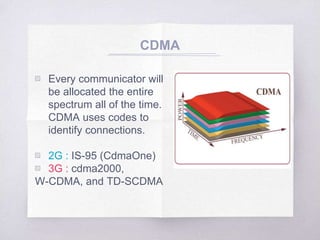
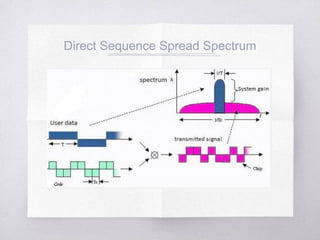
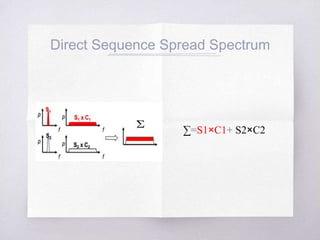
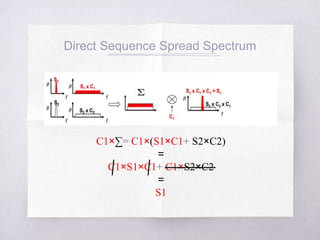
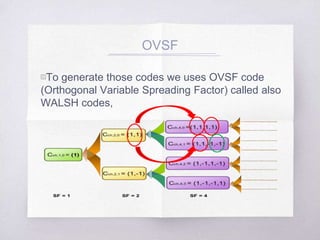
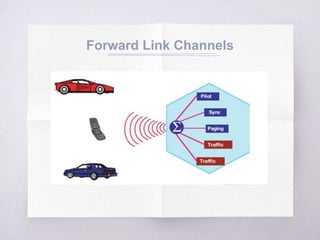
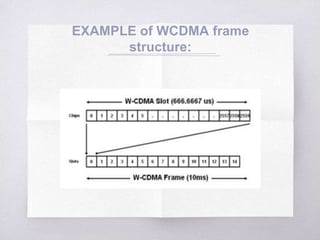
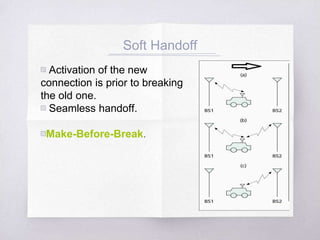
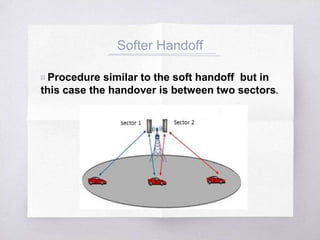
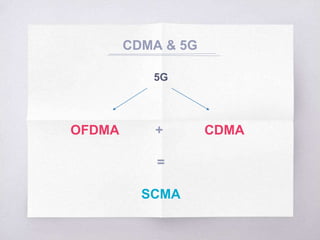
This document discusses Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) concepts. It begins by explaining the need for high-speed data and multiple access techniques like FDMA, TDMA, and CDMA. It describes how CDMA uses direct sequence spread spectrum to allow multiple users to access the same frequency channel by assigning them different spreading codes. The document outlines CDMA's forward and reverse link channels, handoff and power control procedures, advantages like improved capacity and seamless handoffs, and disadvantages like increased complexity compared to other techniques. It concludes by discussing how 5G will combine OFDMA and CDMA using a technique called SCMA.