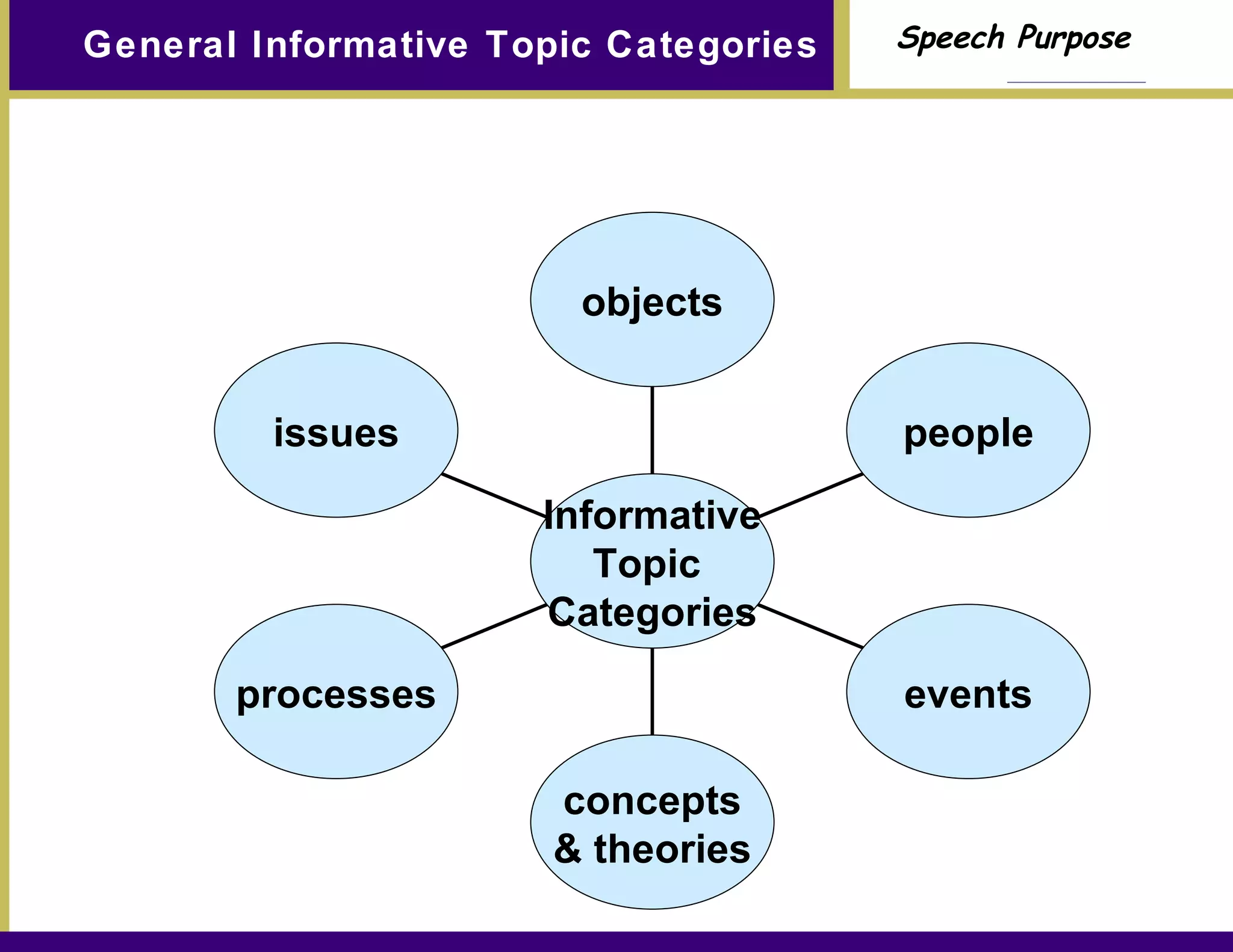
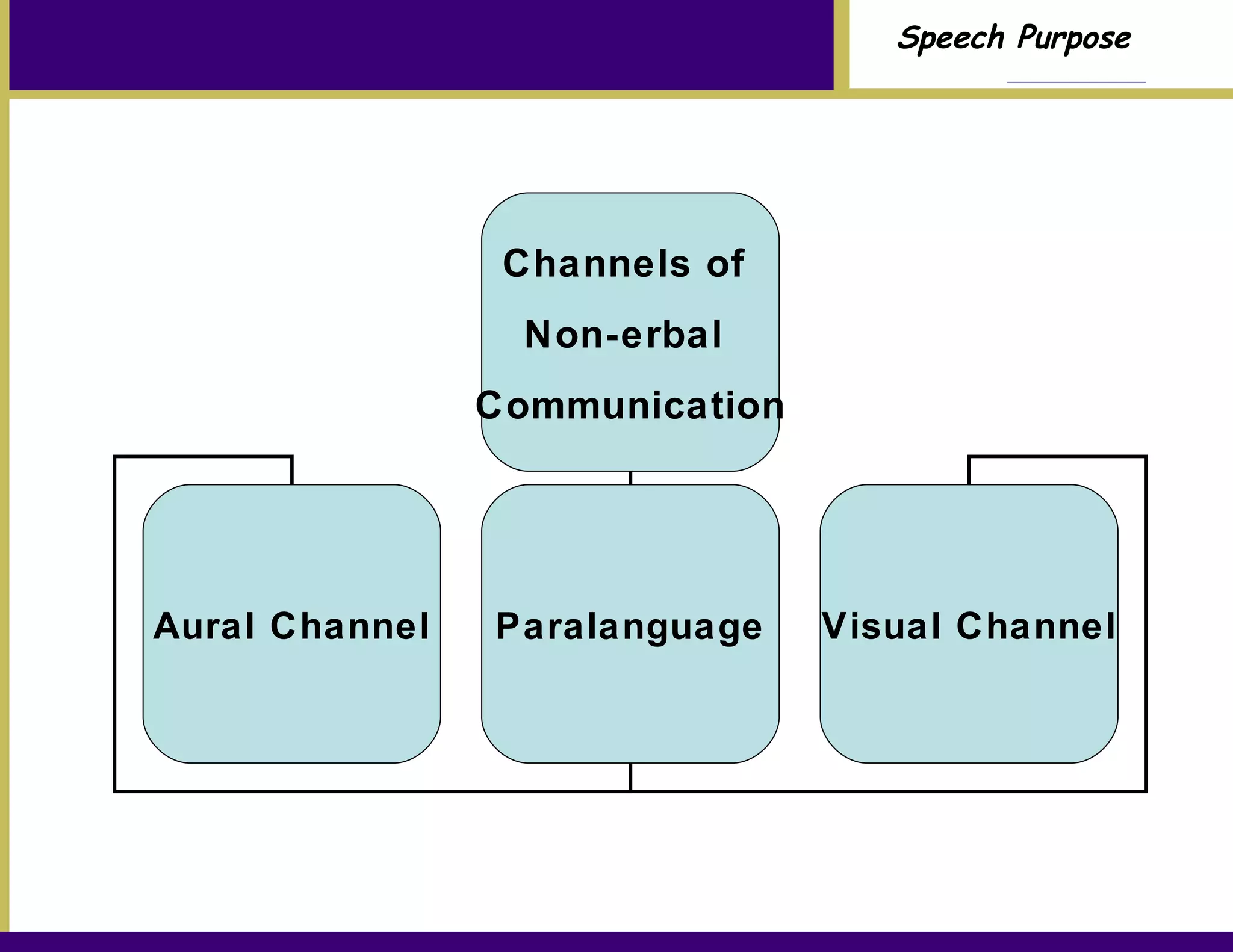
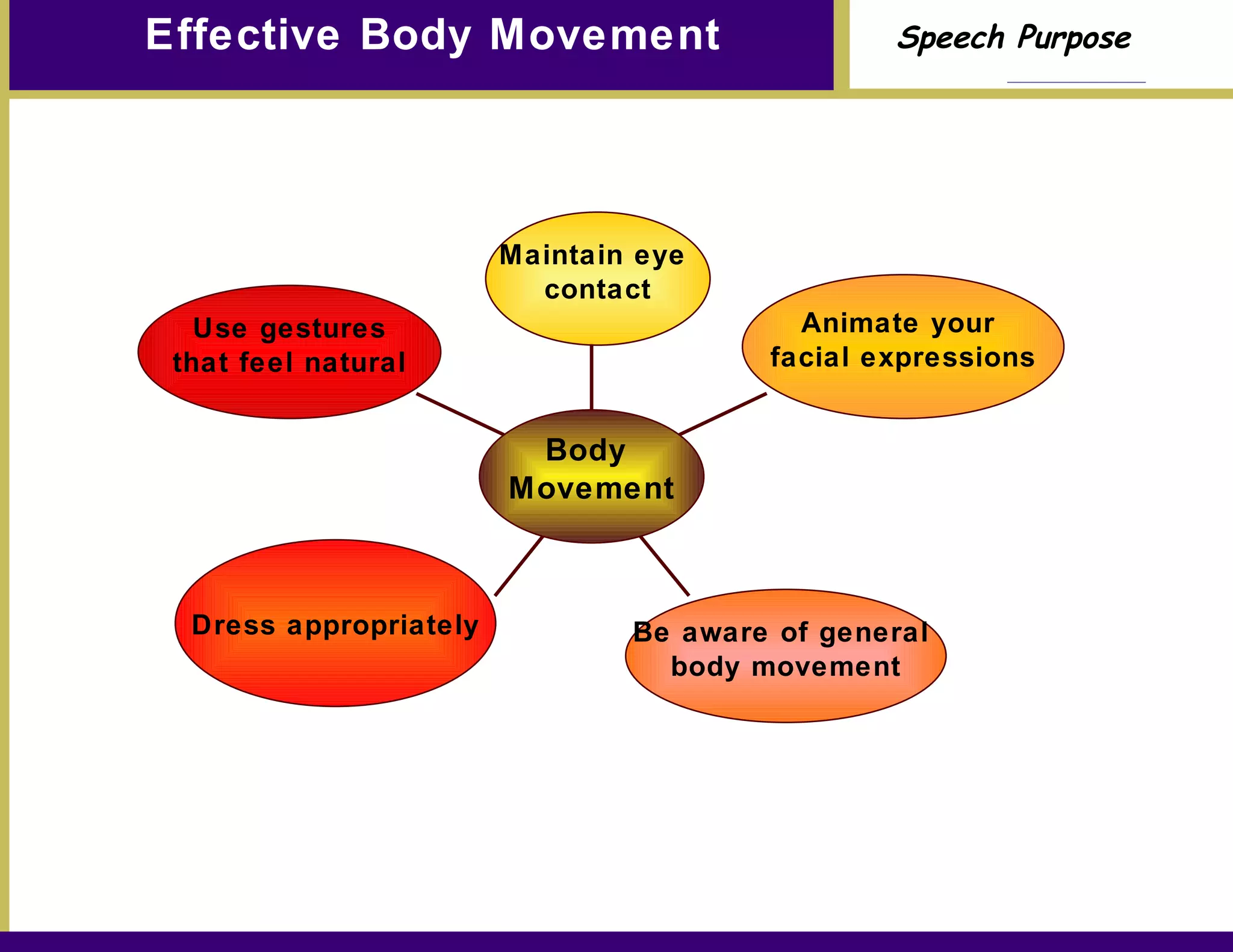
Chapter 7 discusses the purpose of speech, particularly the importance of informing and persuading an audience. It emphasizes the steps to develop a clear topic, general purpose, specific purpose statement, and thesis statement, while highlighting the role of non-verbal communication and professional presentation. The chapter concludes with practical advice for effective delivery and speaker credibility.