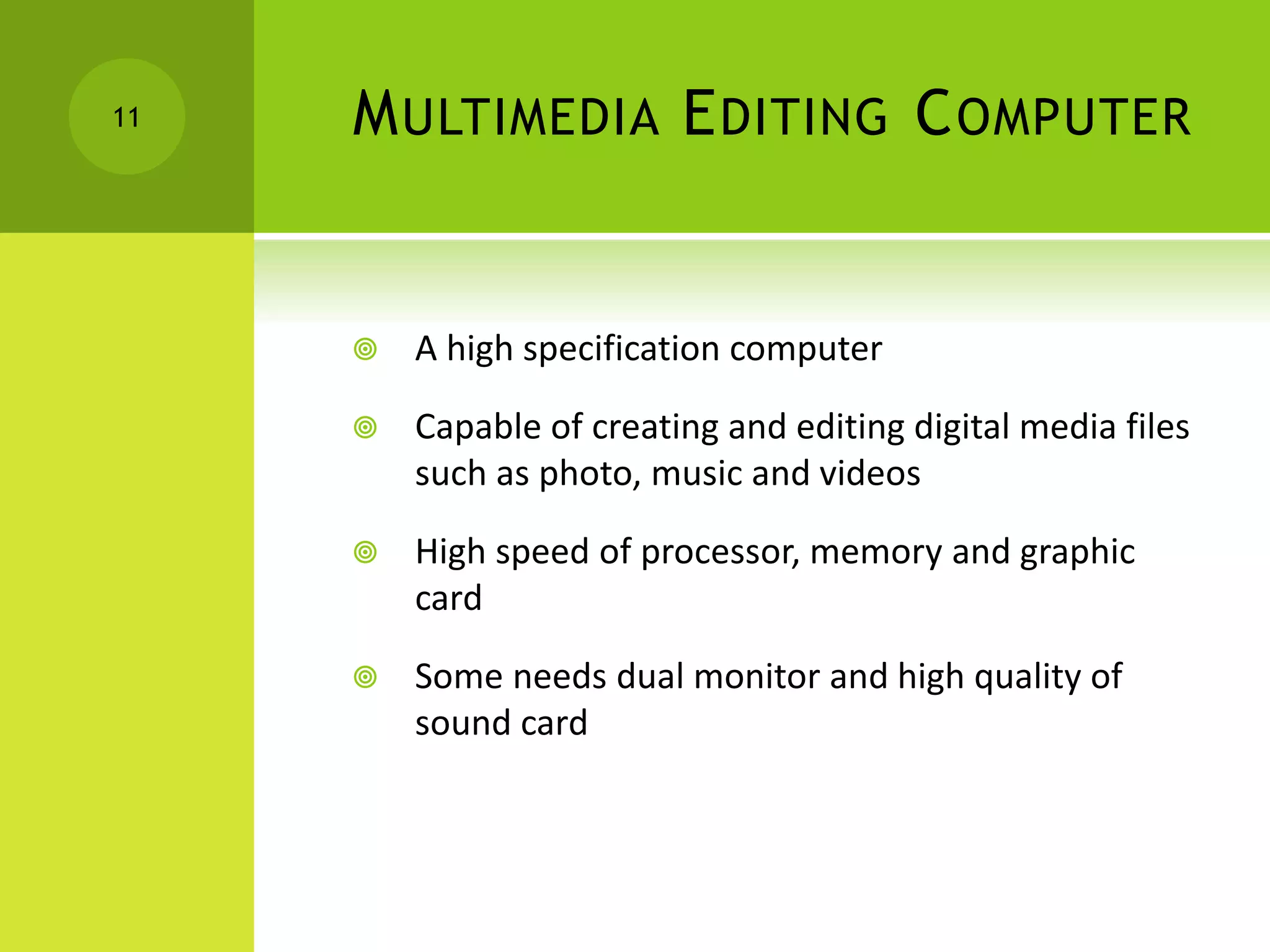
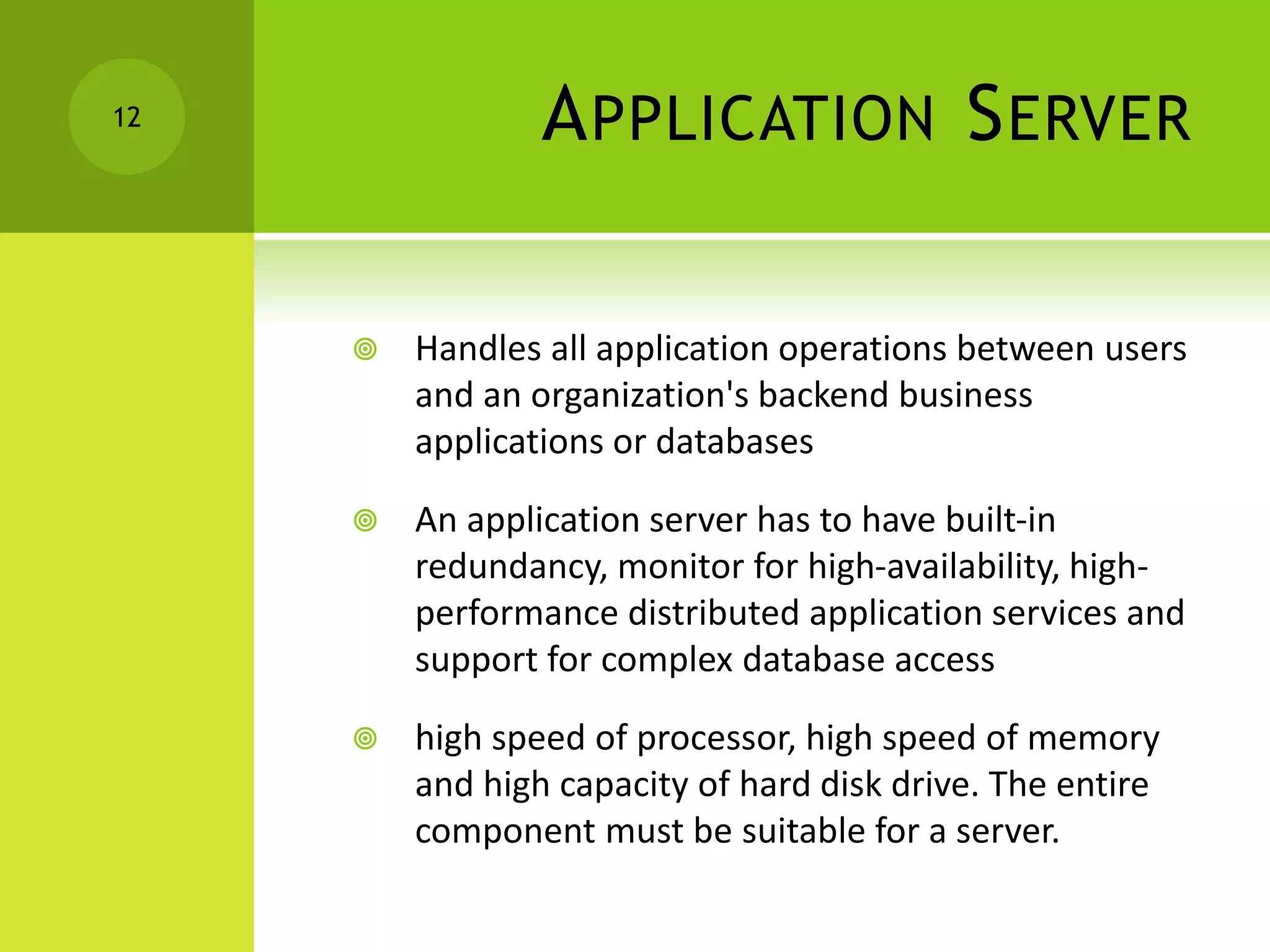
This document provides information about different types of computers and their uses. It defines what a computer is and key terms like users, data, information, hardware, and software. It then describes the evolution of computers and lists the technical specifications of different types of computers. Some types covered include home computers for basic tasks, gaming computers for intensive games, and multimedia computers for editing media. It also discusses application servers for running business applications, and the characteristics of personal computers, servers, mainframes, and supercomputers. The document concludes by covering system software like operating systems and application software.