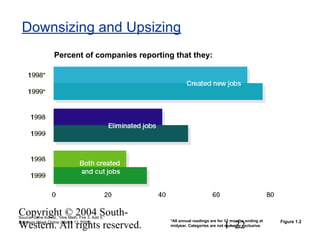
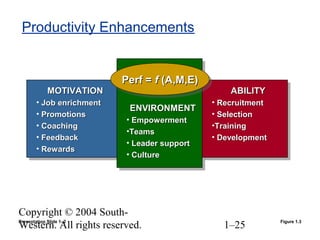
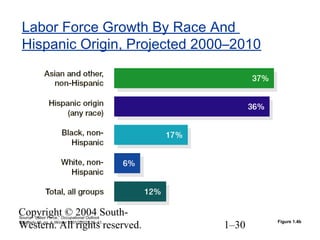
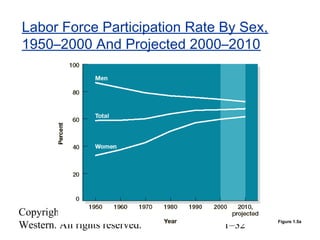
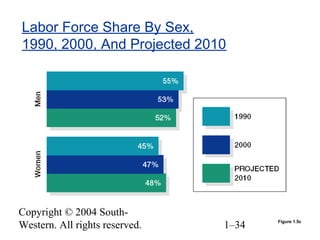
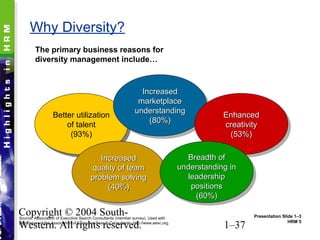
This document provides an overview of key topics in human resource management. It begins by outlining nine learning objectives, including gaining competitive advantage through people, managing the impacts of globalization and technology, and understanding HR's role in areas like change management and developing intellectual capital. The document then discusses competitive challenges like globalization, technology, managing change, developing human capital, responding to the market, and containing costs. It provides details on how these challenges influence human resource practices. Specific HR functions like recruitment, training, compensation and benefits are also examined. The document concludes by looking at important social and demographic issues that impact HRM like the changing workforce composition and attitudes toward work-life balance.