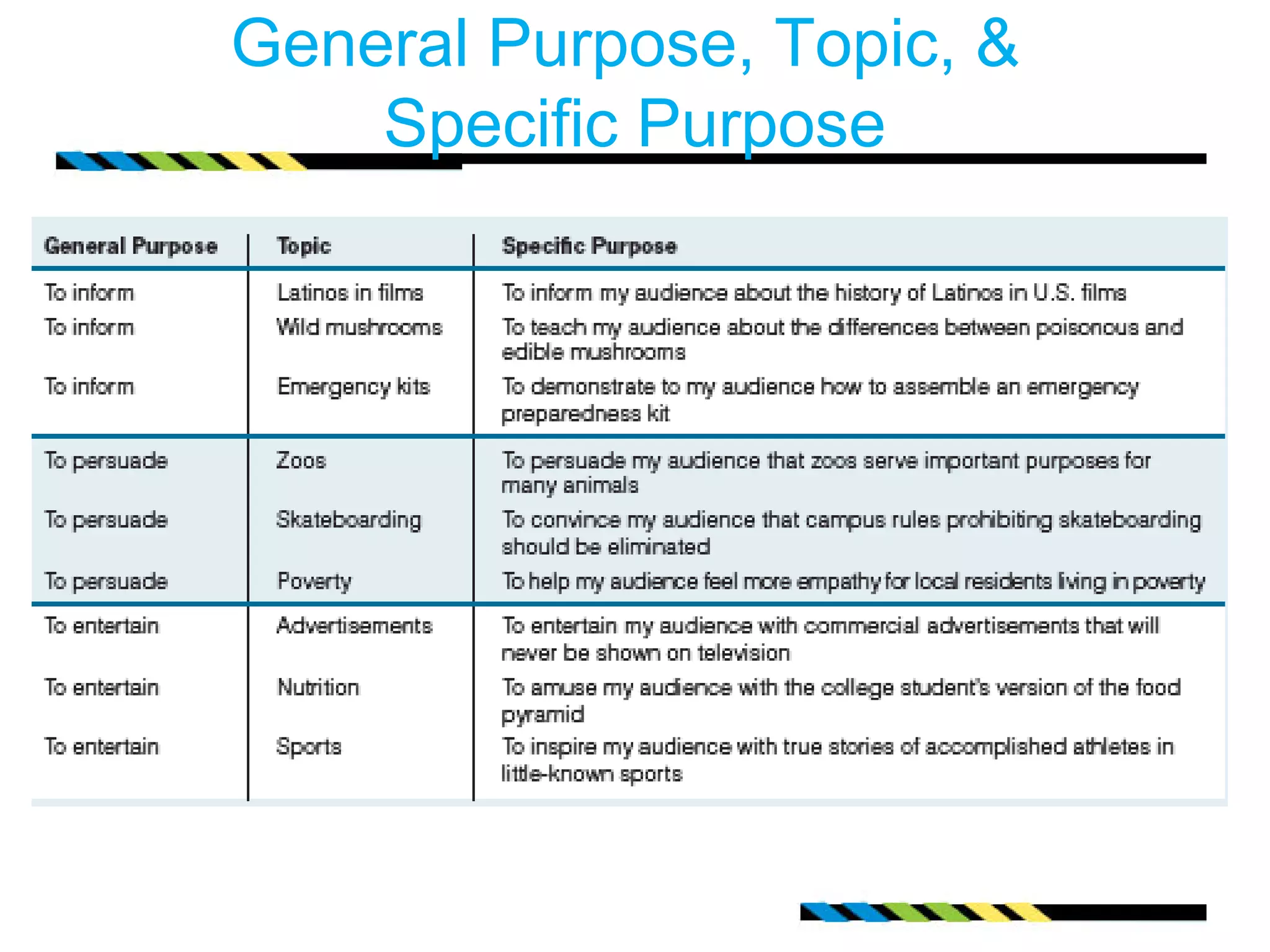
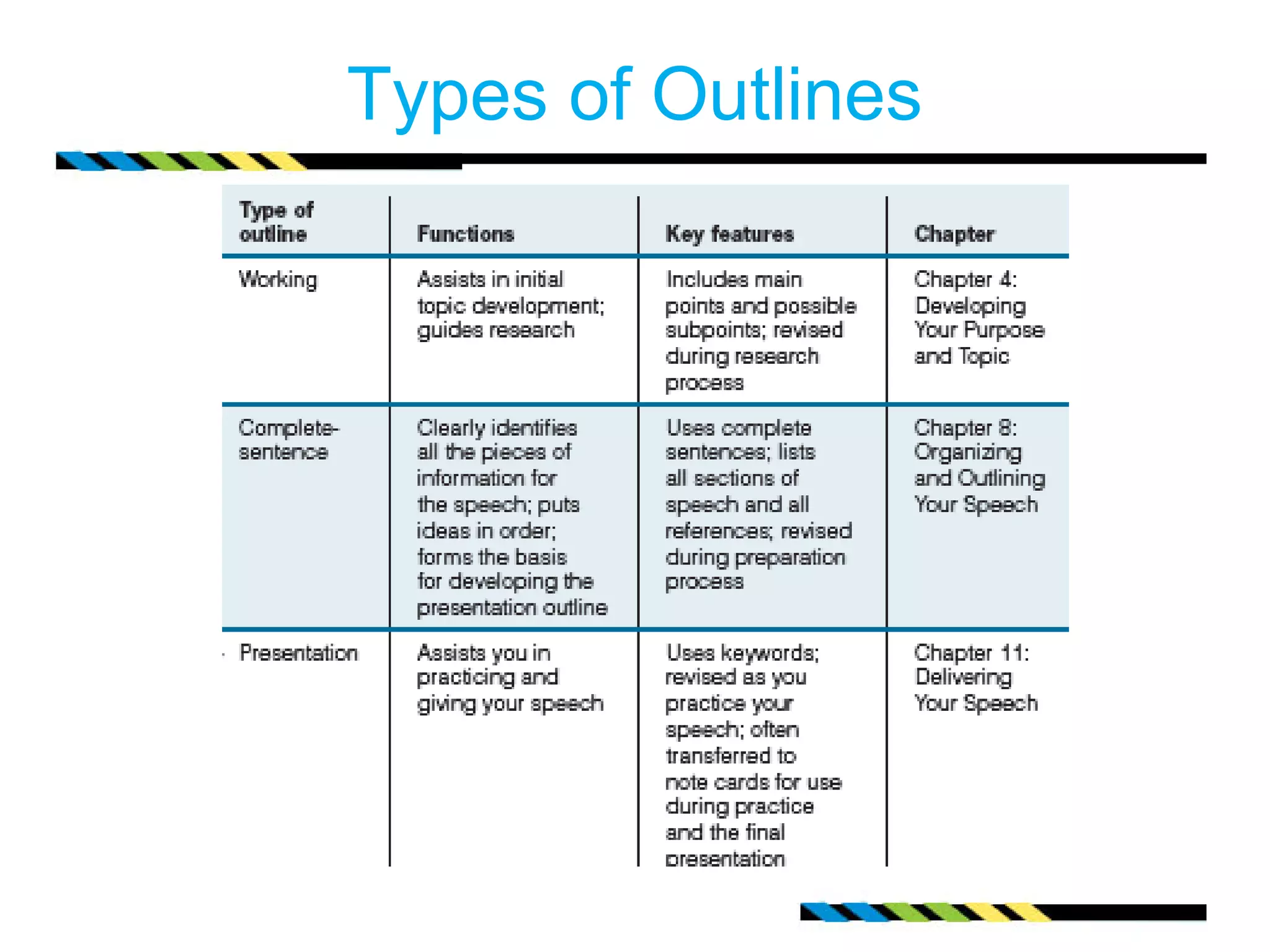
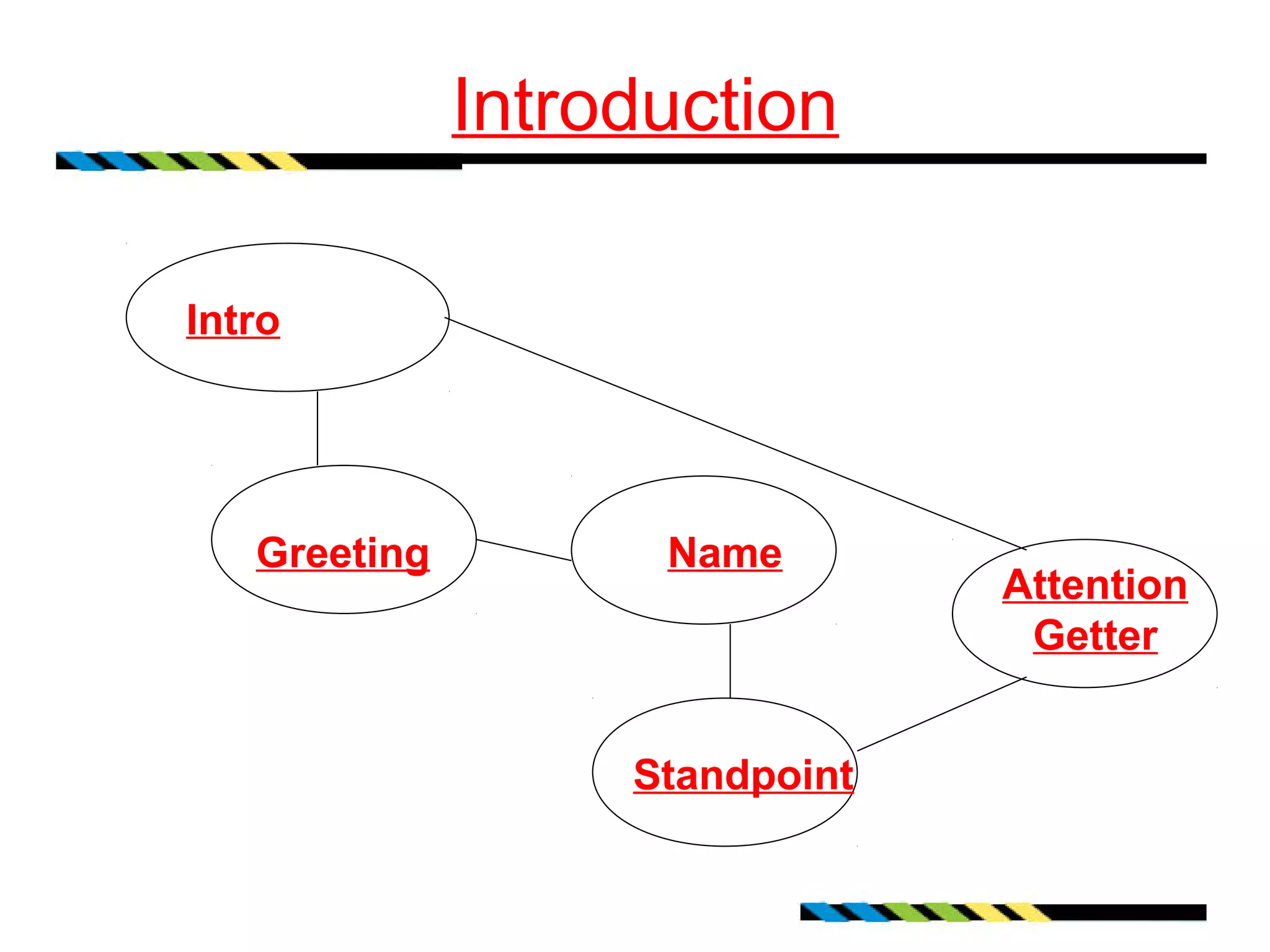
This document provides guidance on developing the purpose and topic for a speech. It discusses determining the general purpose as either to inform, persuade, or entertain. It also covers brainstorming possible topics by considering interests, audience, resources, and time. The document emphasizes identifying the specific purpose or message for the audience. It recommends formulating a thesis statement that captures the central idea. Finally, it offers tips for building an outline to guide topic development and keep the speaker focused on the general and specific purposes.