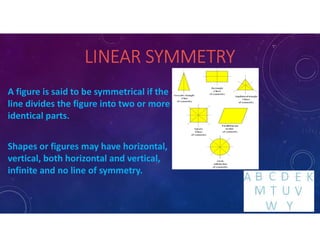
This document presents a maths project on symmetry by Riya Ben of class 7. It defines symmetry as identical matching of two or more parts of a figure after folding or flipping. A line of symmetry, also called an axis of symmetry, is an imaginary line that divides a shape into two identical pieces. There are different types of symmetry including linear symmetry where a line divides a figure into identical parts, rotational symmetry where a shape is rotated around a central point, and reflection symmetry where a shape matches its mirror image when reflected across a dividing line.