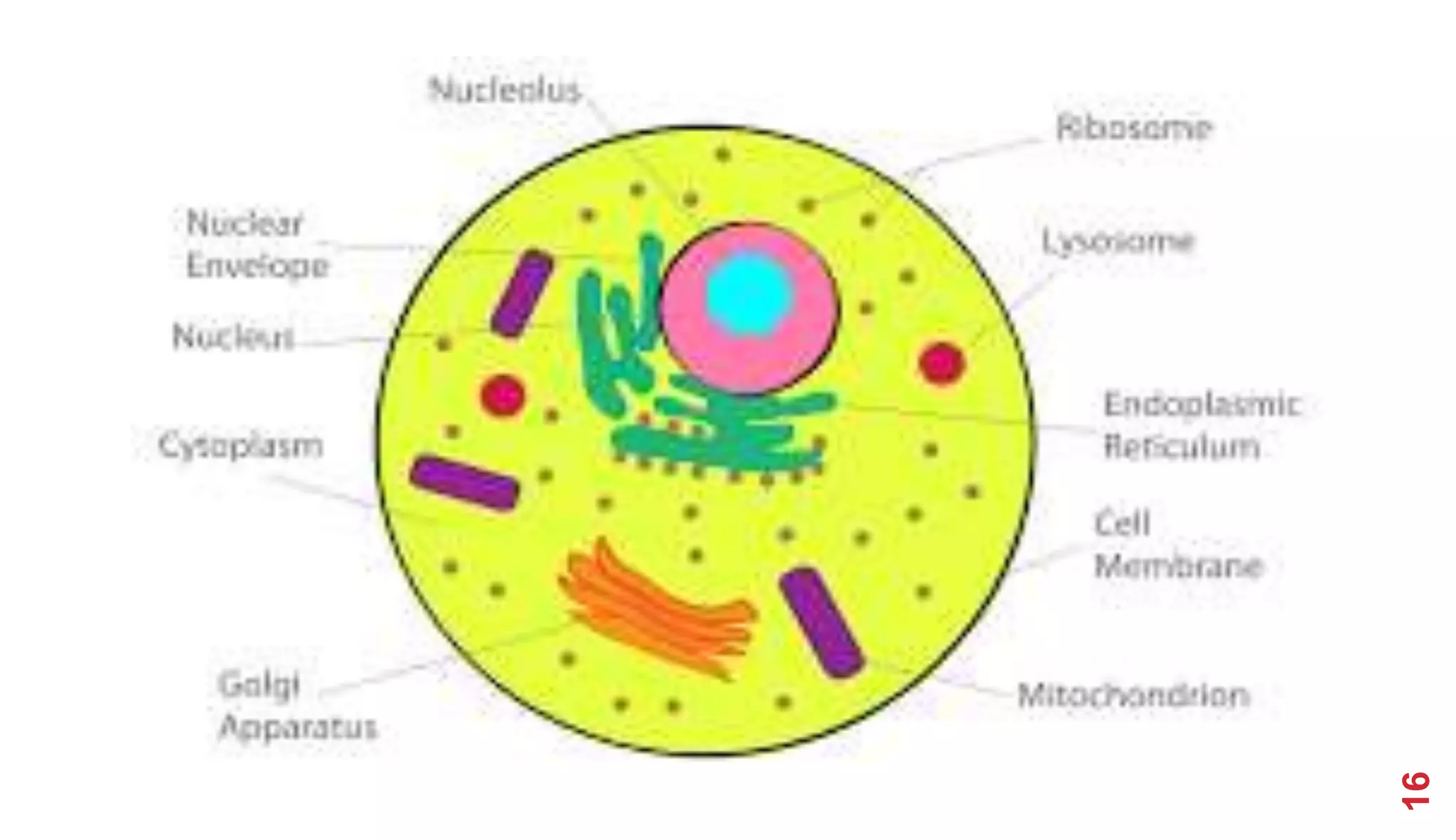
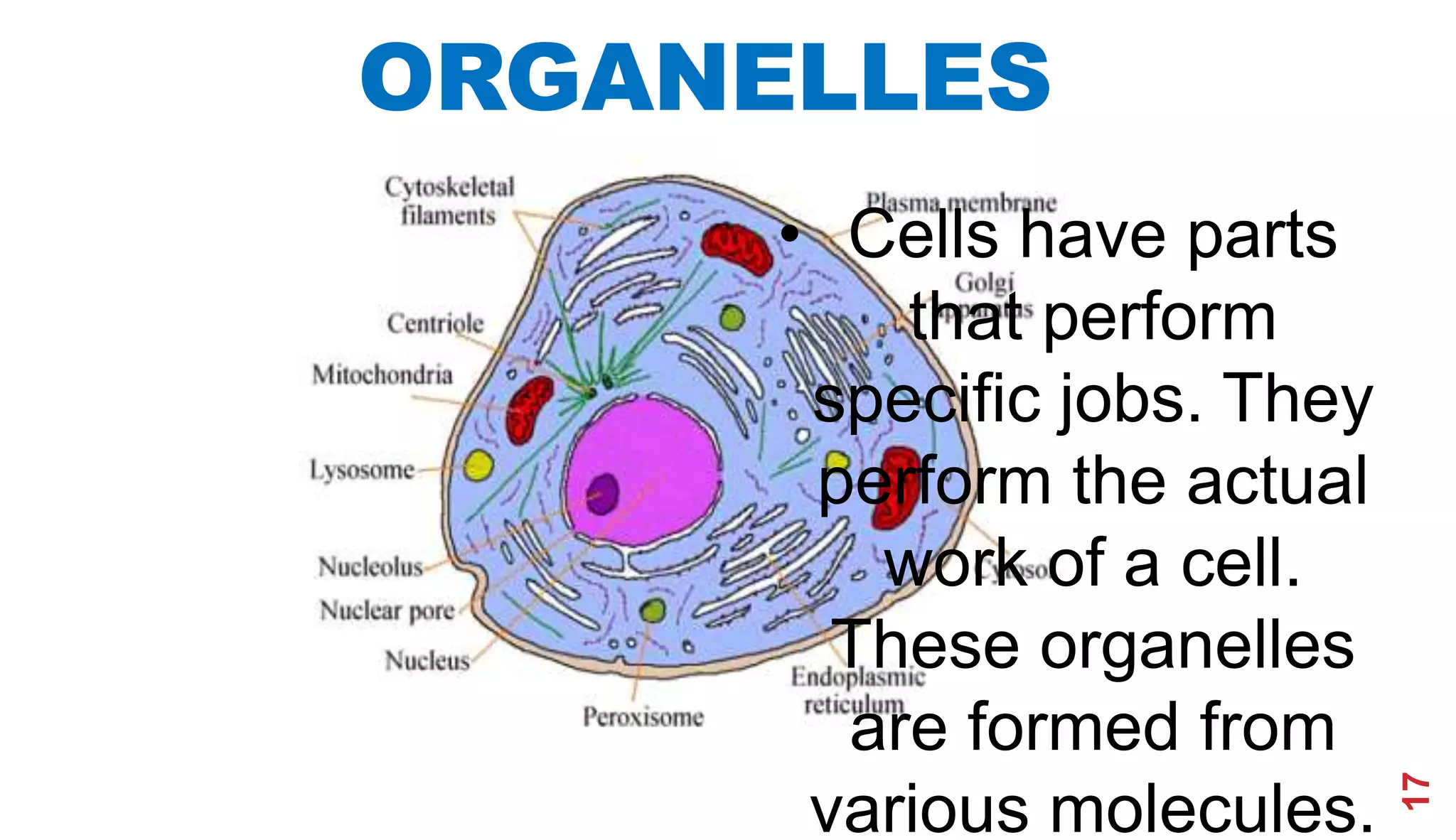
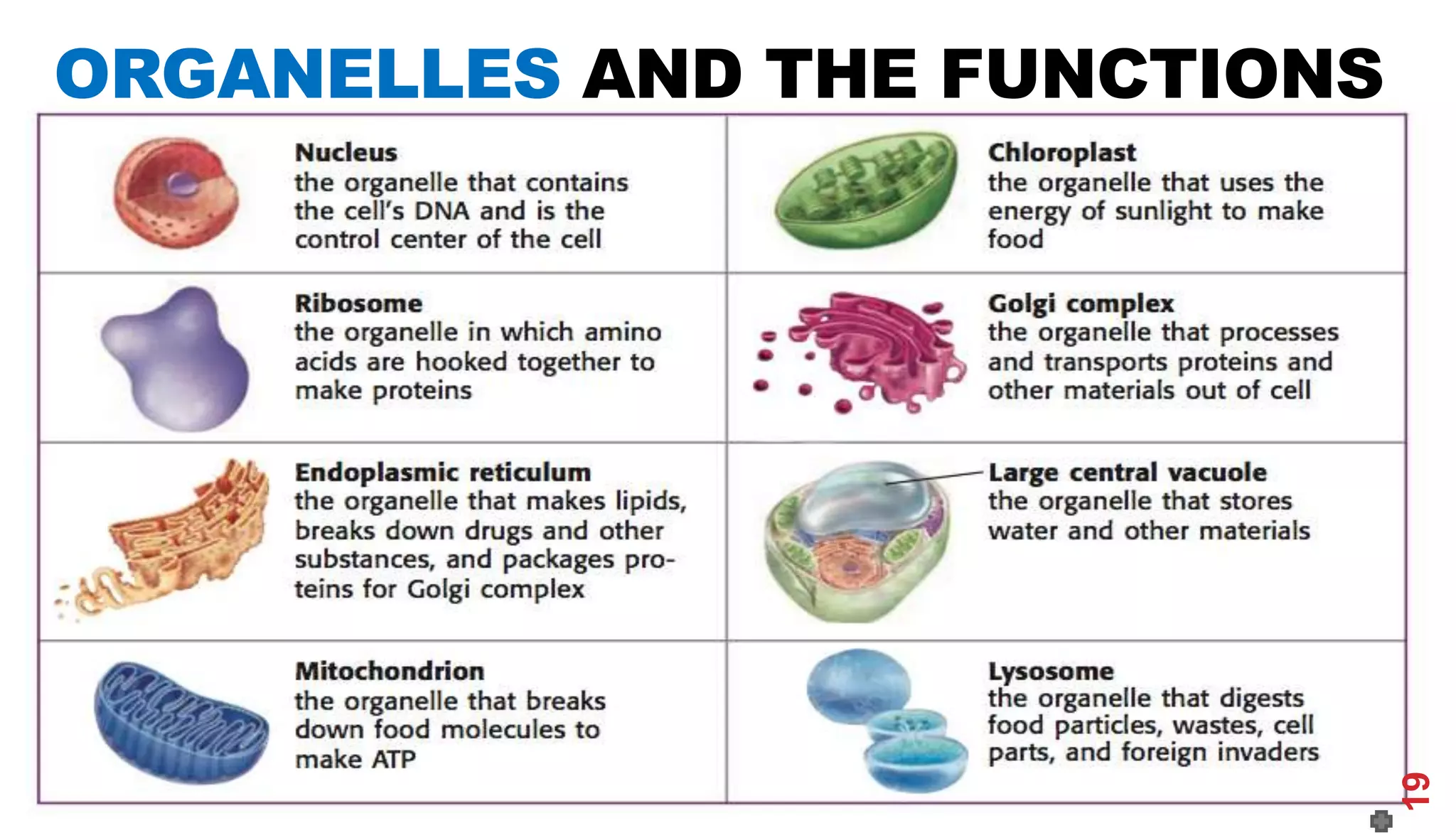
