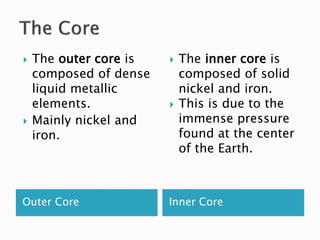
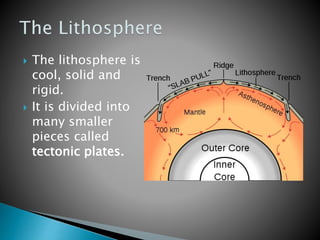
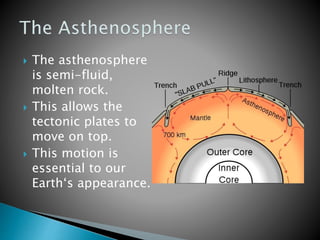
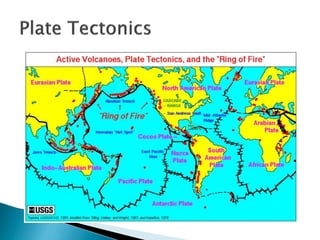
The Earth is composed of four main spheres - the geosphere (solid rock and soil), atmosphere (air), hydrosphere (water), and biosphere (living organisms). The geosphere makes up the solid interior of the planet and can be divided into the crust, mantle, and core based on its chemical composition. The crust is broken into tectonic plates that move atop the asthenosphere due to its semi-molten state. Tectonic activity at plate boundaries like earthquakes and volcanic eruptions shape the Earth's surface over time through weathering and erosion.