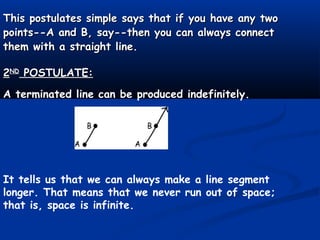
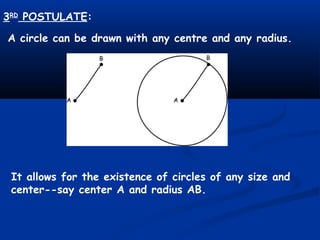
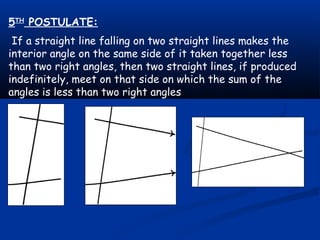
Euclid was a Greek mathematician from Alexandria known as the "Father of Geometry". In his influential work Elements, he deduced the principles of Euclidean geometry from 5 postulates (axioms) for plane geometry related to drawing lines and circles. The postulates state that a line can be drawn between any two points, a line can be extended indefinitely, a circle can be drawn with any center and radius, all right angles are equal, and if two lines intersect another such that the interior angles on the same side sum to less than two right angles, the two lines will intersect on that side. Euclid's work was foundational and served as the main geometry textbook for over 2000 years.