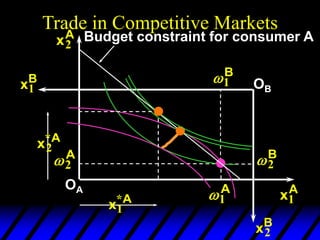
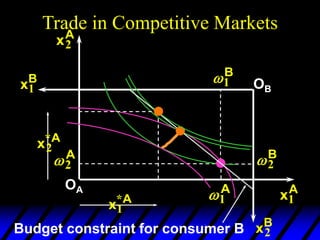
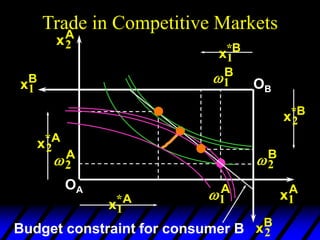
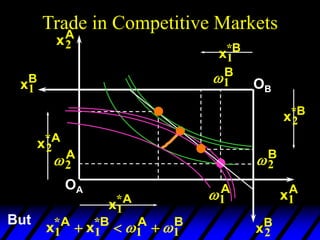
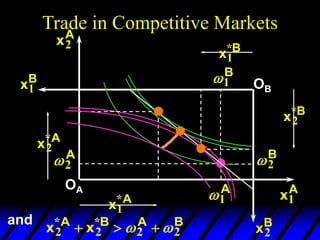
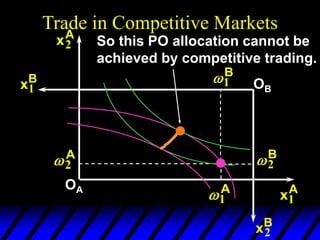
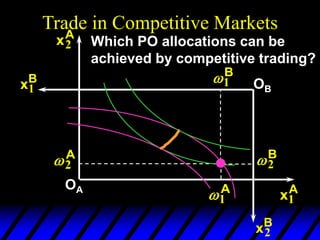
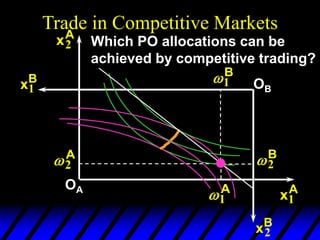
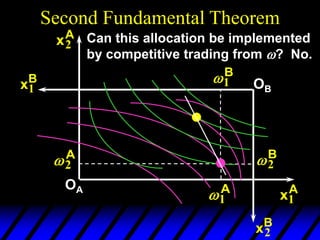
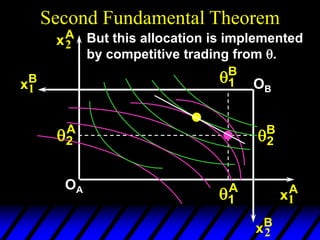
This document describes an Edgeworth box model of exchange between two consumers, A and B. It summarizes the key aspects of the model, including:
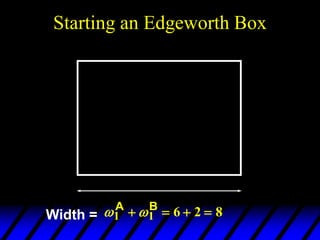
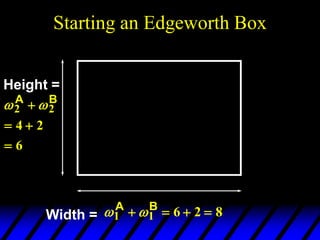
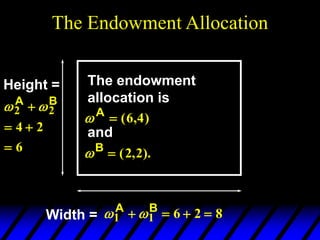
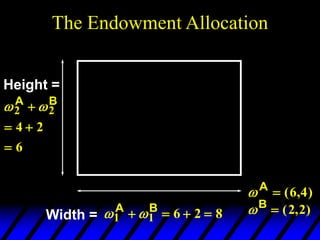
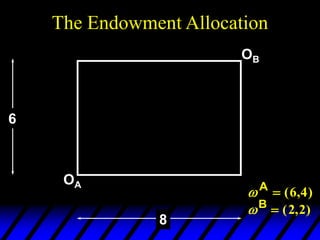
