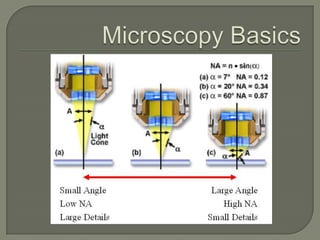
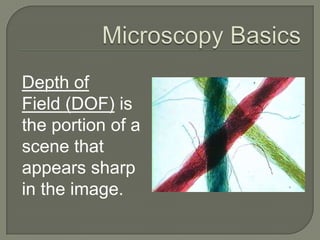
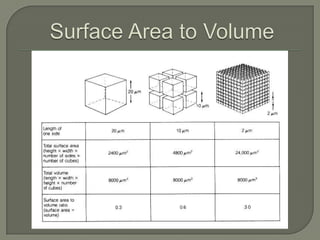
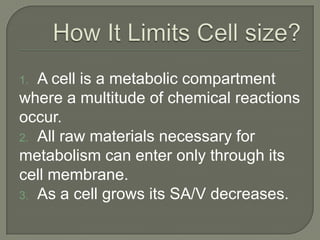
The document discusses the discovery of cells and the development of cell theory. It explores key figures like Van Leeuwenhoek, Hooke, Brown, Schleiden, and Schwann and their contributions to early microscopy and the understanding that cells are the basic unit of life. It also summarizes different types of microscopes used to study cells, including optical, stereo, transmission electron, and scanning electron microscopes. Specimen preparation techniques for microscopy are outlined. Finally, it addresses why cells are small through the relationship between surface area and volume.