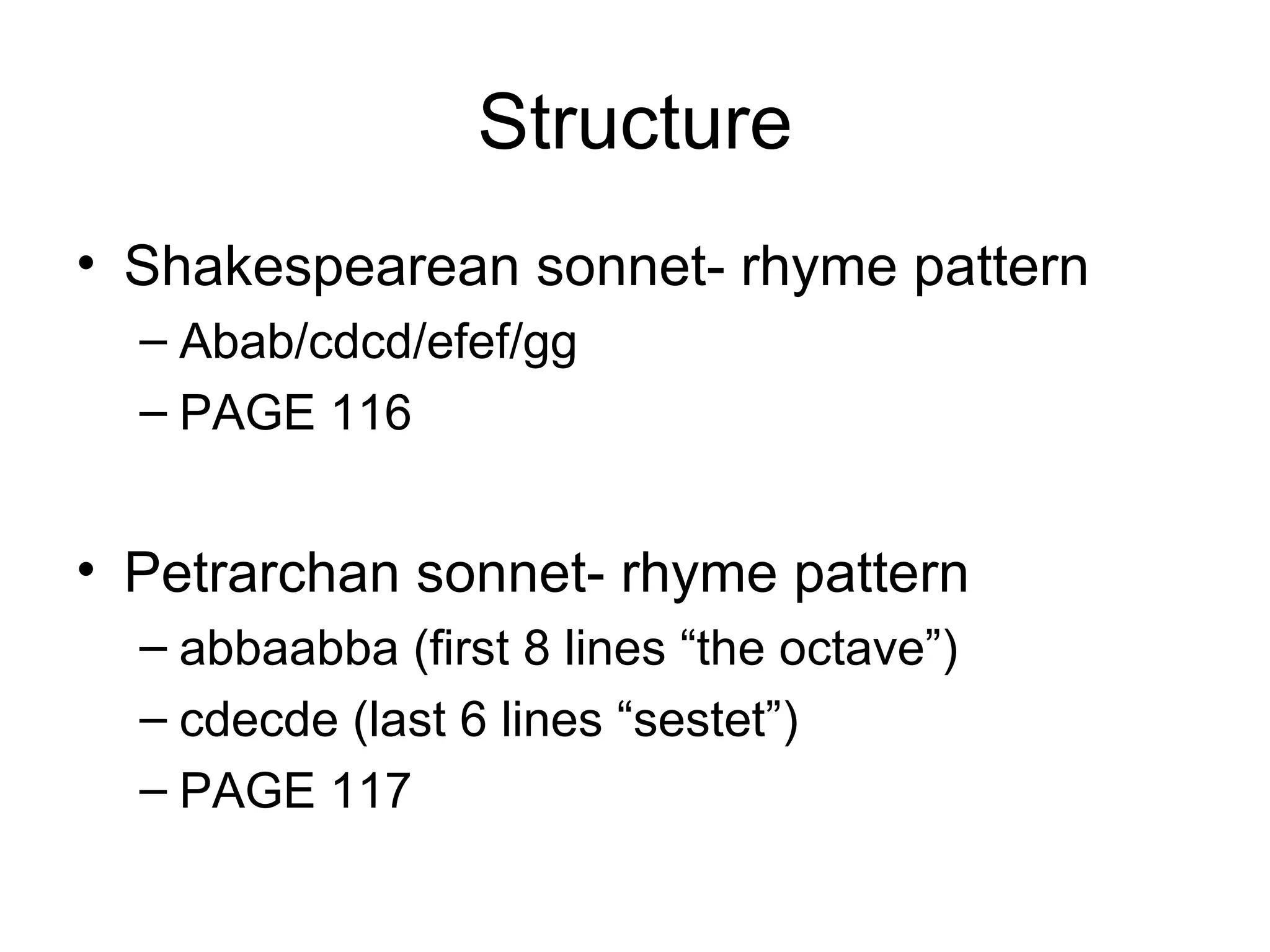
The document provides an overview of different elements of poetry including characterization, point of view, plot, setting, theme, diction, imagery, figurative language, rhythm, sound, structure, symbolism, and free verse. It also provides tips for analyzing poems based on these different elements and outlines assignments for students to write poems using various poetic techniques.