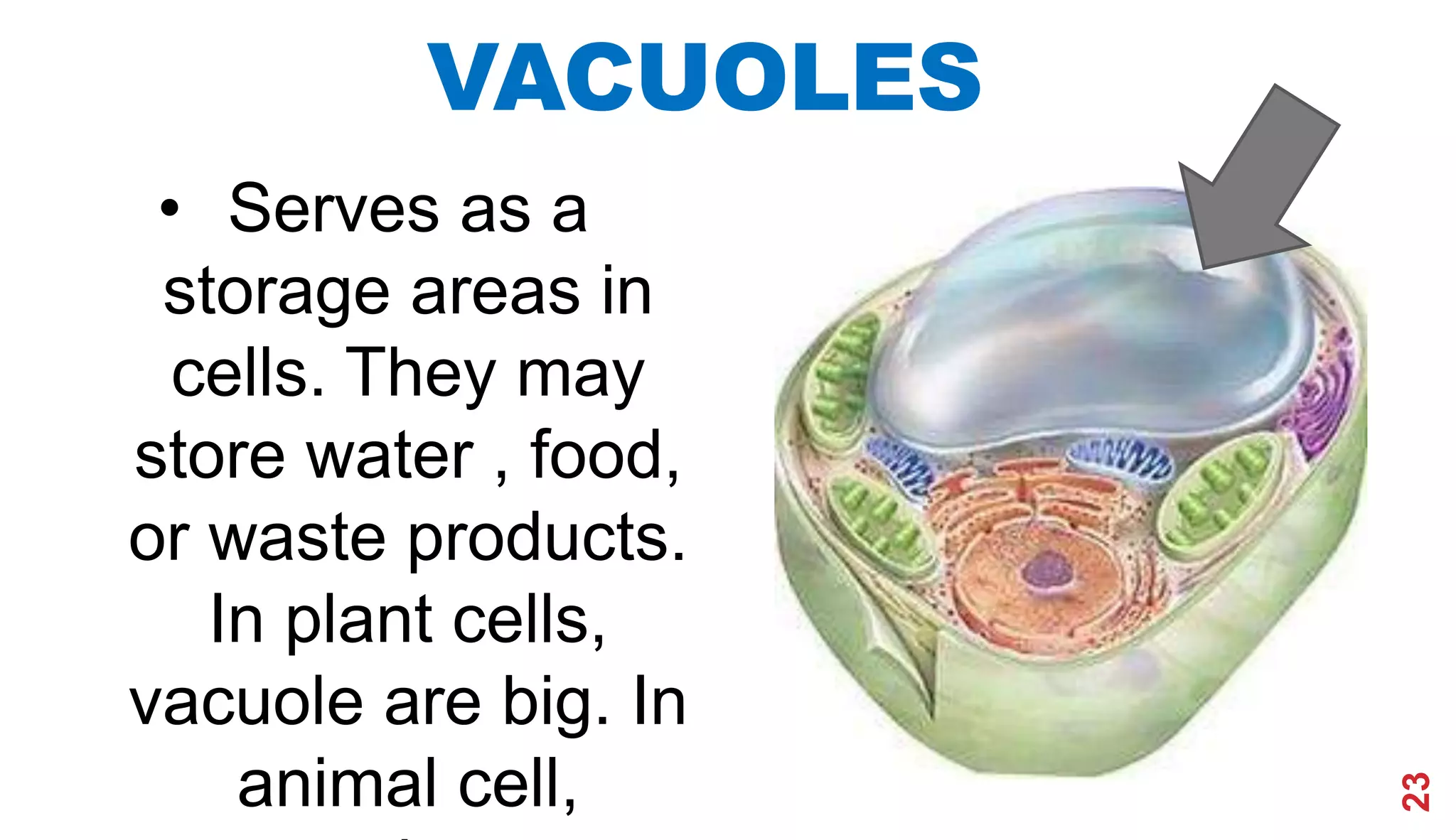
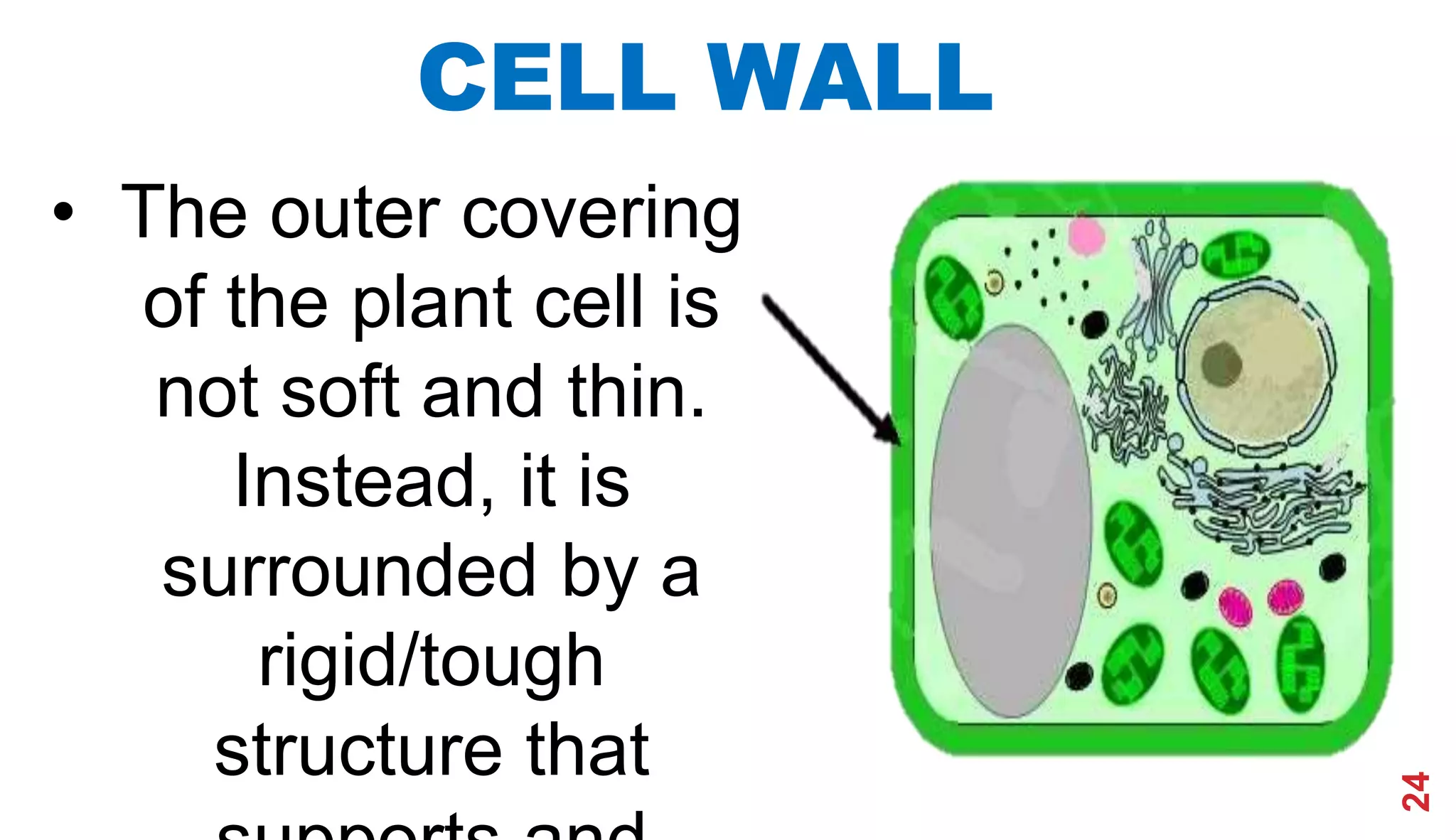
