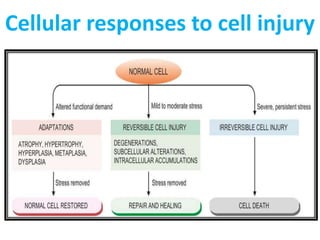
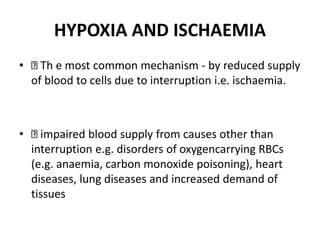
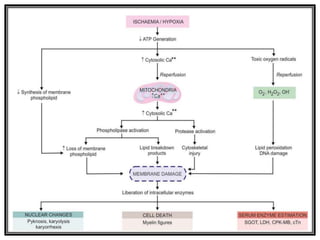
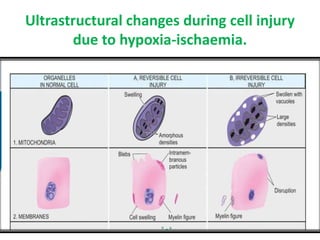
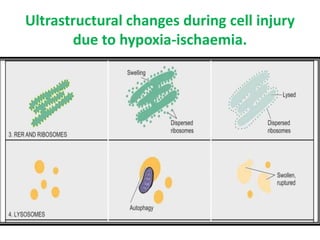
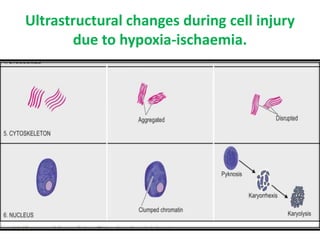
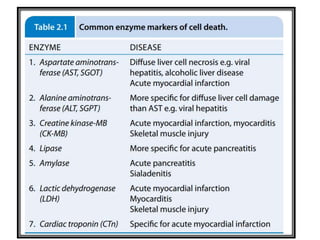
This document discusses cell injury, cellular adaptations, and cellular aging. It covers various causes of cell injury including genetic factors, hypoxia/ischemia, physical and chemical agents, microbes, immunological reactions, nutritional imbalances, and aging. The pathogenesis of cell injury is described as involving factors related to the injurious agent and host response, common underlying mechanisms, and typical morphological and functional consequences. Reversible cell injury causes ATP depletion, acidosis, membrane pump damage, and reduced protein synthesis, while irreversible injury involves mitochondrial dysfunction, calcium influx, membrane damage, and activation of destructive enzymes leading to cell death.