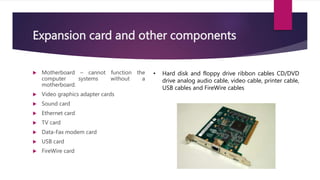
The document provides an overview of computer systems including:
1) It describes the main components of a computer system including hardware, software, firmware, and users.
2) It explains the evolution of computers from early mechanical calculating devices to modern electronic computers.
3) It outlines the four generations of computers and how they progressed from using vacuum tubes to integrated circuits.