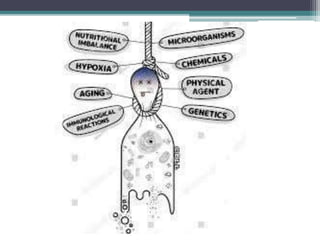
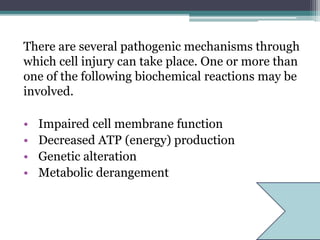
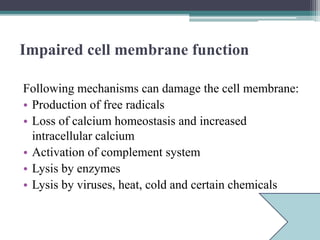
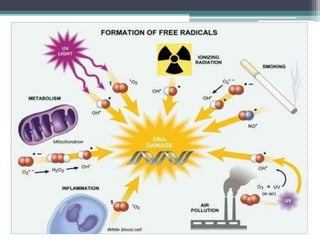
Cell injury can occur when cells encounter physiological stresses or pathologic stimuli that exceed their adaptive capacity. There are several potential mechanisms of cell injury, including impaired cell membrane function, decreased ATP production, genetic alterations, and metabolic derangements. Free radicals can damage cell membranes through lipid peroxidation and degradation of proteins and nucleic acids. Loss of calcium homeostasis and an increase in intracellular calcium can also impair cell membrane function. Decreased ATP production during hypoxia or hypoglycemia compromises important cellular processes. Genetic alterations from toxins, radiation, or viruses may disrupt protein and enzyme synthesis. Exposure to toxins can also cause metabolic derangements leading to cell injury.