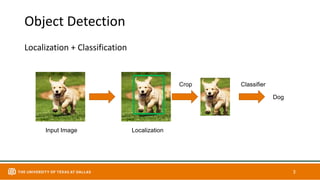
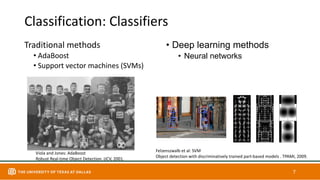
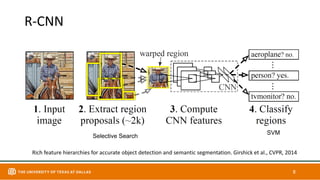
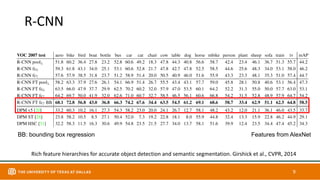
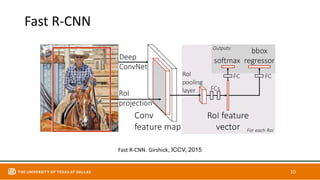
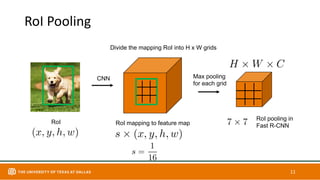
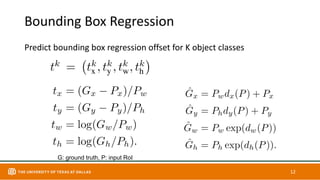
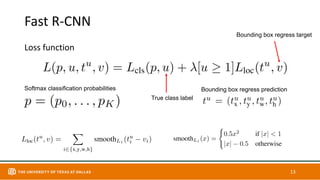
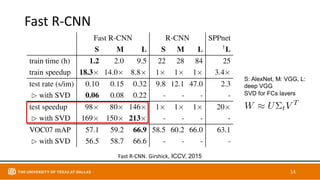
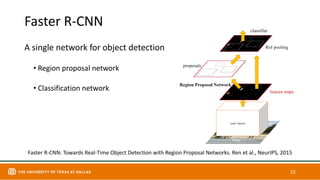
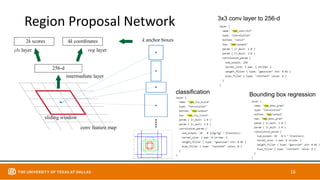
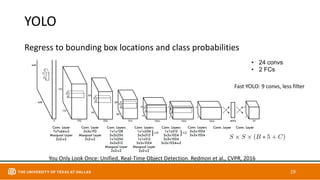
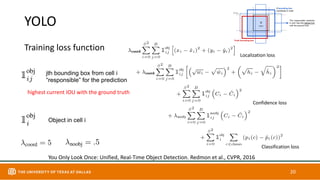
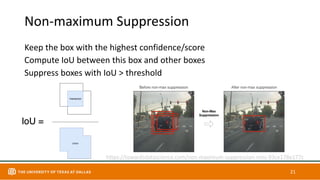
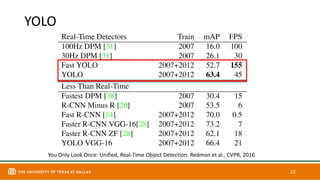
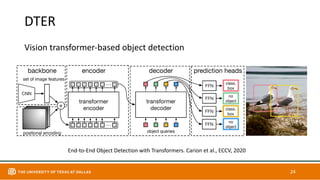
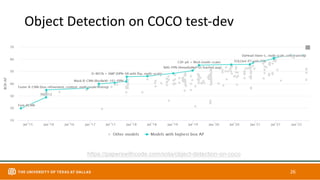
This document discusses object detection techniques including two-stage detectors like R-CNN and Faster R-CNN which use region proposals and classification, and one-stage detectors like YOLO that perform end-to-end detection. It also covers transformer-based detectors like DTER that use attention and object queries for set prediction. Traditional methods used hand-crafted features and classifiers while deep learning methods leverage features from neural networks. Localization identifies objects in images while classification determines the object class.