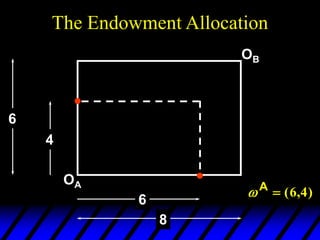
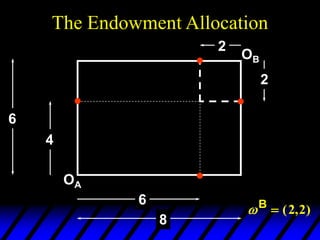
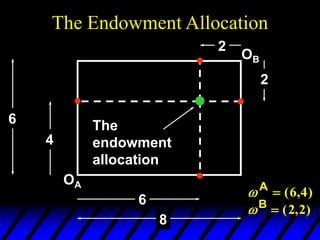
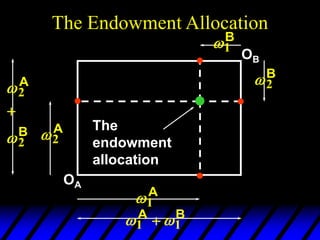
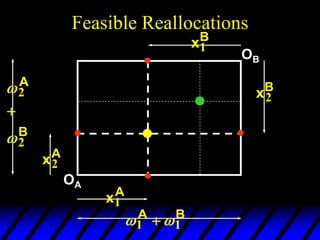
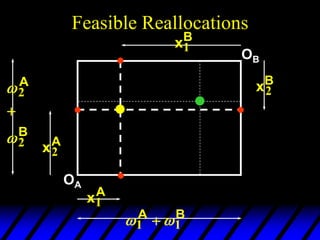
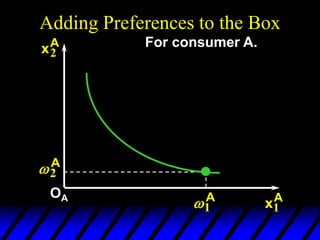
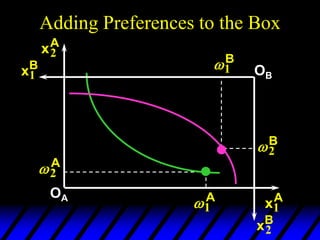
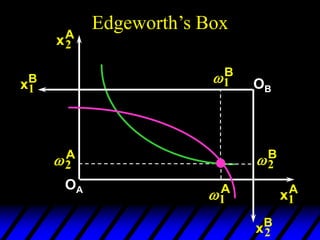
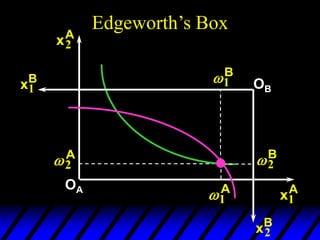
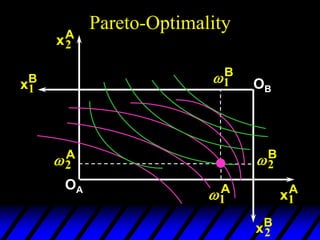
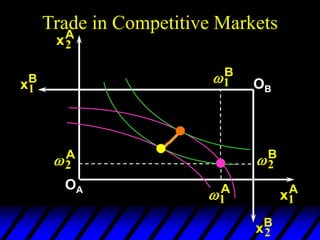
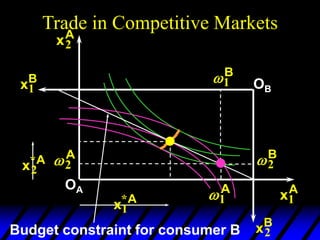
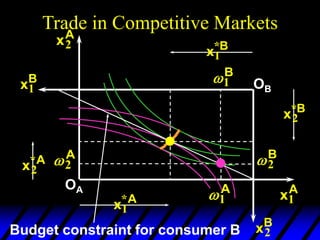
1) The endowments of goods 1 and 2 for each consumer define the dimensions of the Edgeworth box. All points within the box represent feasible allocations.
