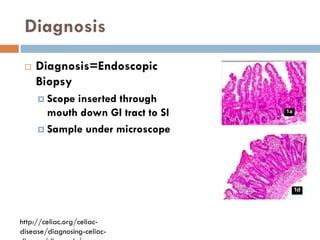
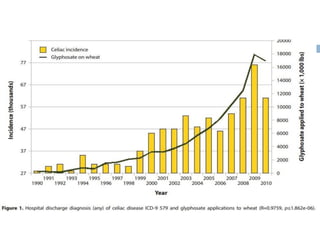
This document provides information about celiac disease and gluten intolerance for dietitians and college students. It defines celiac disease as an autoimmune disorder triggered by ingesting gluten, which can damage the small intestine and cause health problems. Symptoms of celiac disease are described. The key differences between celiac disease, gluten sensitivity, and gluten intolerance are outlined. Living with a gluten-free diet in a college setting is discussed, including resources for gluten-free dining options on campus.