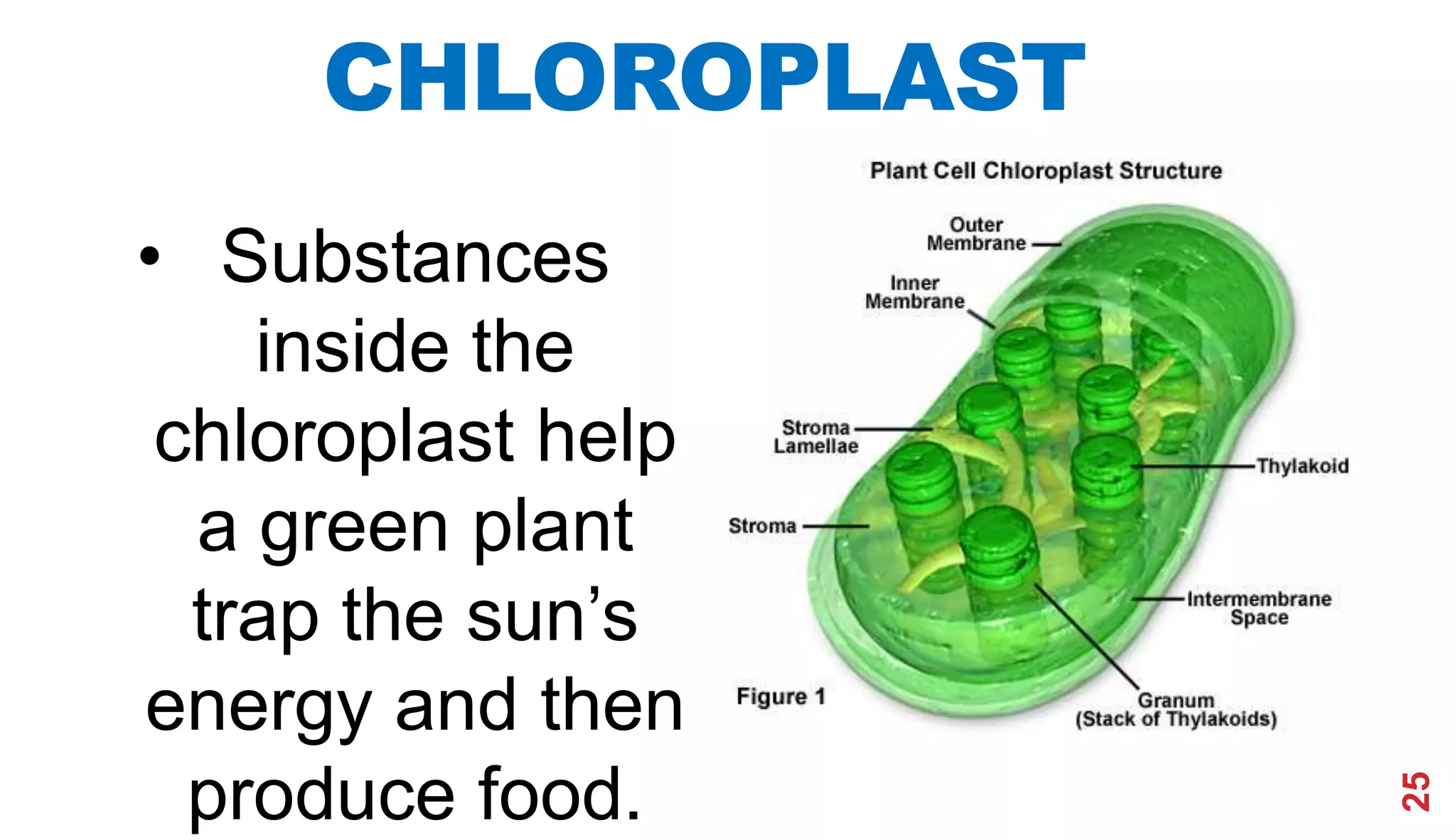
1. The history of cell theory began with early observations of cells in the 17th century by Robert Hooke and refinements in the 19th century by Theodor Schwann and Matthias Schleiden.
