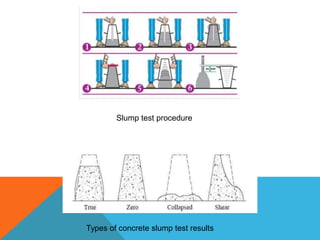
The document is a technical presentation discussing the utilization of ceramic waste as a raw material in concrete, highlighting the potential benefits such as cost reduction and environmental protection. It includes materials used, testing methods, and results indicating improved compressive strength with up to 15% ceramic waste content. The conclusion emphasizes the advantages of using ceramic waste and suggests future opportunities for industry development and waste management.