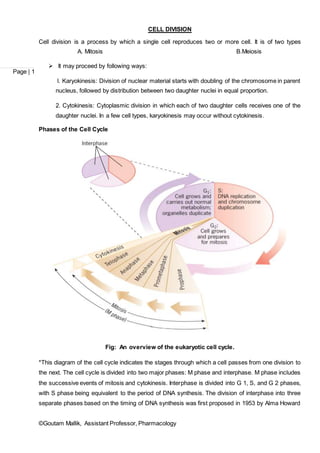
Cell division is the process by which a cell divides into two daughter cells. There are two main types of cell division: mitosis and meiosis. Mitosis produces two identical daughter cells during normal cell growth and replacement. It involves four phases - prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Meiosis produces gametes like sperm and egg, and involves two cell divisions that reduce the chromosome number by half to produce four haploid cells. The cell cycle is the series of events that cells go through as they grow and divide. It consists of interphase and the M phase, which includes mitosis and cytokinesis.