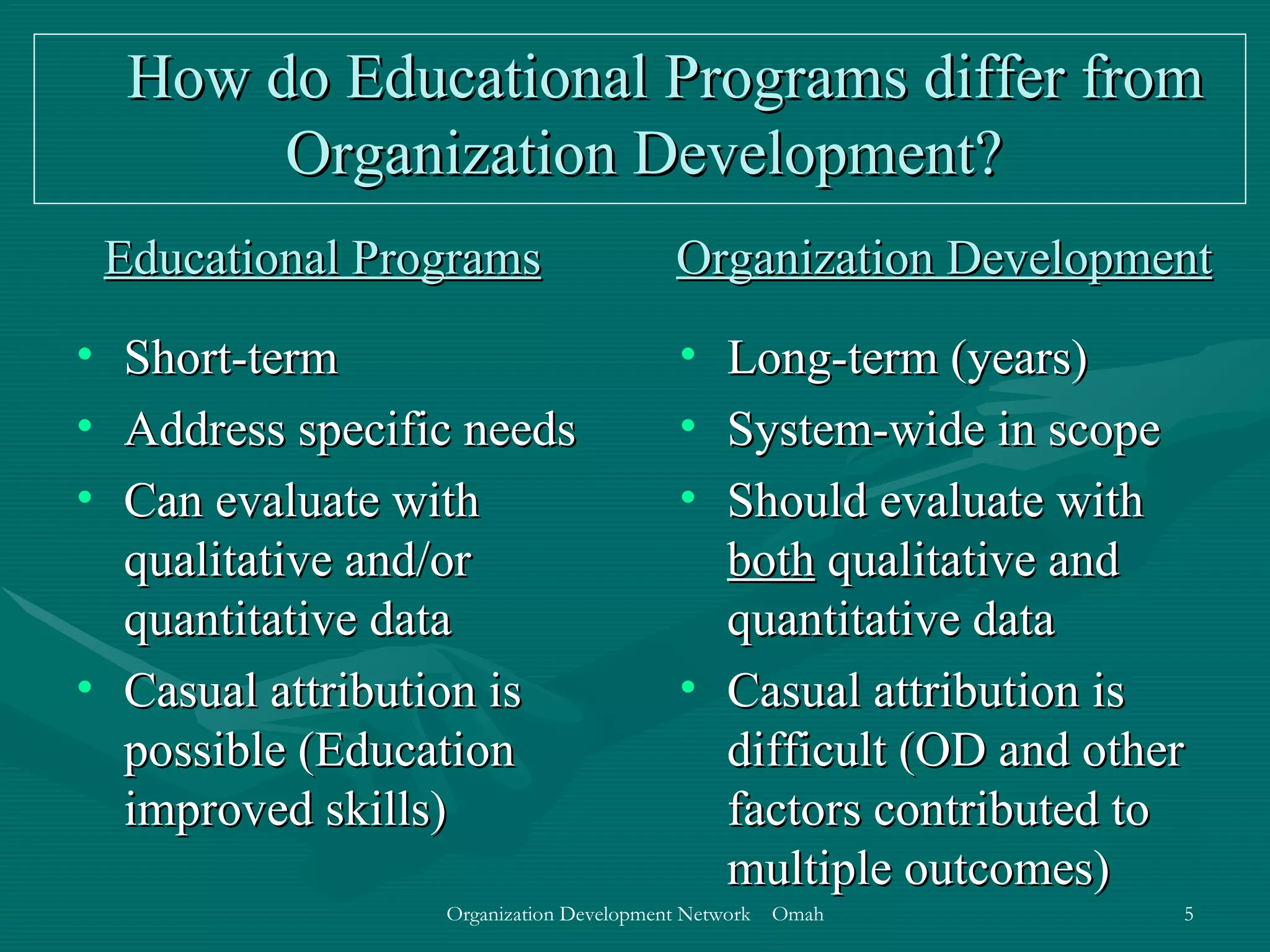
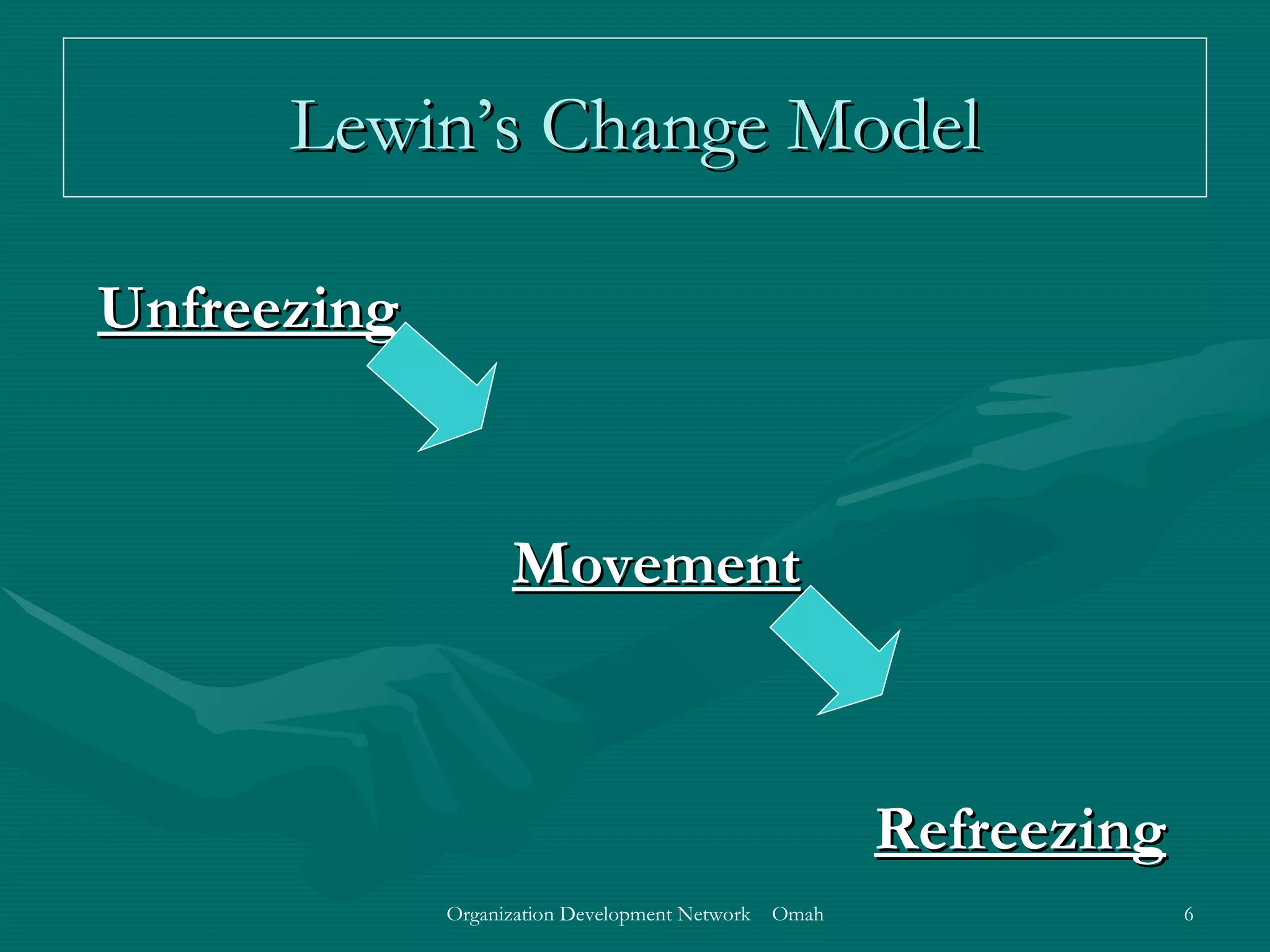
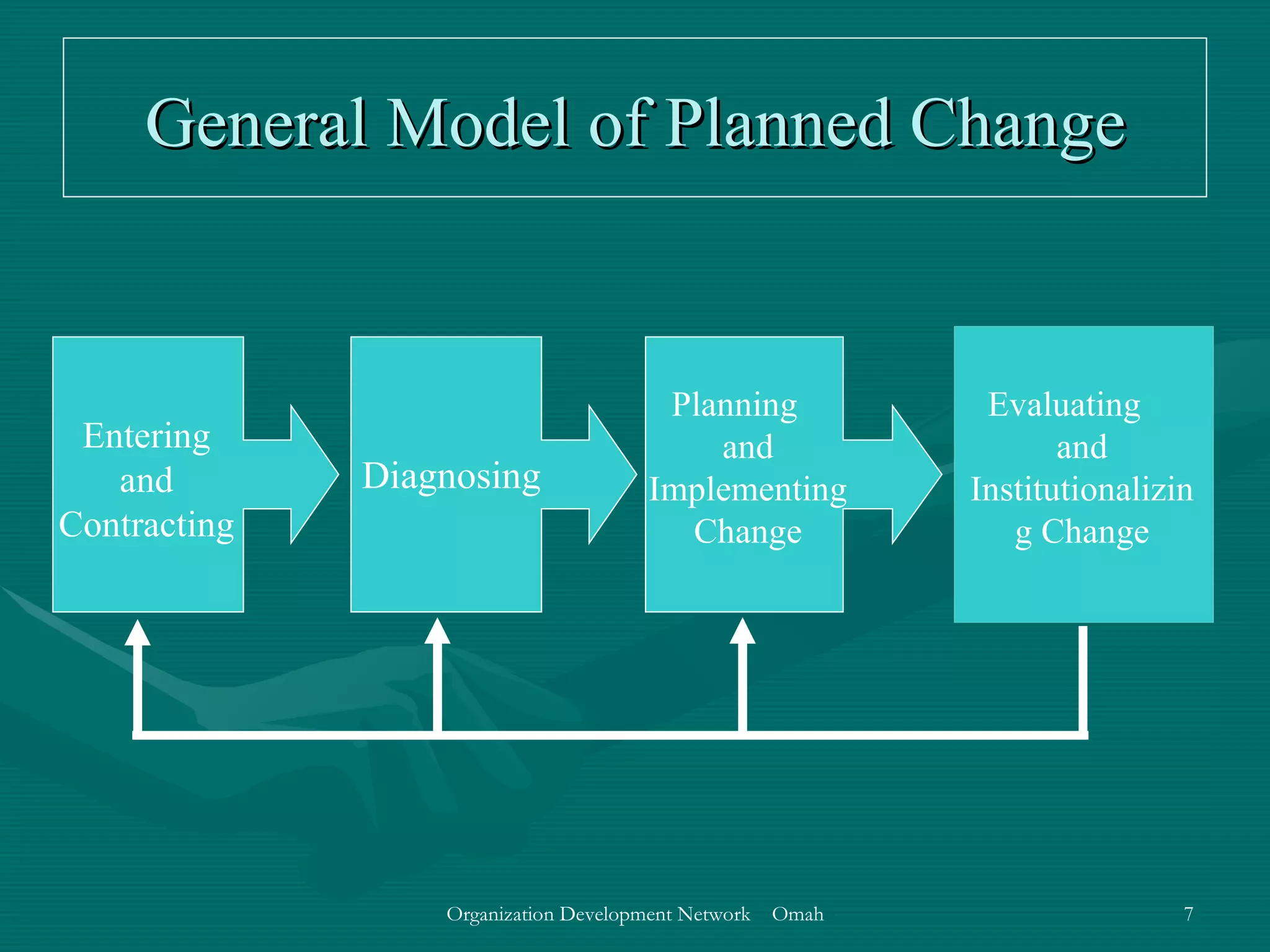