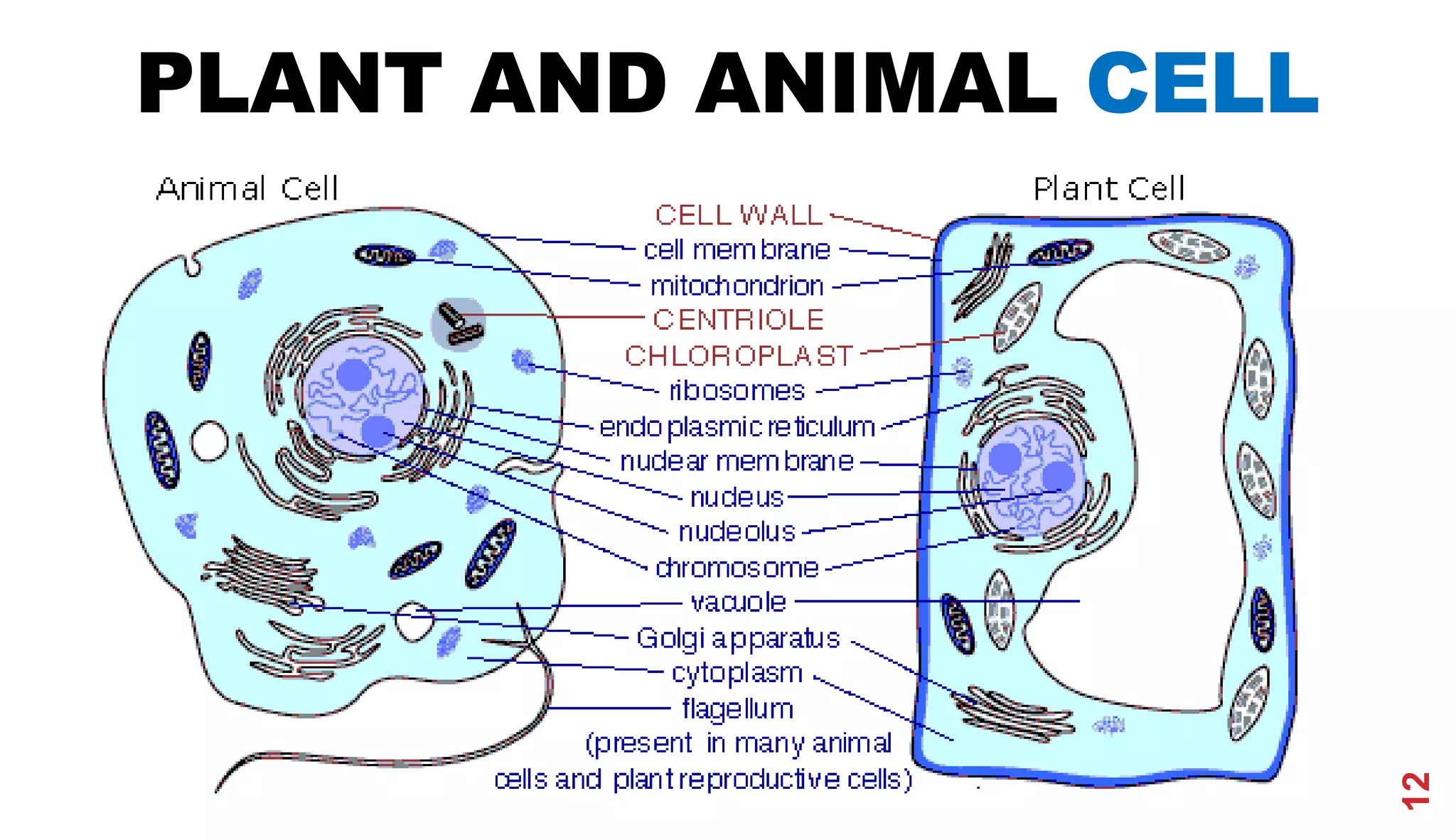
2. Schwann and Schleiden developed the cell theory which stated that the cell is the basic unit