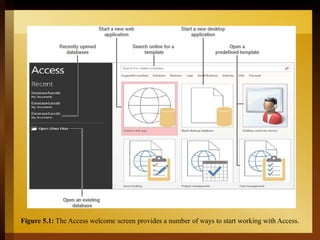
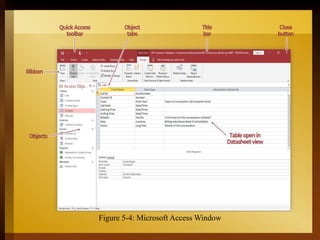
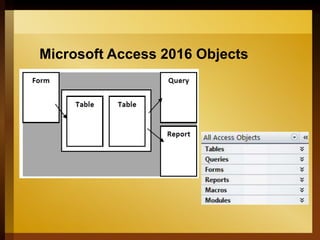
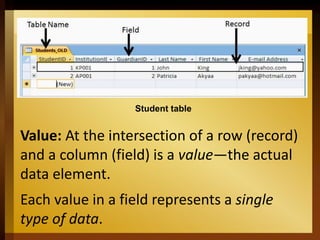
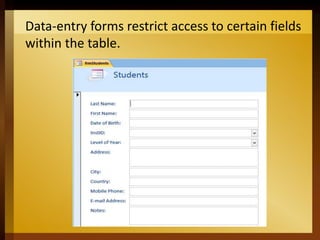
The document provides an overview of Microsoft Access 2016, a database management system designed for efficient data storage and retrieval. It explains key components such as tables, queries, forms, and reports, emphasizing their roles in organizing and managing data. The document also includes instructions for getting started with Access, including creating and opening databases.