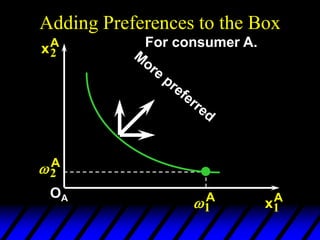
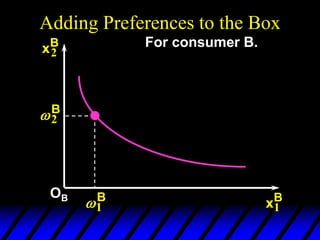
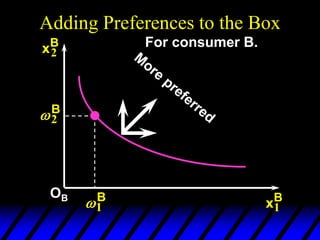
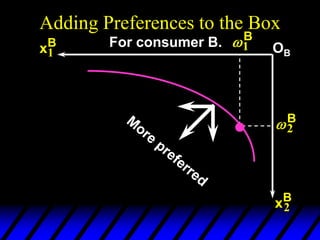
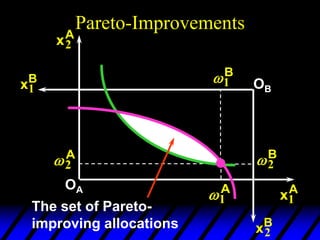
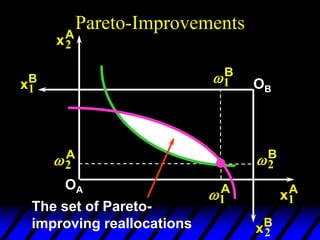
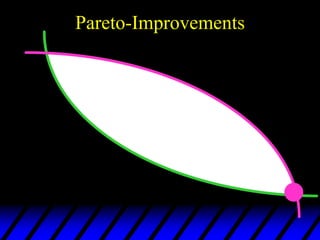
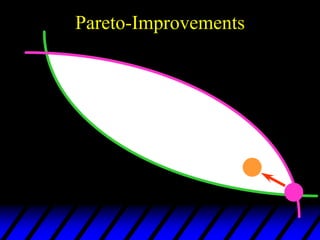
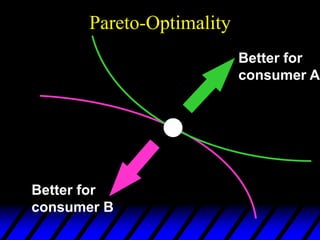
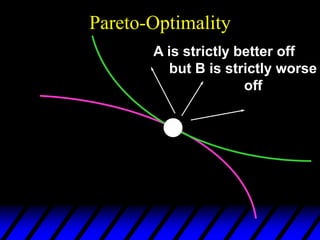
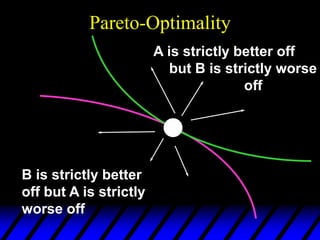
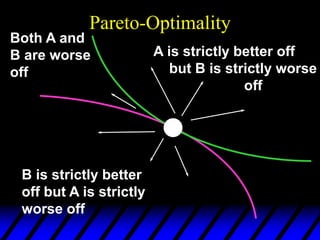
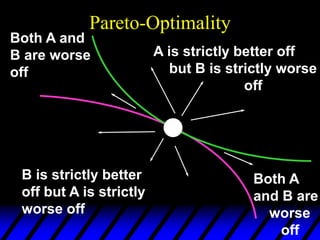
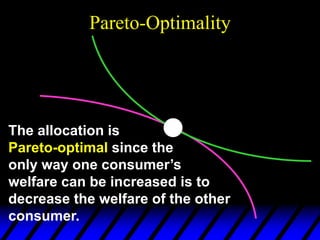
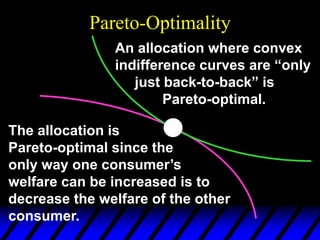
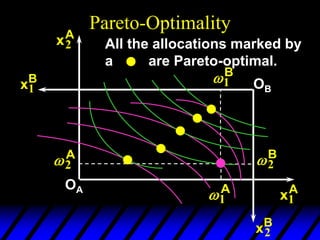
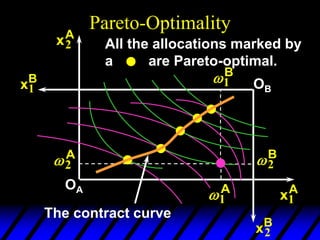
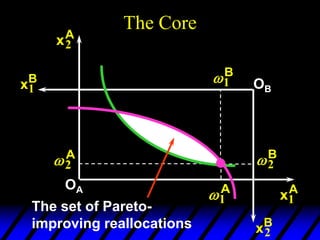
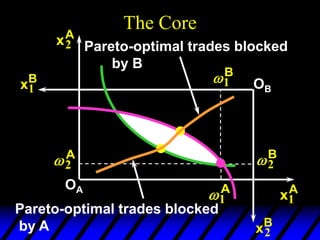
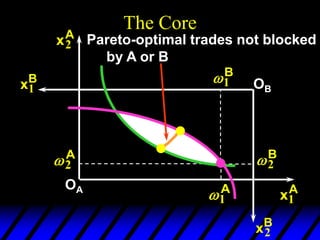
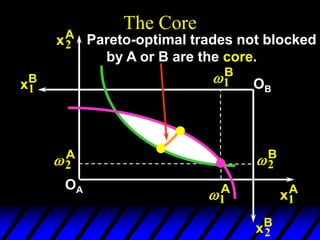
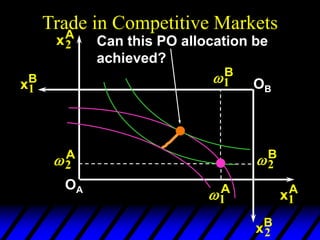
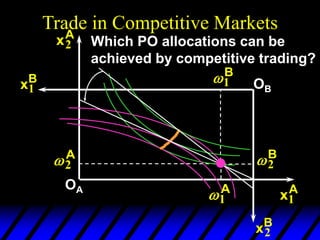