of structure and function in living things.
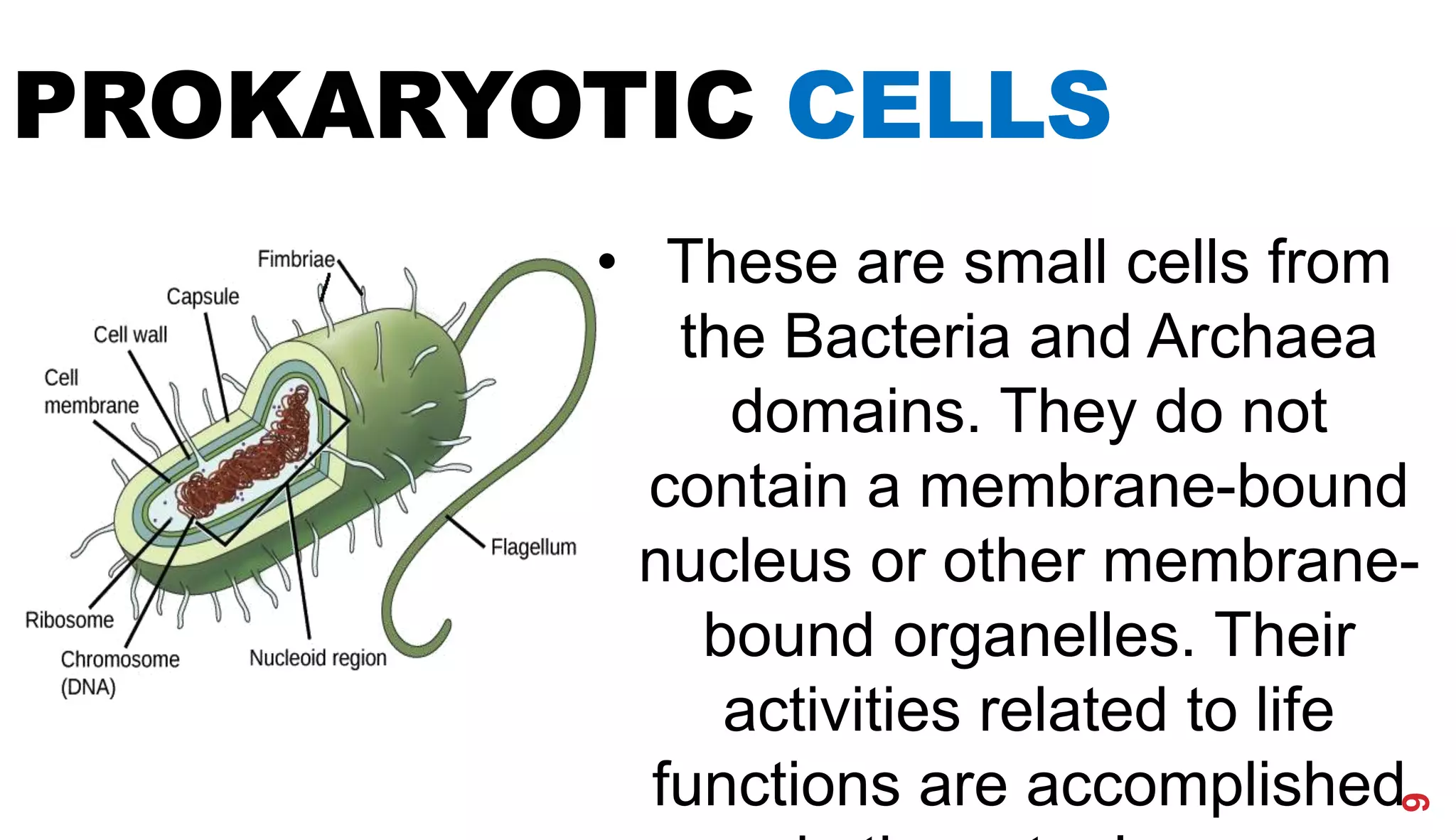
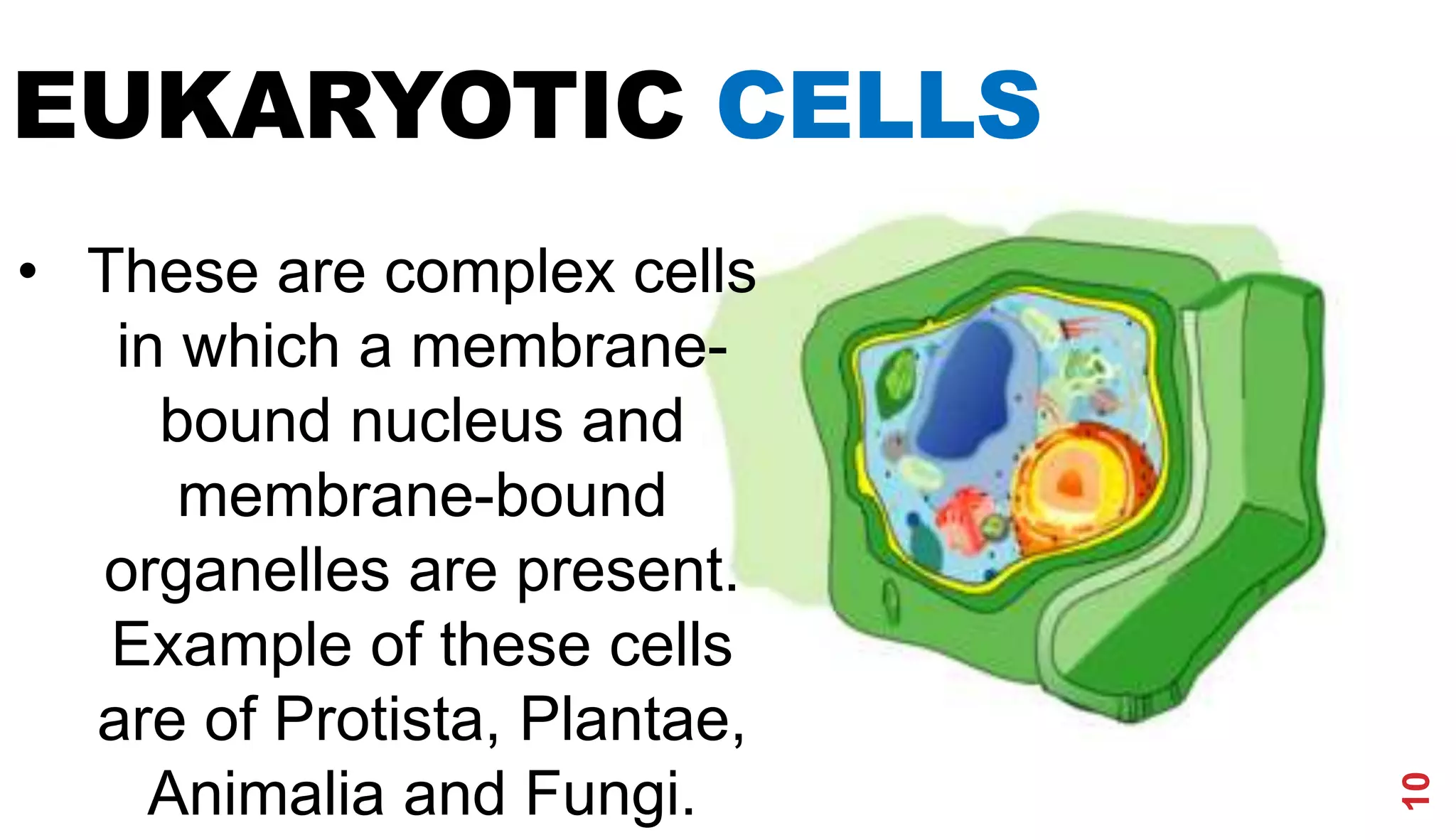
