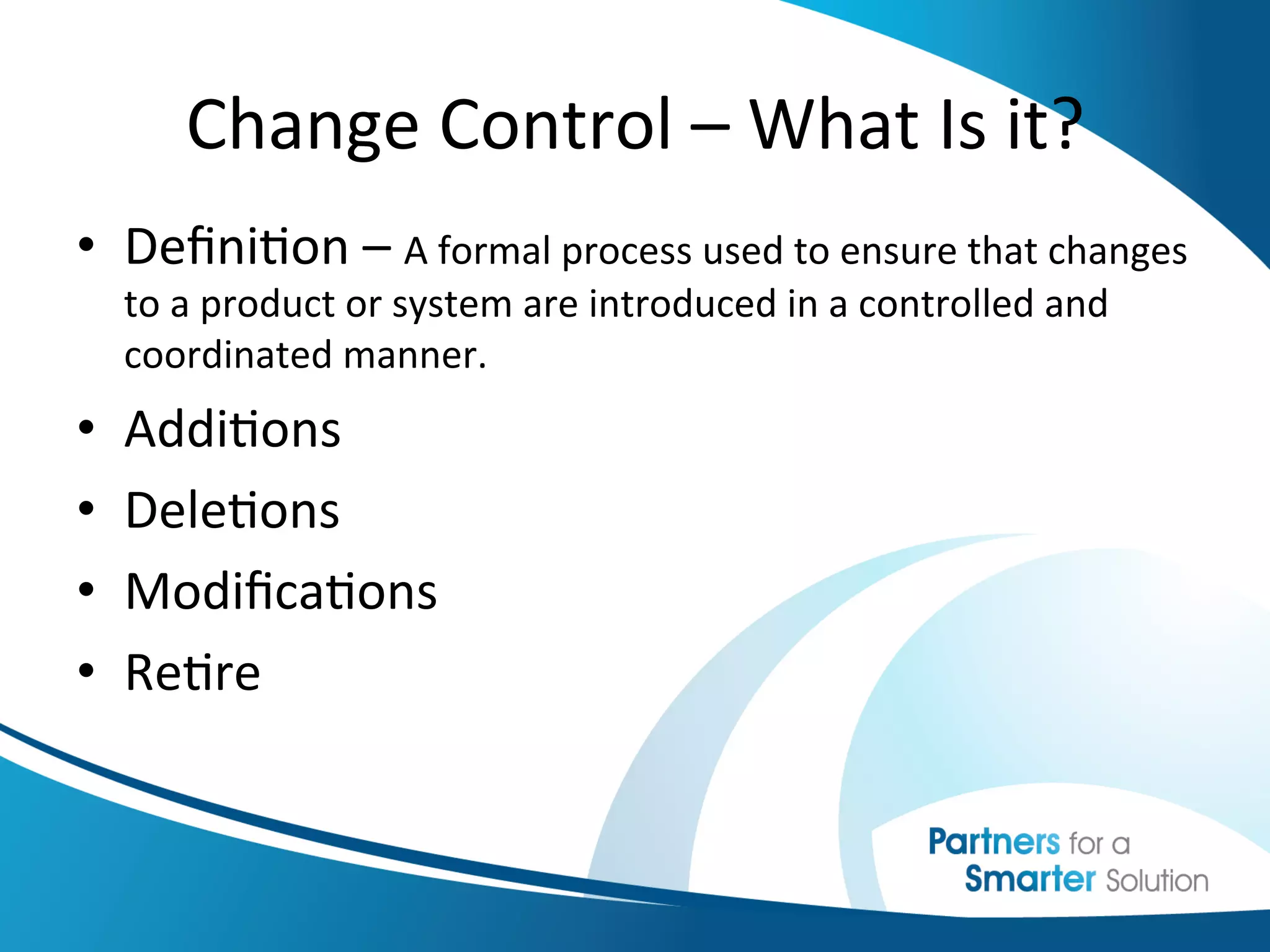
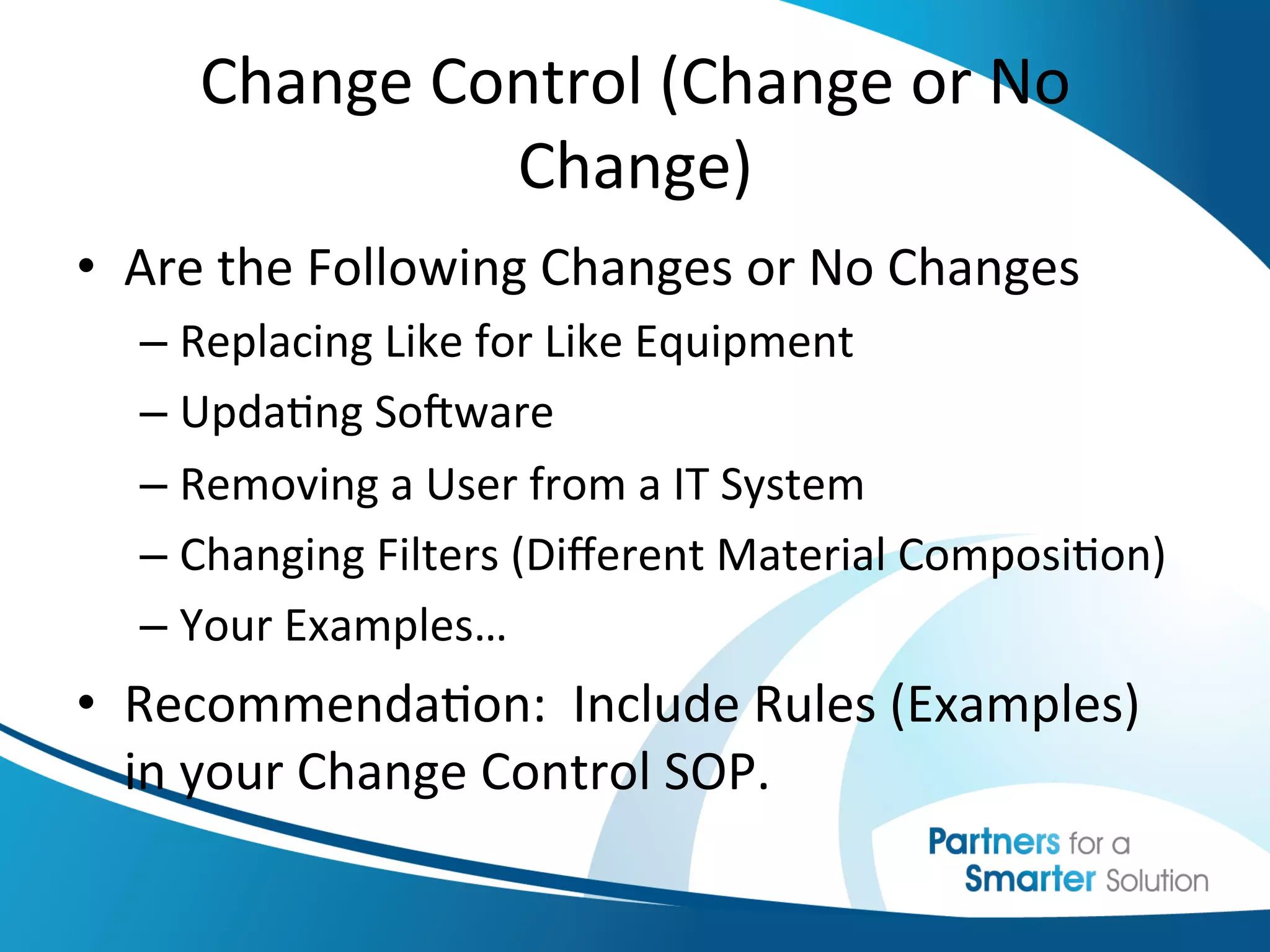
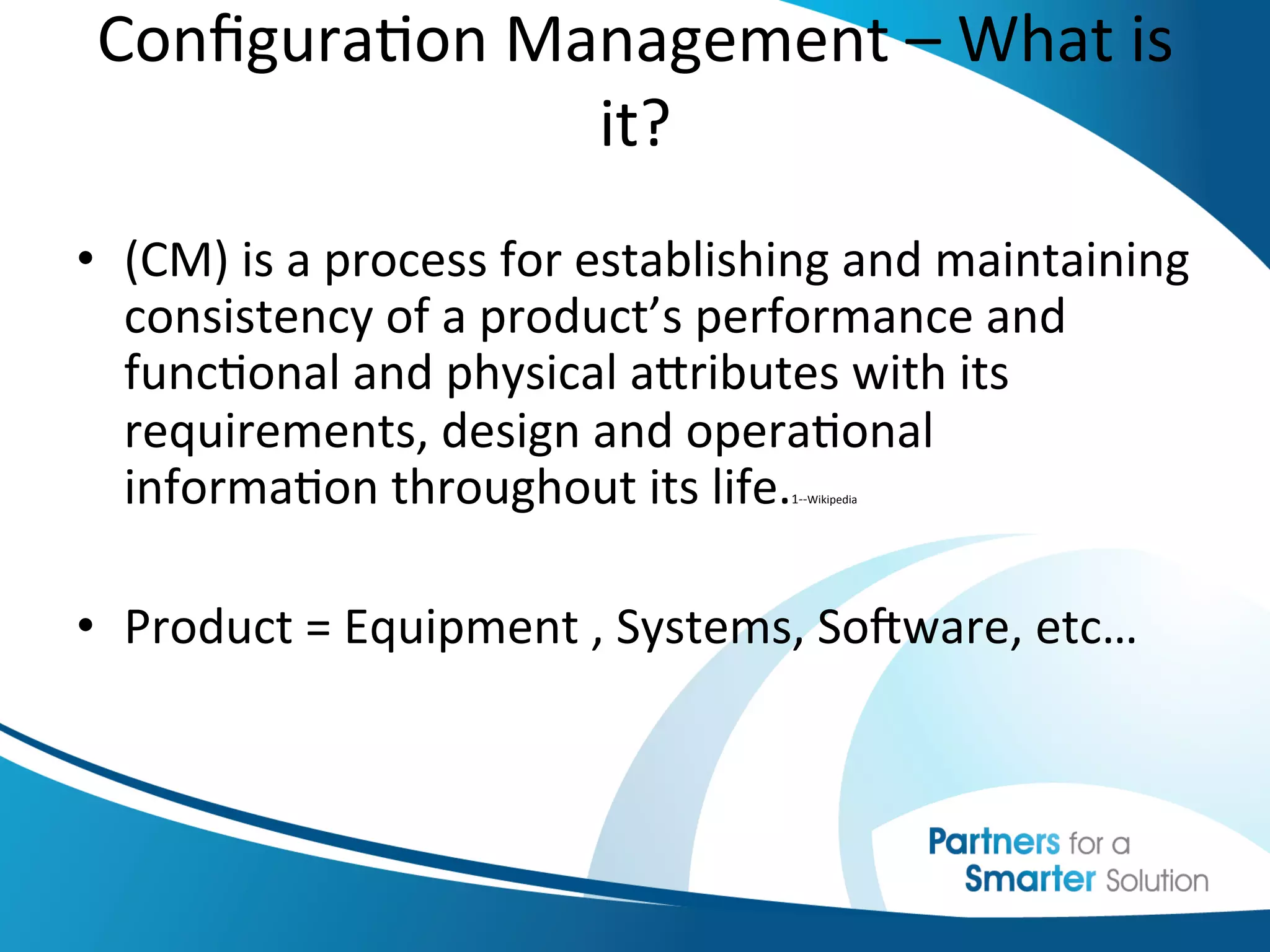
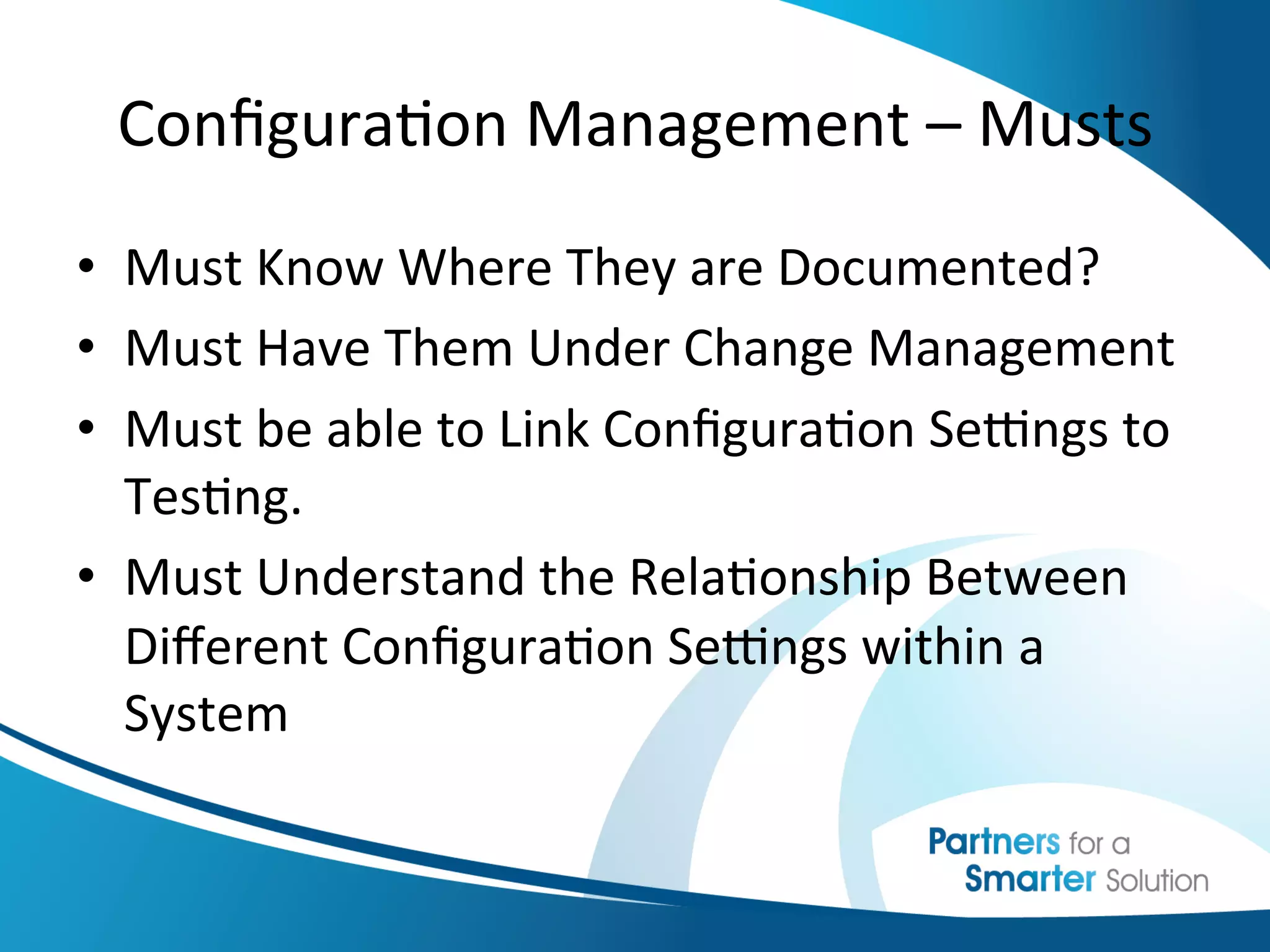
This document discusses change control and configuration management. It defines change control as a formal process for introducing changes to a product or system in a controlled manner. It discusses what constitutes a change versus no change. It emphasizes the importance of change control and having clearly defined change processes. It also discusses configuration management as maintaining consistency of a product's attributes and requirements. It provides examples of configuration management and discusses where configurations are typically documented. It stresses the importance of having configurations under change management and understanding how configurations relate to each other.