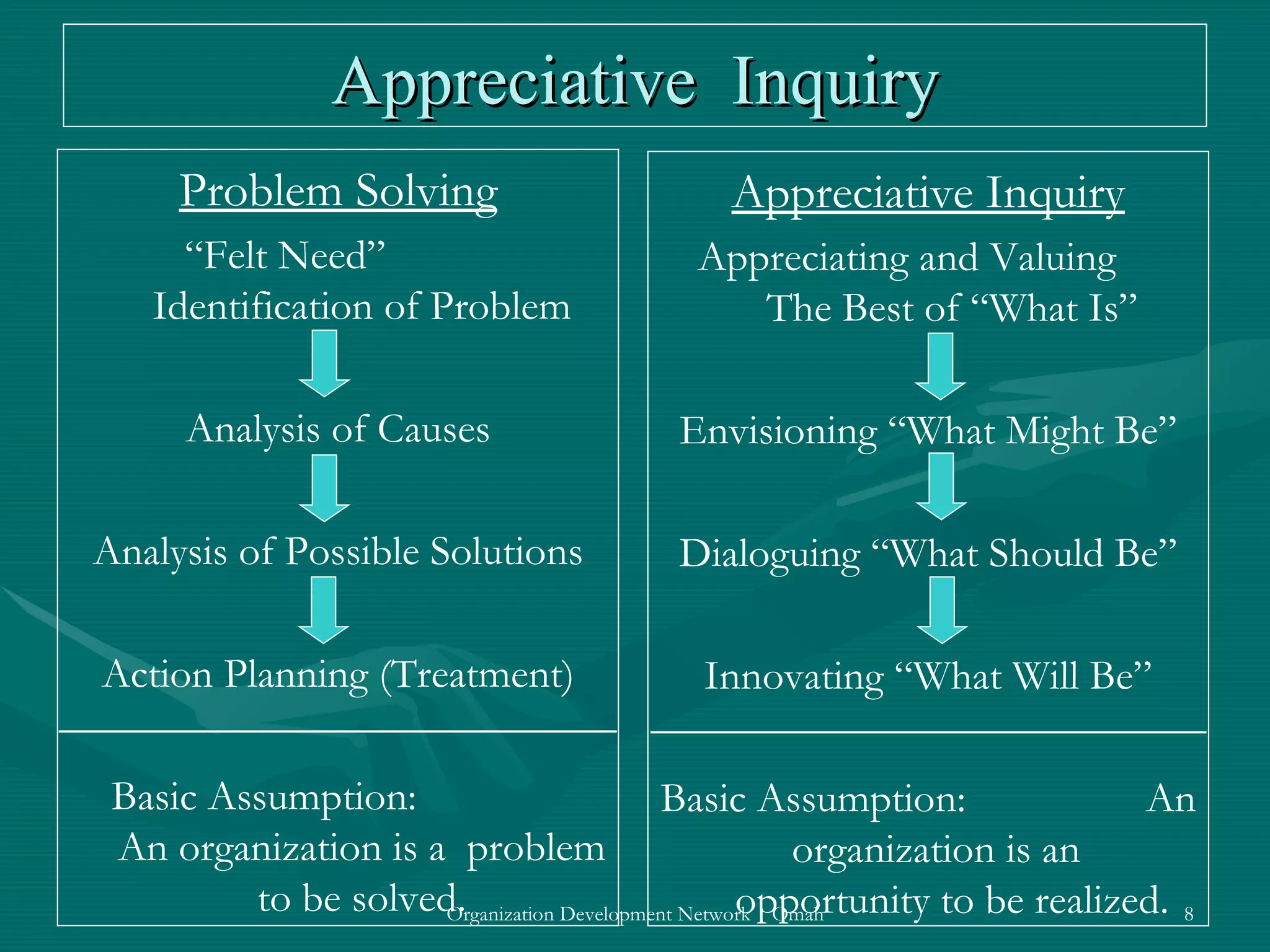
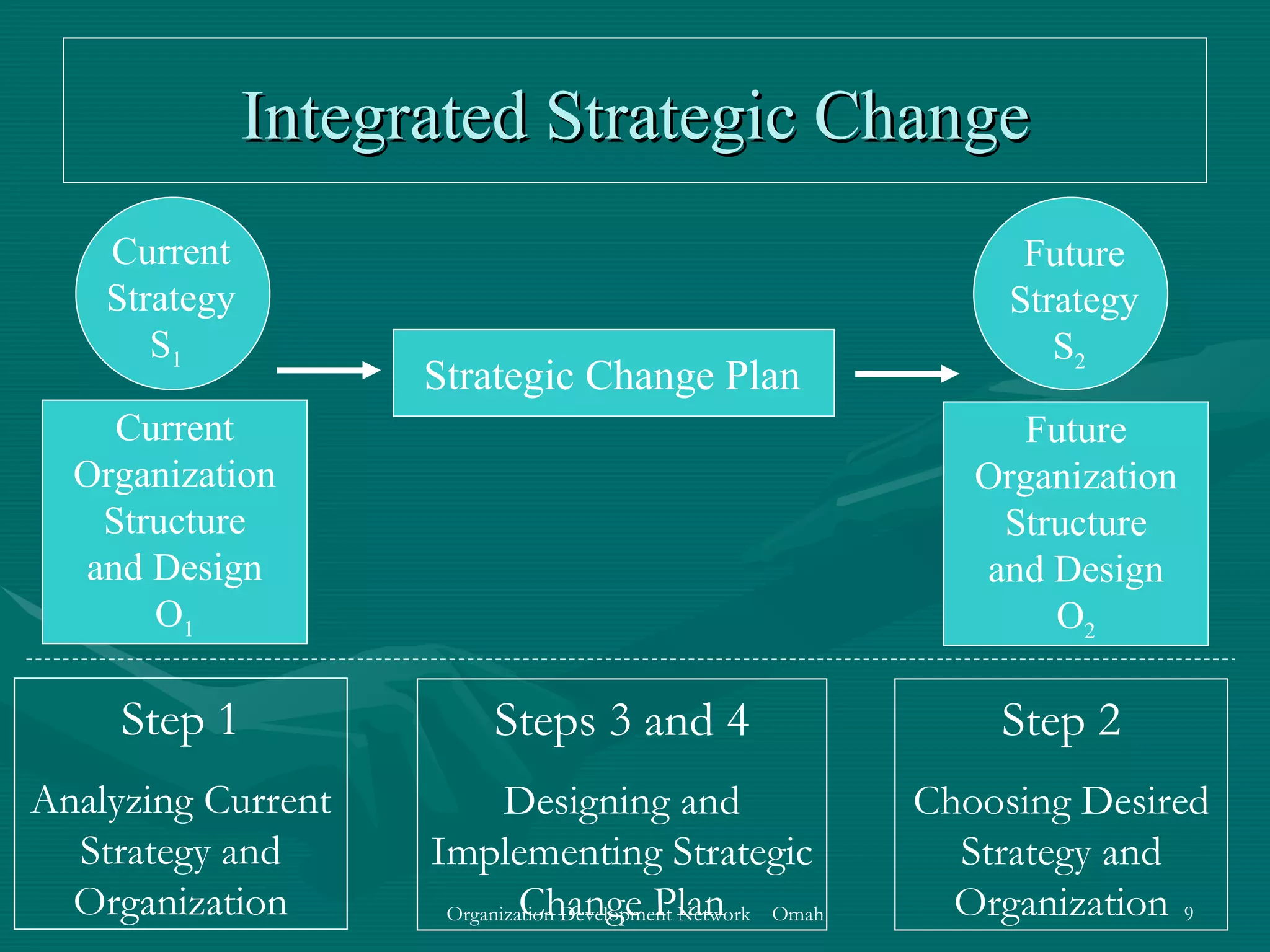
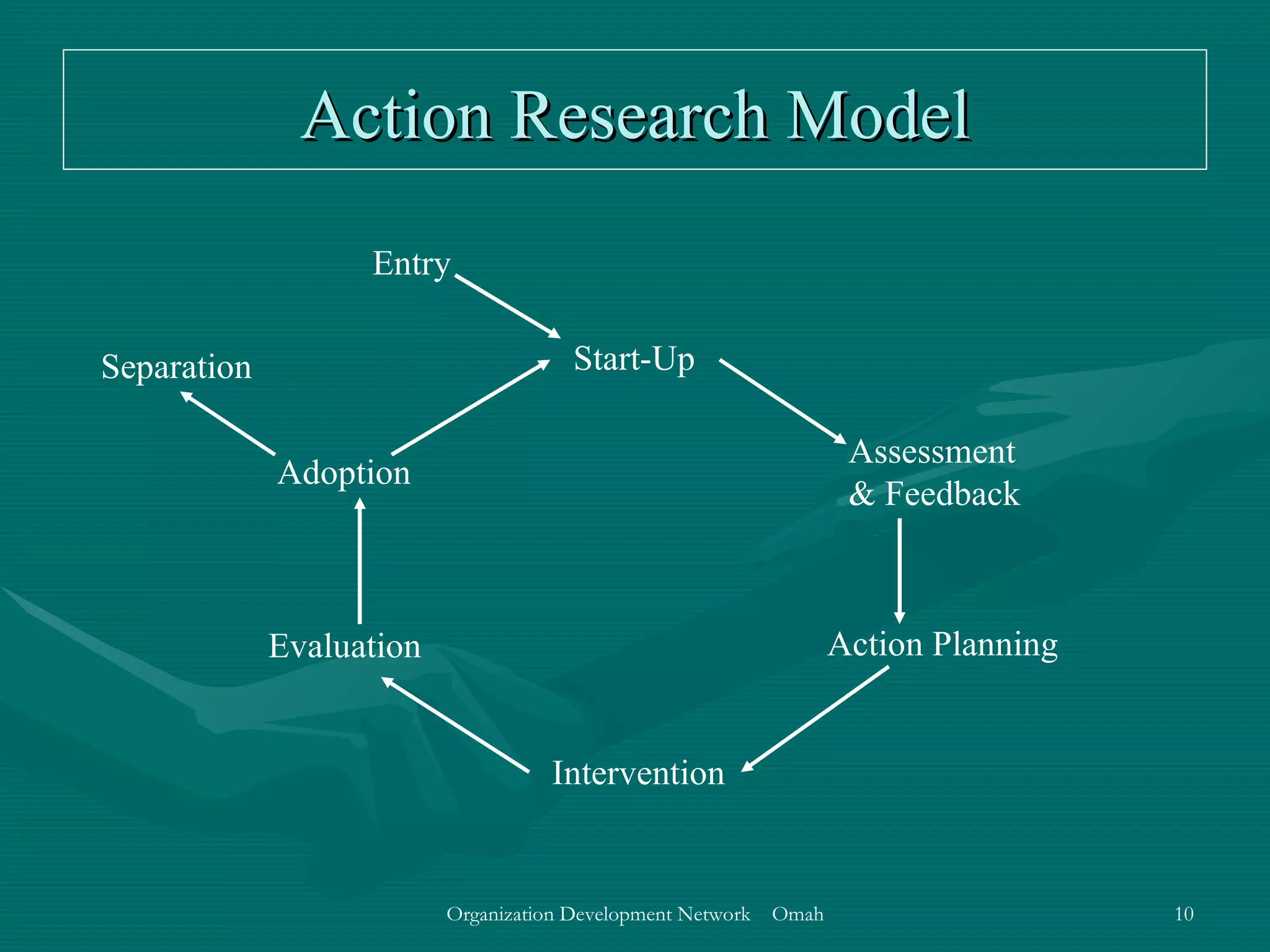
This document discusses evaluation and feedback in the change process. It provides definitions of key terms like evaluation, feedback, and institutionalizing change. It also describes common models of change like Lewin's change model and appreciative inquiry. Additionally, it discusses different evaluation strategies like periodically monitoring outcomes and using implementation feedback. Case examples are also provided to illustrate how evaluation and feedback were used during organizational changes at companies.