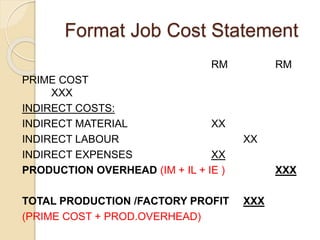
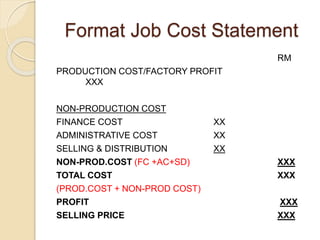
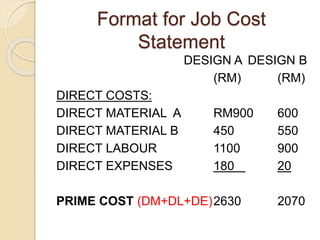
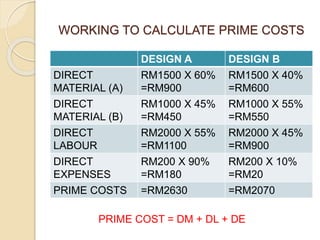
Job costing involves tracking costs for individual jobs or orders according to customer specifications. There are three main types: job costing for single orders completed in a workshop, batch costing for identical units produced in quantities, and contract costing for large projects. Job costing requires identifying each job and directly charging material, labor, and other costs. The costs are accumulated on a job cost card or sheet to calculate the total, factory, and selling costs for each job. Profits are determined using either a markup on total cost or margin on the selling price.













![HOW TO CALCULATE PROFIT?
2. PROFIT MARGIN
PROFIT IS CALCULATED BASED ON
SELLING PRICE.
FORMULA:
PROFIT = [%PROFIT MARGIN/(100%-
PROFIT MARGIN %)] X TC
PROFIT= [20%/100%-20%] X RM200 =RM50](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture5-200822124525/85/ACC-116-JOB-COSTING-16-320.jpg)






![WORKING TO CALCULATE
PROFIT FOR DESIGN B
PROFIT IS BASED ON SELLING
PRICE/PROFIT MARGIN
FORMULA:
PROFIT = [%PROFIT MARGIN/(100%-
PROFIT MARGIN %)] X TC
= 20%/(100%-20%) X RM2950
=( 20%/80% )X RM2950
= RM737.50](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture5-200822124525/85/ACC-116-JOB-COSTING-27-320.jpg)
