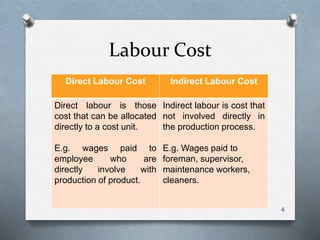
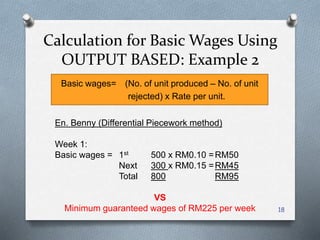
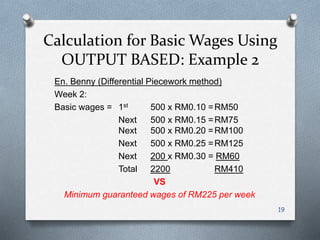
This document discusses methods for remunerating labor costs. It differentiates between direct and indirect labor costs. It also describes two main methods for remunerating labor: time-based and output/performance-based. Time-based pays employees based on hours worked, with overtime rates. Output-based pays based on units produced, which can be straight piecework or have tiered rates. The document provides examples to demonstrate calculating wages under each method and compares the advantages and disadvantages of each.