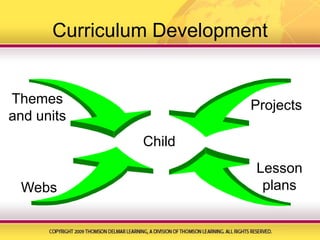
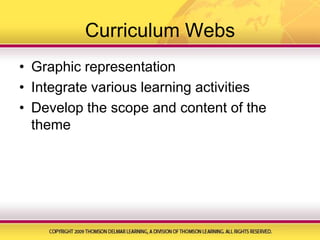
The document discusses various aspects of developing curriculum for early childhood education, including that curriculum should be child-centered, involve families, and encourage learning through play and doing. It also describes several popular curriculum models like Montessori, Head Start, Bank Street, and Reggio Emilia. Special considerations for multiculturalism, children with special needs, and managing behavior are addressed. The document provides guidance on creating age-appropriate indoor and outdoor environments, selecting materials, integrating technology, and using themes, projects, and lesson plans in curriculum development. It emphasizes the importance of ongoing observation and assessment to evaluate children's learning and development.