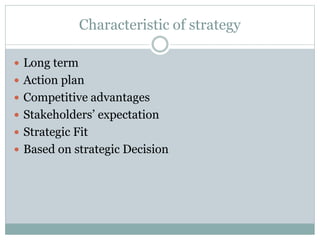
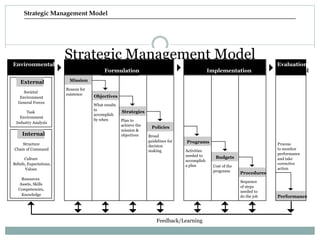
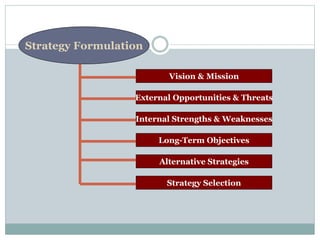
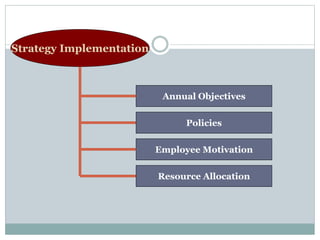
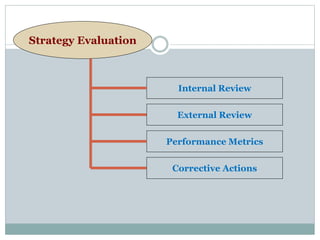
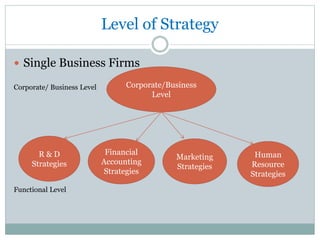
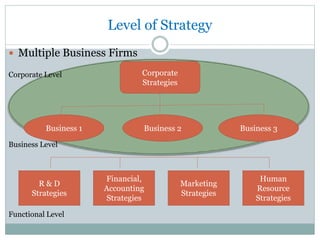
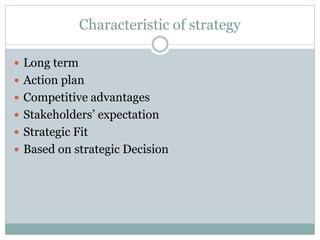
Strategic management involves developing a strategy to achieve long-term organizational objectives. It is a process that includes formulating strategy, implementing strategy, and evaluating strategy. Strategic decisions require top management involvement, large resource commitments, and consideration of external factors. Strategies can be formulated at the corporate, business, and functional levels. The strategic management process helps organizations effectively plan for and adapt to changes in their environment.