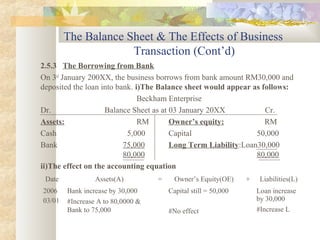
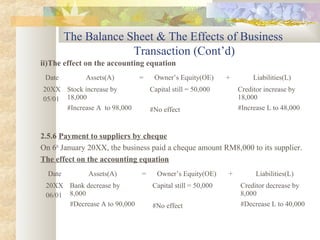
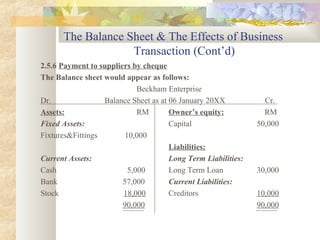
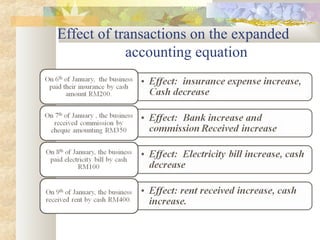
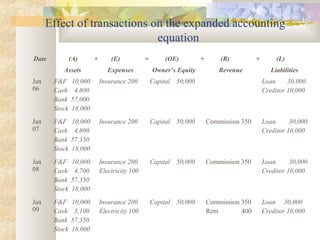
The document discusses key accounting concepts such as the accounting equation, balance sheet, assets, liabilities, owner's equity, revenues, and expenses. It also explains how business transactions affect the accounting equation and how to record purchases and sales of inventory through journal entries. The relationship between the income statement and accounting equation is demonstrated.