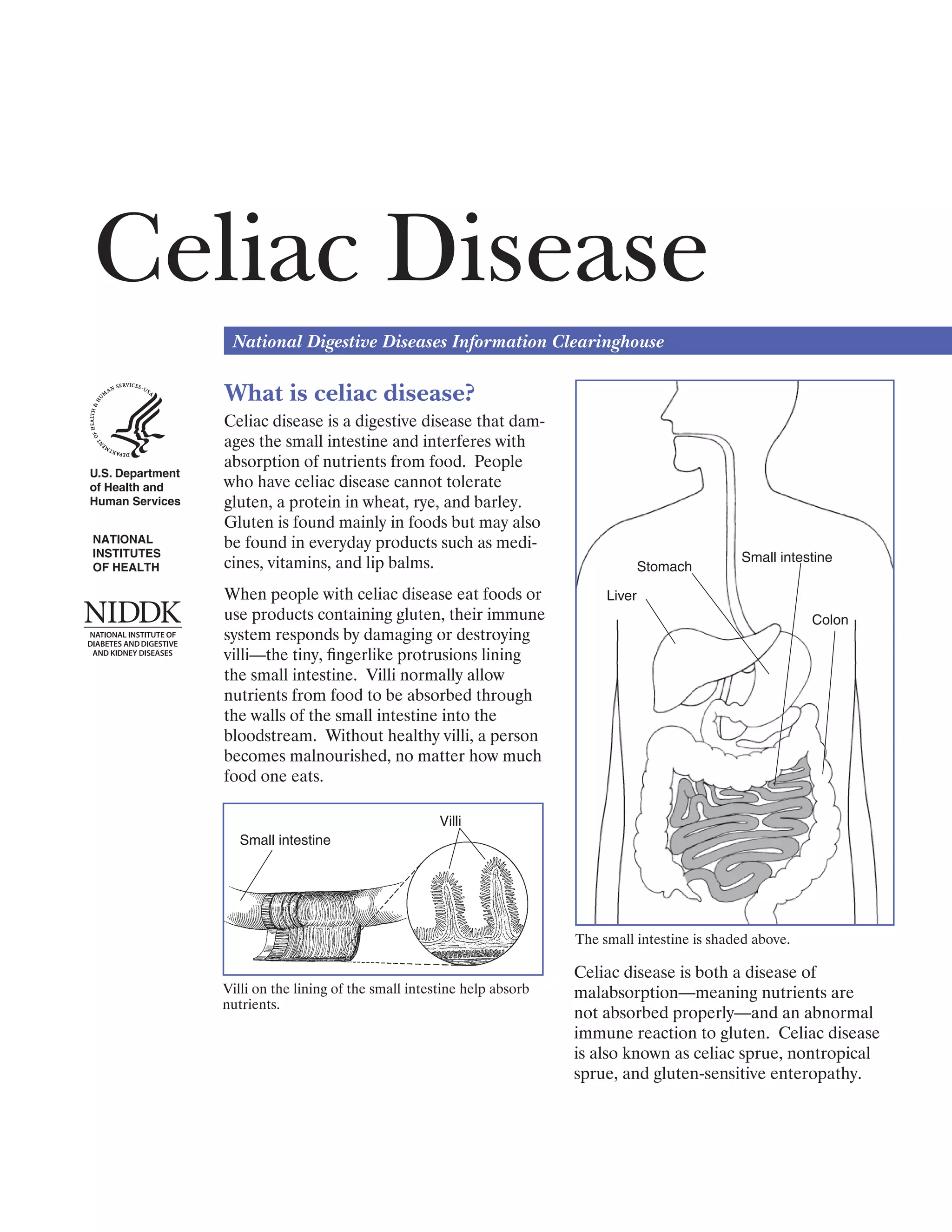
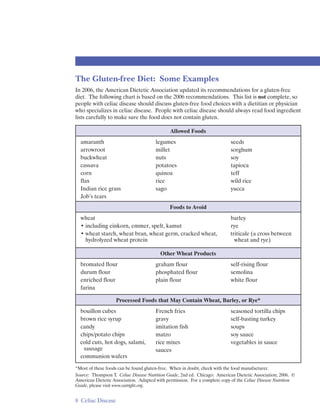
Celiac disease is a digestive disease where eating gluten damages the small intestine and interferes with nutrient absorption. It is an immune reaction to eating gluten, found in wheat, rye, and barley. When people with celiac disease eat gluten, their immune system attacks and damages villi in the small intestine, preventing nutrient absorption. Celiac disease affects about 1 in 133 people in the United States and is underdiagnosed due to its varied symptoms. It is diagnosed through blood tests detecting antibodies and confirmed with a small intestine biopsy. There is no cure for celiac disease other than a lifelong gluten-free diet.