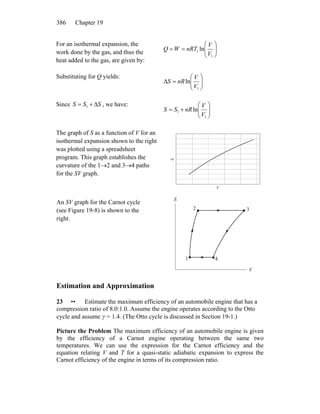
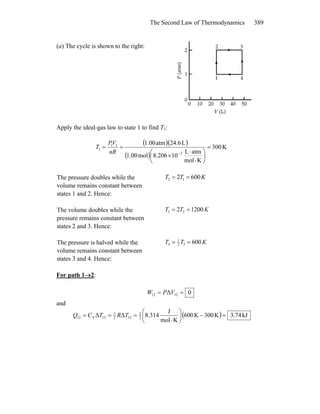
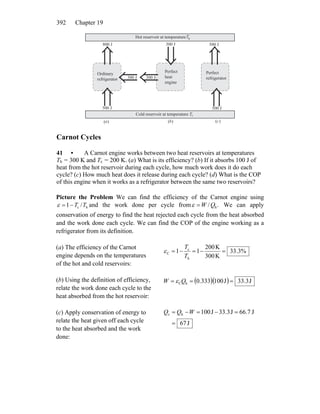
1) The document discusses the processes involved in a Carnot cycle for an ideal gas, including isothermal expansion and compression and adiabatic processes.
2) It examines the efficiencies of Carnot engines and refrigerators, noting that engines are more efficient when the temperature difference is large, while refrigerators are more efficient when the temperature difference is small.
3) It then shows how assuming the heat engine statement of the second law is false would allow using a refrigerator to violate the refrigerator statement of the second law by creating a perpetual motion machine.