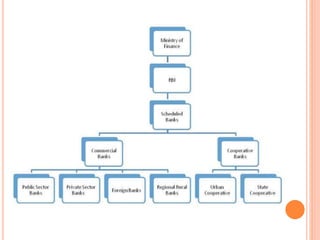
The document discusses the operations management in banking, highlighting the importance of creating value while adhering to regulatory frameworks. It outlines the role of information technology in banking, including its impact on customer service, data management, and new product development. Additionally, it addresses trends in technology adoption, challenges faced by banks, and suggestions for enhancing operational efficiency and service delivery.