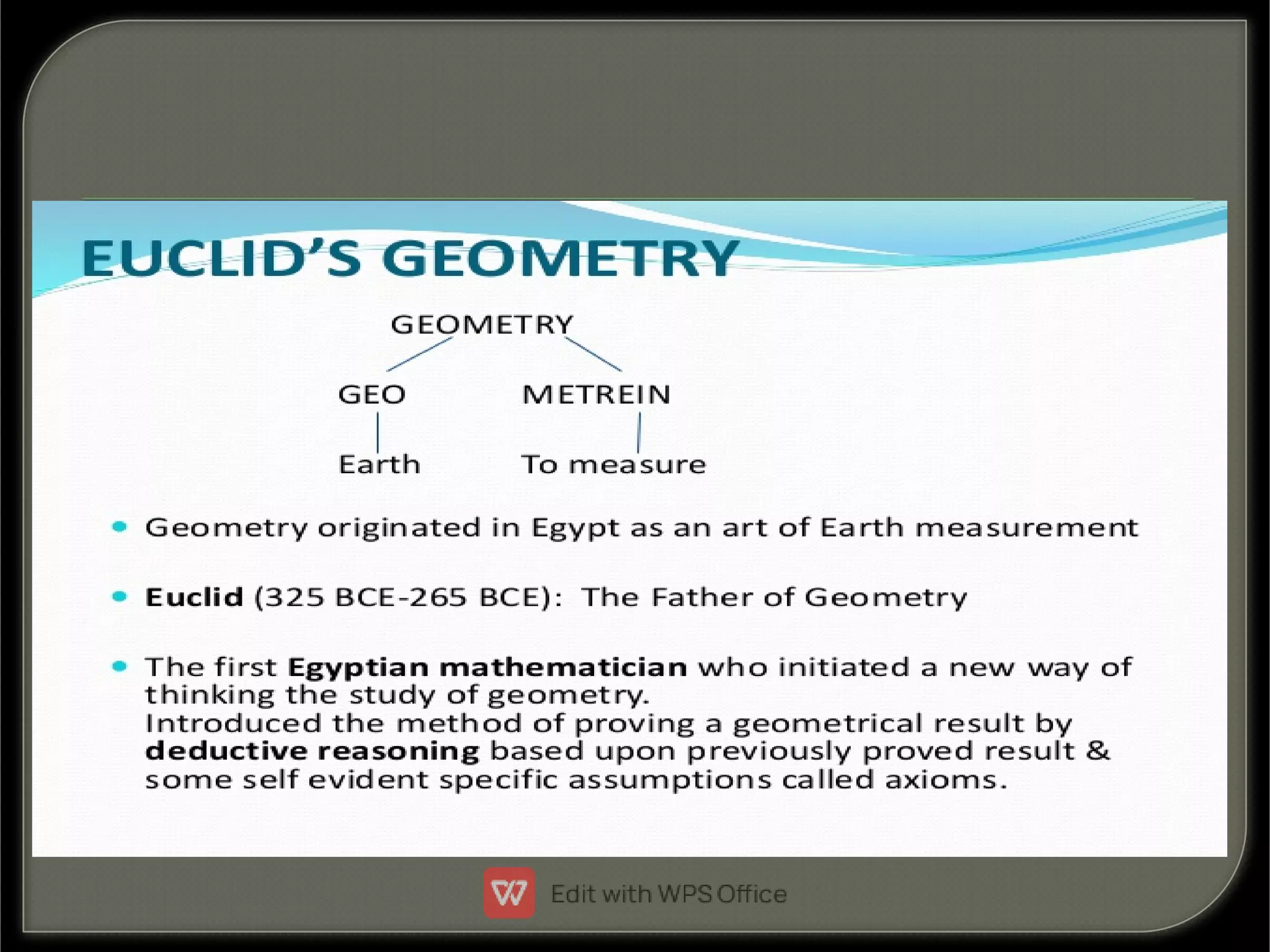
Euclid's Geometry laid the foundations of geometry through a set of axioms and theorems. It began with a few basic assumptions considered self-evident (axioms) and logically proved new geometric relationships (theorems) using deductive reasoning. Euclid compiled hundreds of theorems in this manner. Some key aspects included:
