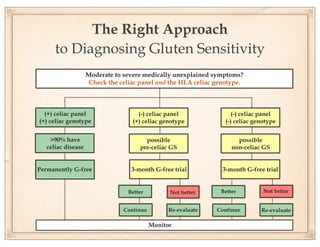
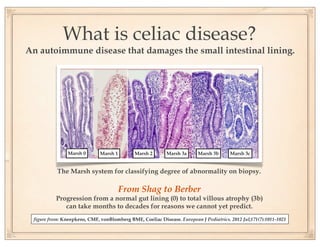
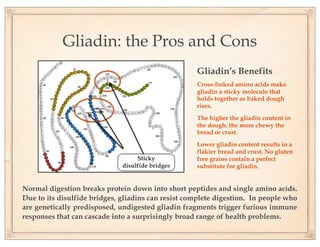
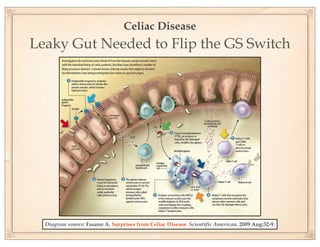
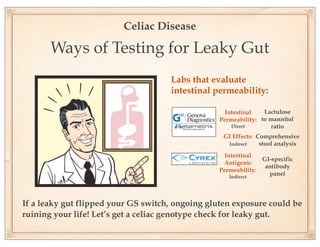
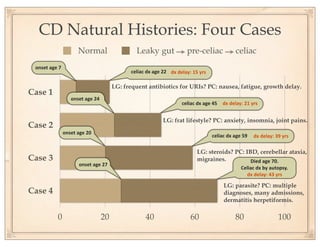
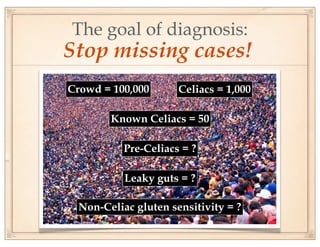
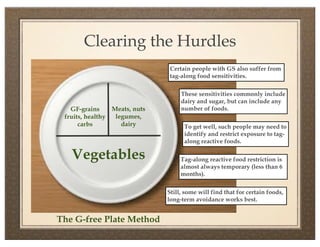
The document discusses gluten sensitivity, its related medical conditions (wheat allergy, celiac disease, non-celiac gluten sensitivity), and the complexity involved in diagnosing and treating these conditions. It emphasizes the importance of a systems medicine approach for patients with unexplained symptoms possibly related to gluten, as conventional celiac panels may not provide sufficient information. Additionally, the document highlights the need for awareness of dietary management and potential health risks associated with gluten exposure.