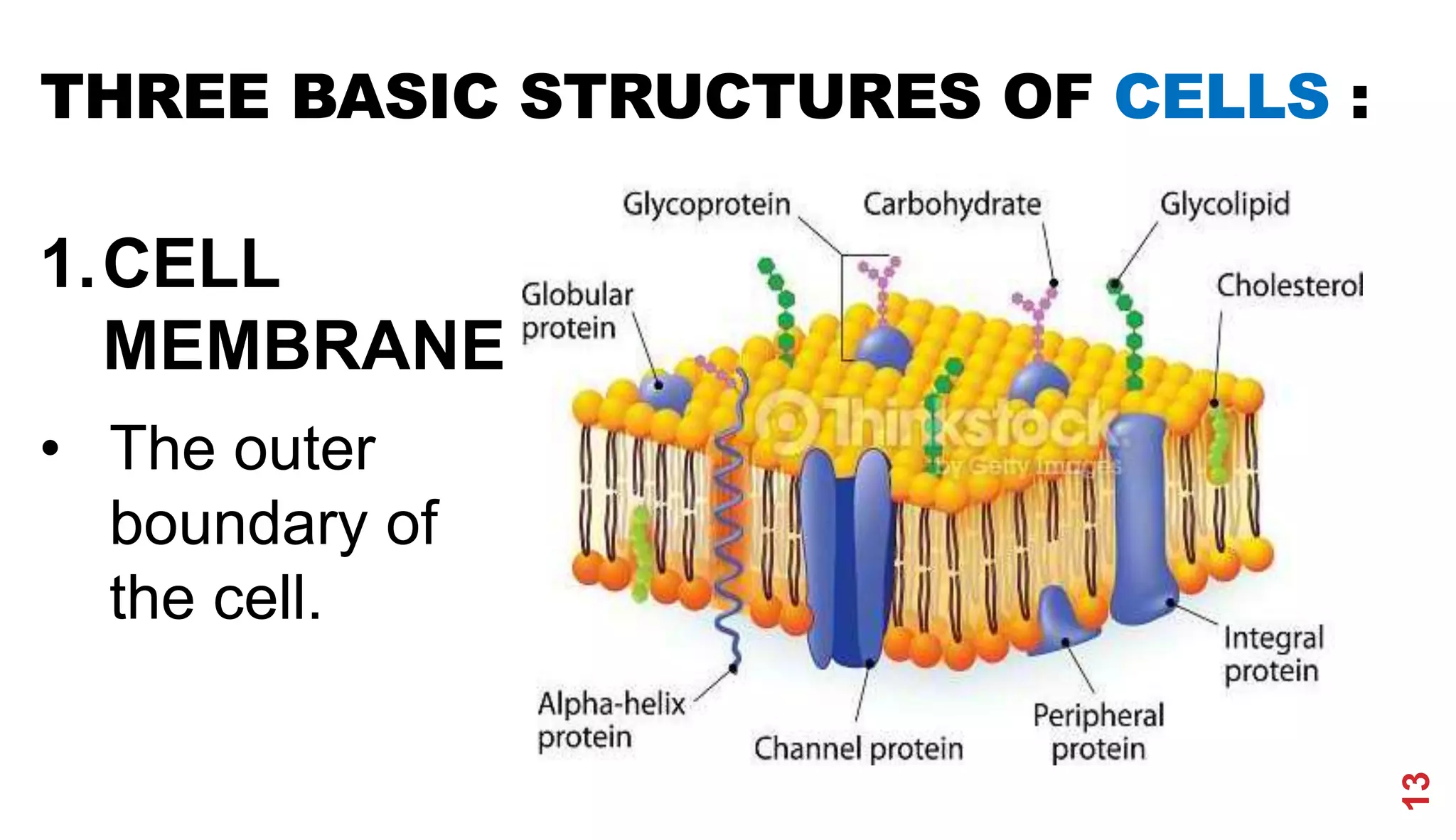
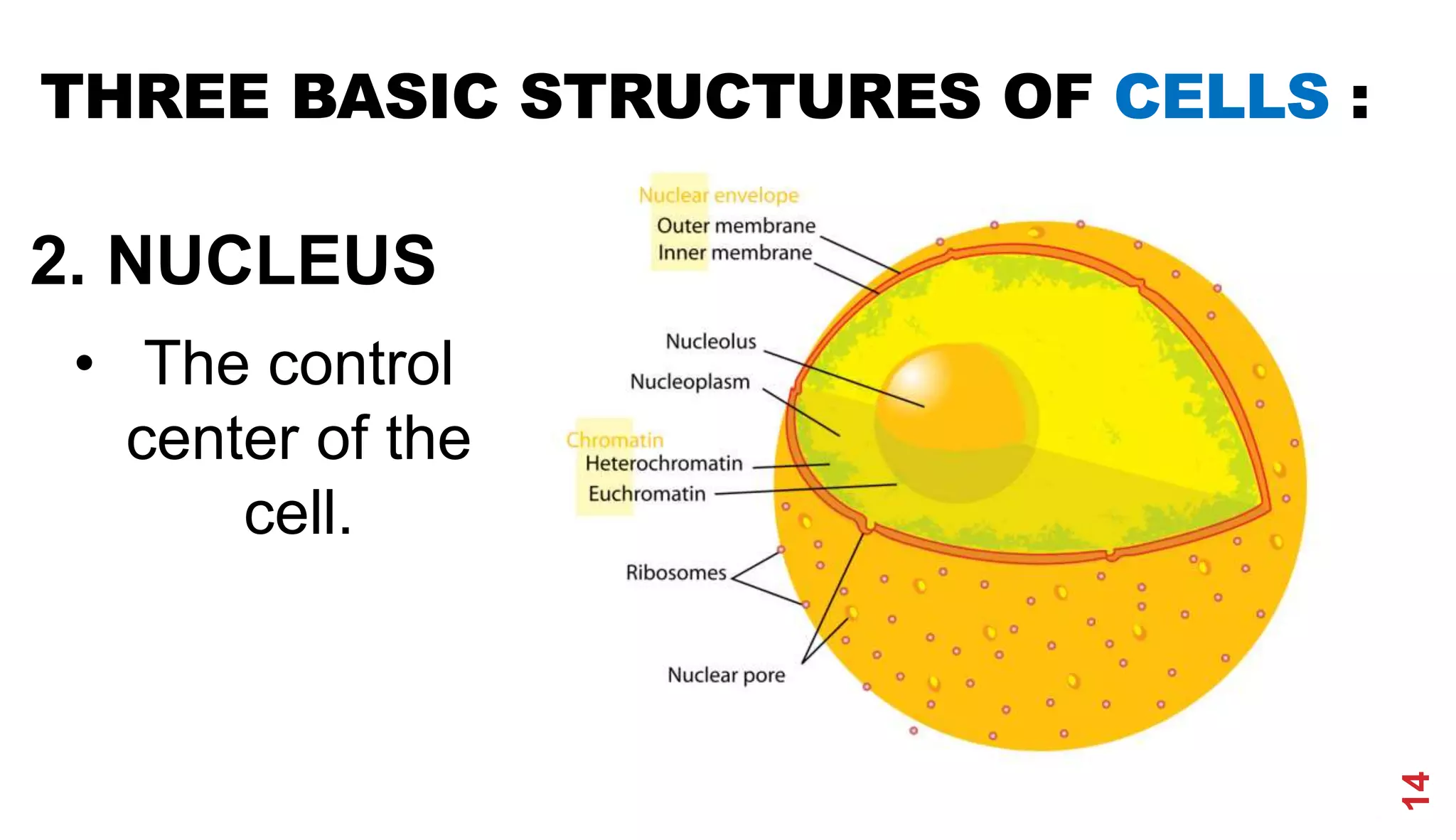
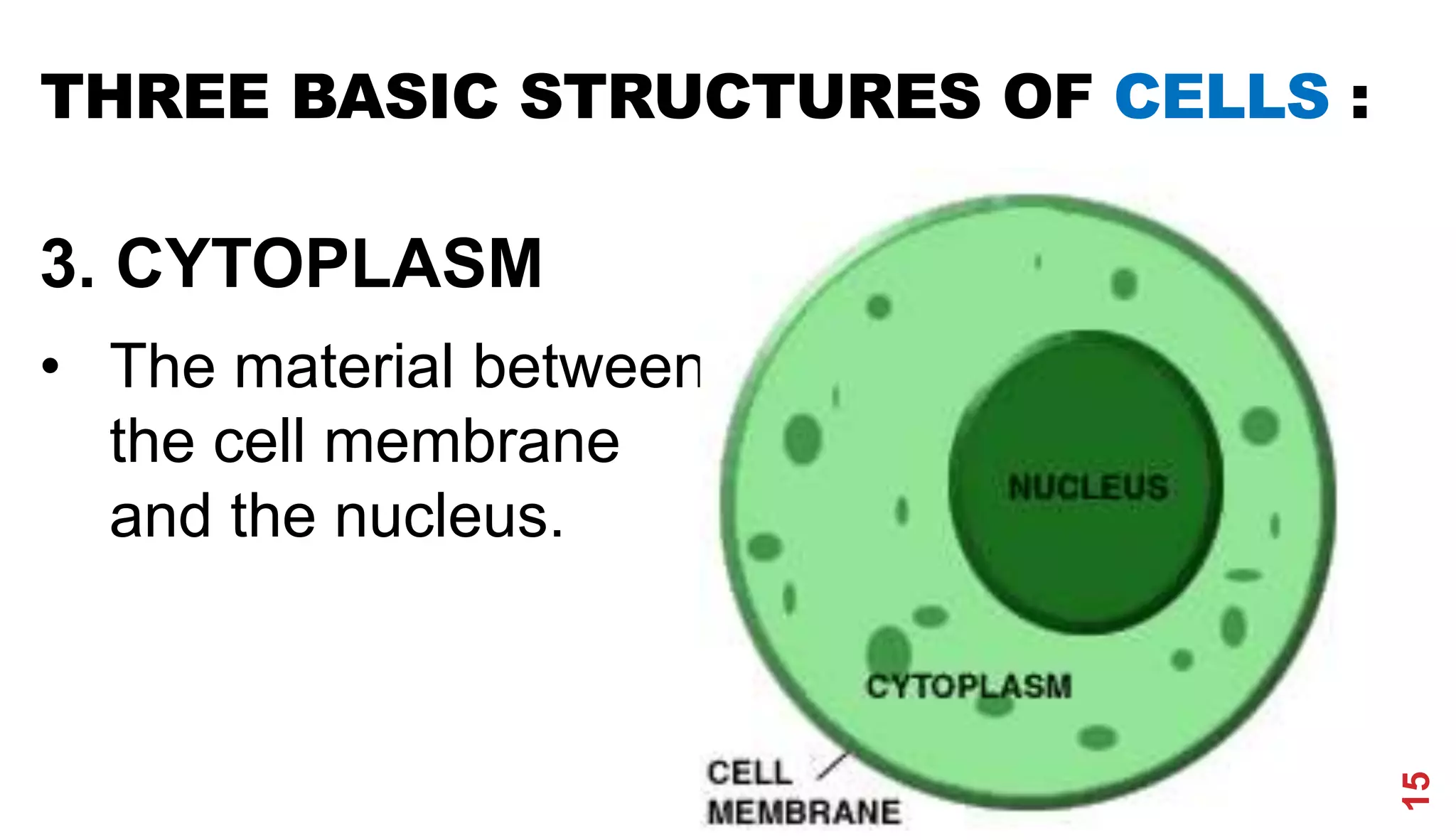
3. Modern cell theory recognizes that all living things are composed of cells, cells arise from preexisting cells, and the cell is the basic functional unit of life.