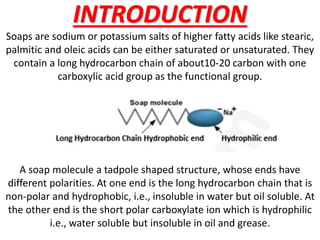
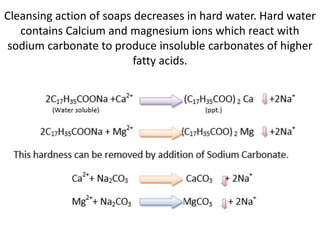
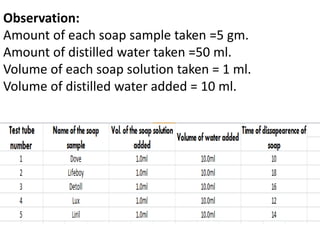
Soaps are salts of fatty acids that have a hydrophilic polar end and a hydrophobic non-polar end. This structure allows soap molecules to surround dirt and grease particles, forming micelles that emulsify the particles and suspend them in water. The document describes an experiment to compare the foaming capacities of different commercial soaps. Samples of five soaps were dissolved and shaken in test tubes, then the time taken for the foam to disappear was measured and compared. The soap with the highest foaming capacity, taking the longest time for the foam to disappear, was determined to be Lifeboy soap.