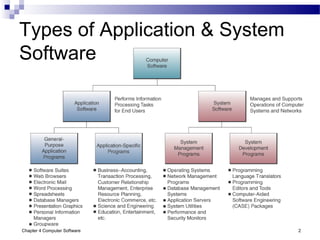
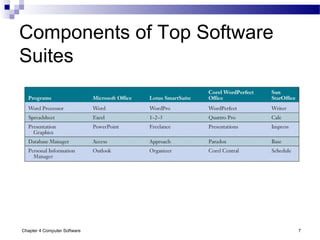
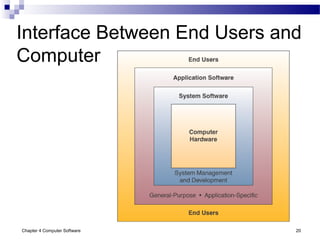
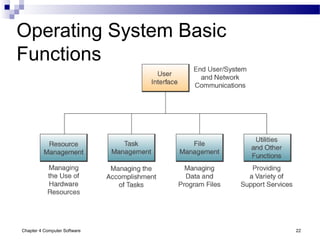
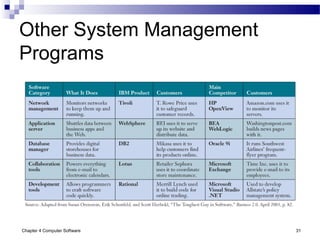
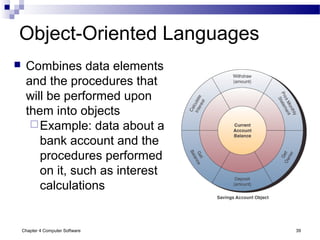
Chapter 4 of 'Management Information Systems' by O'Brien and Marakas discusses computer software, including types of application and system software, such as general-purpose and custom software. It covers tools for productivity, integrated packages, and the roles of operating systems, programming languages, and licensing in software development. The chapter emphasizes application software's functionality, user interfaces, and trends like open-source licensing.