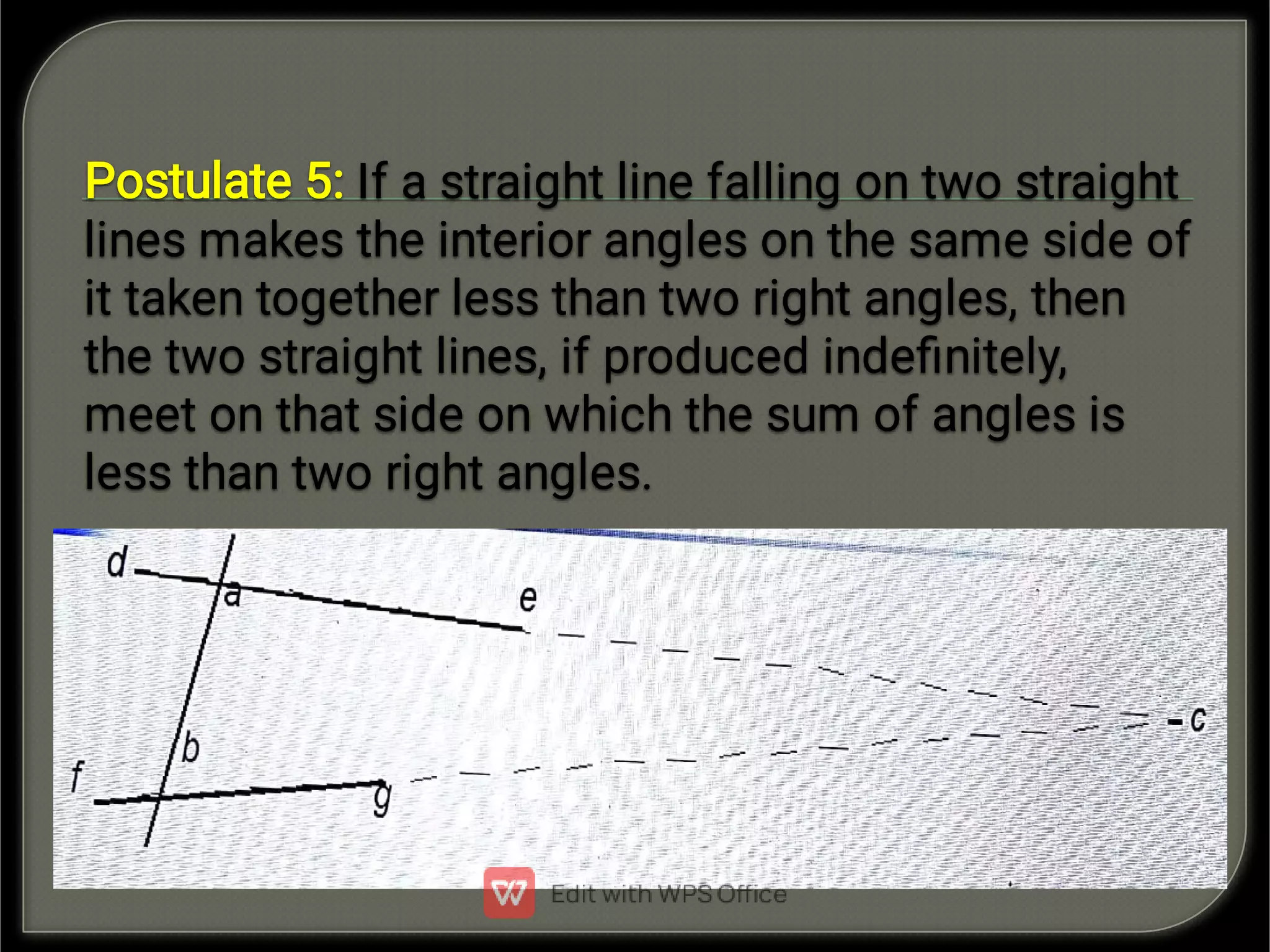
- Euclid stated five postulates on basic geometric objects like points, lines and circles.
- His work defined the relationships and properties of lines, angles and areas through precise definitions and logical reasoning.
- Euclid's work was highly influential and formed the basis of geometry for over 2000 years, establishing the axiomatic method in mathematics.