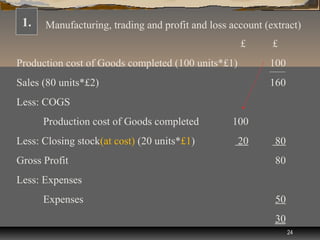
The document discusses manufacturing accounting concepts including:
1) Production cost is made up of direct materials, direct labor, direct expenses, and factory overhead expenses.
2) Factory overhead expenses include indirect materials, indirect labor, and indirect expenses related to factory operations.
3) A manufacturing account shows the production cost of goods completed during an accounting period.
4) Goods may be transferred to the trading account at either production cost or a transfer price that includes a factory profit markup.