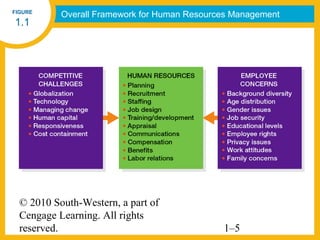
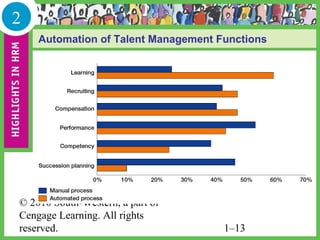
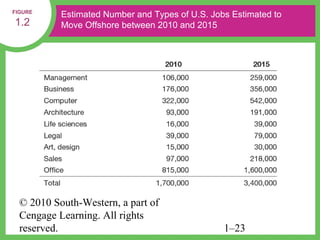
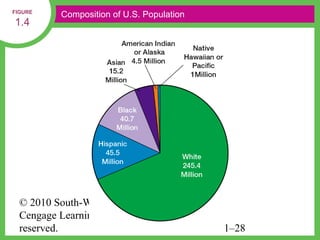
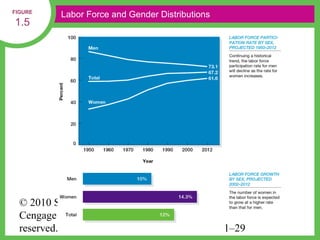
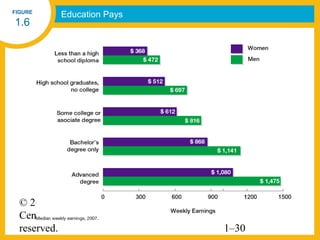
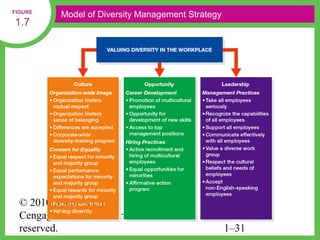
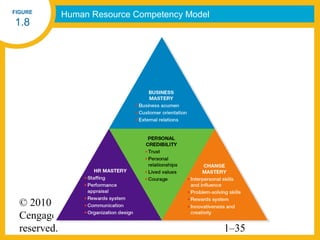
HR managers must demonstrate competencies in areas such as communication, critical thinking, relationship building, and change management. They provide guidance to help organizations achieve their goals through strategic workforce planning and development.