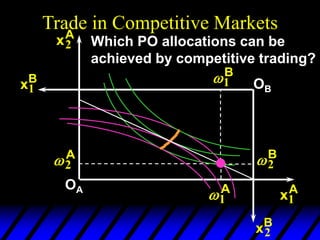
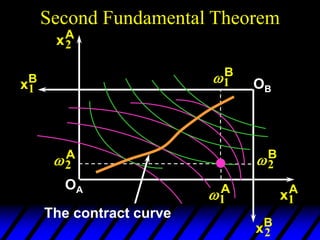
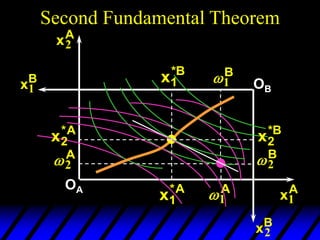
2) Pareto-improving allocations make at least one consumer better off without making the other worse off. The set of Pareto-optimal allocations form the contract curve.
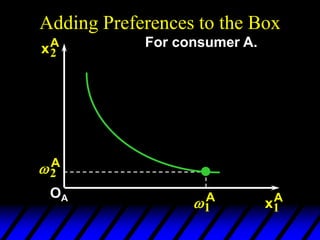
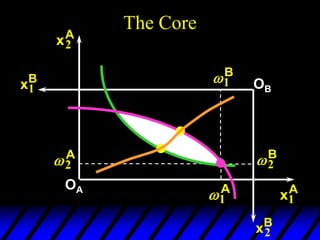
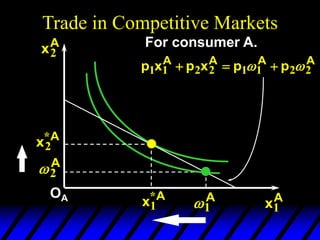
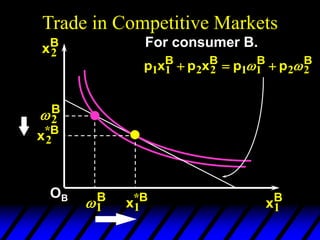
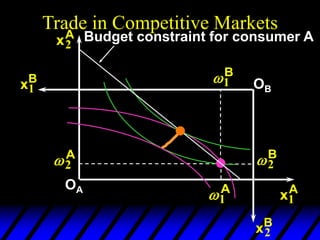
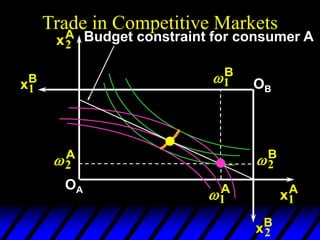
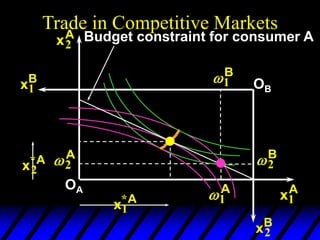
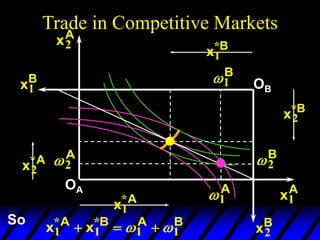
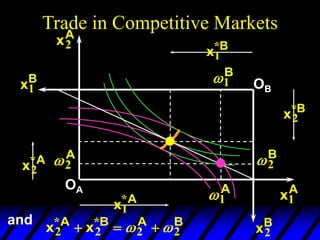
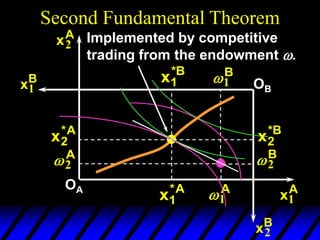
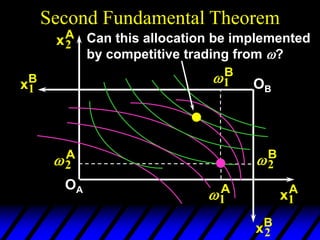
3) In competitive markets, each consumer maximizes utility given market prices. General equilibrium occurs when resulting demands clear both markets. This determines a core allocation from trade.