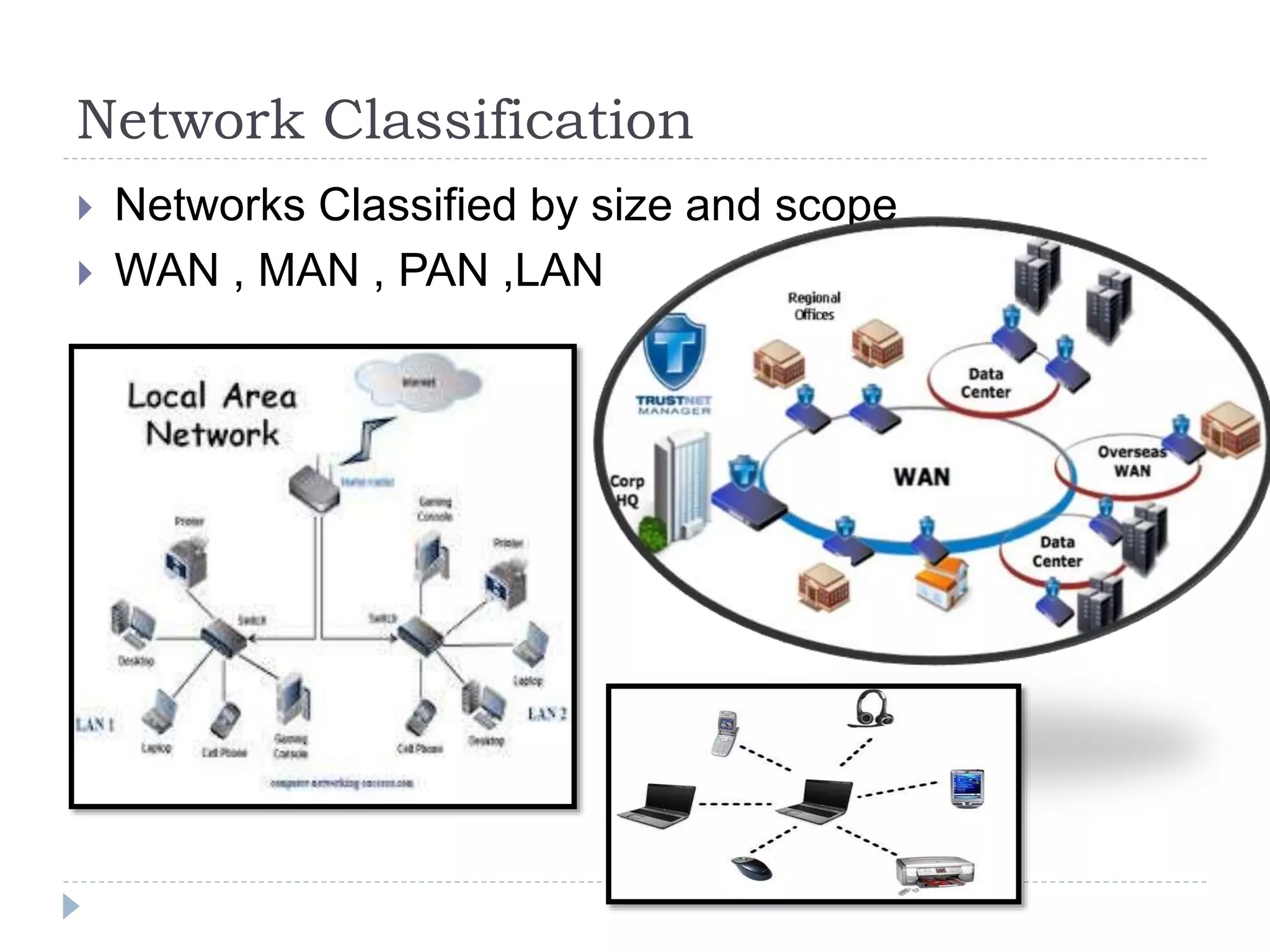
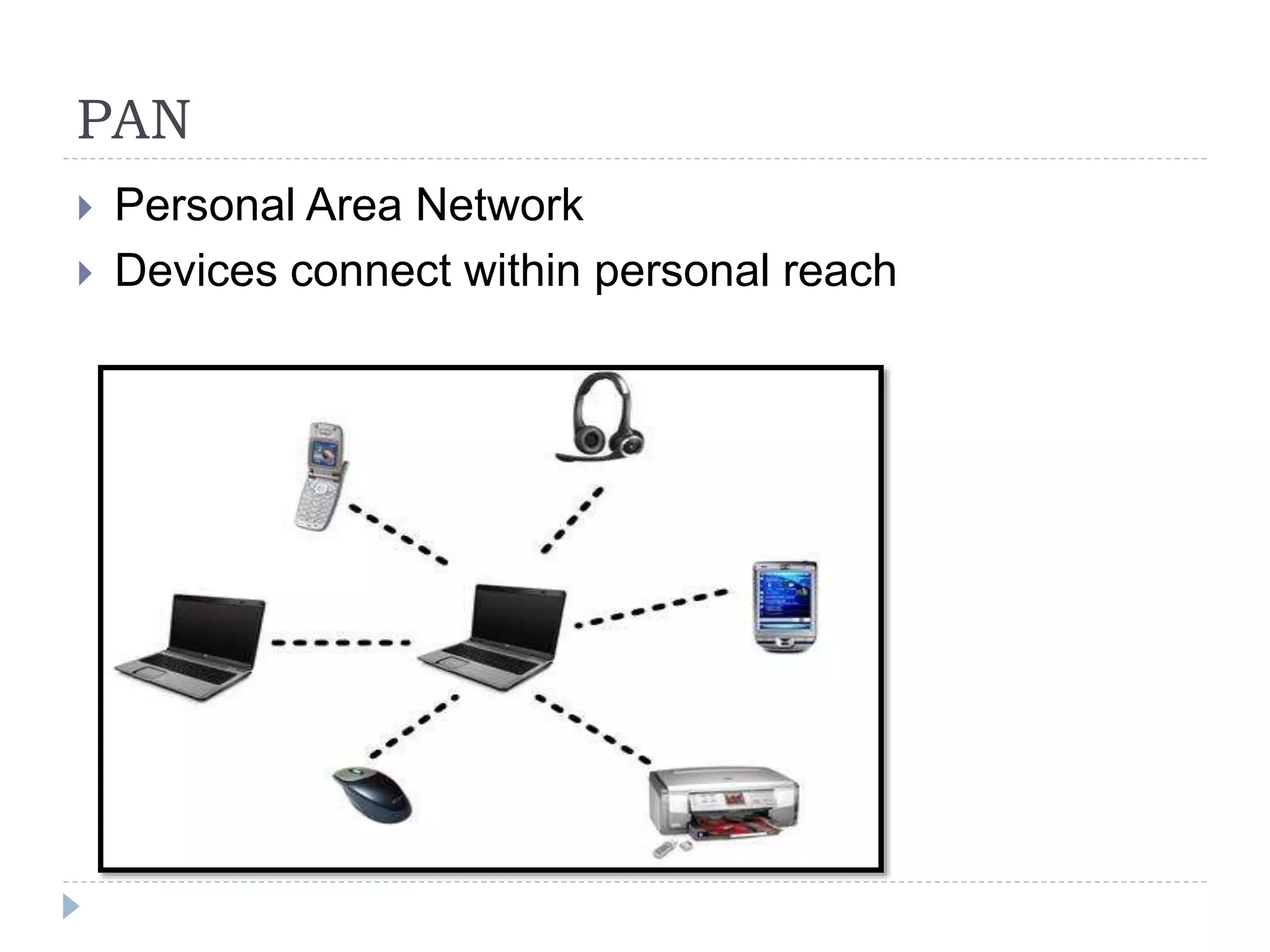
The document discusses different types of computer systems. It describes supercomputers as the largest type used for complex tasks like simulations. Mainframes are less powerful than supercomputers and are used by large organizations. Mini computers fall between mainframes and microcomputers. Microcomputers are generally personal computers that use x86 architecture and Windows. Other computer types discussed include laptops, netbooks, servers, PDAs, and embedded systems in devices like cars and planes. The document also covers computing environments like home, business, and networking.