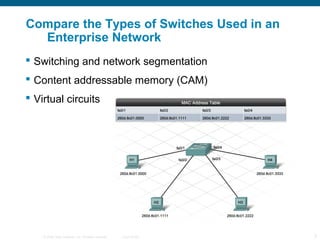
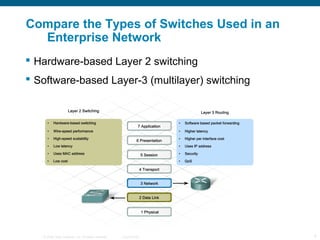
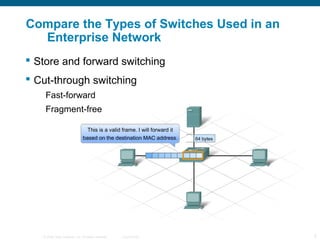
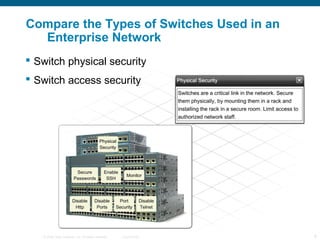
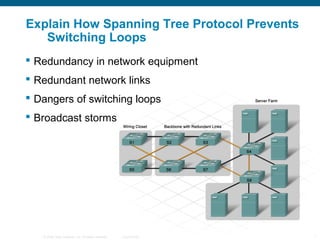
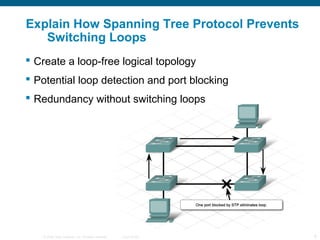
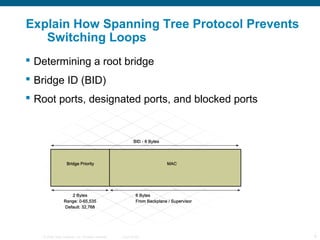
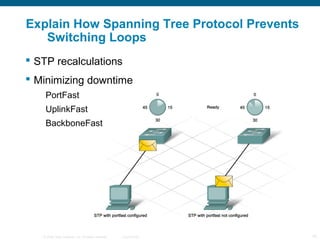
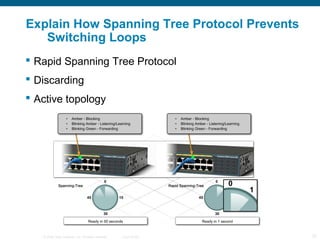
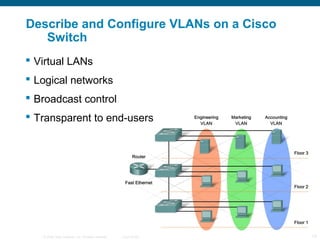
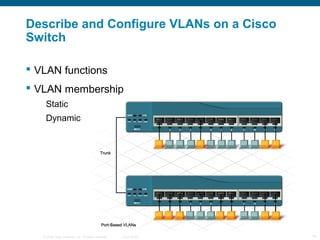
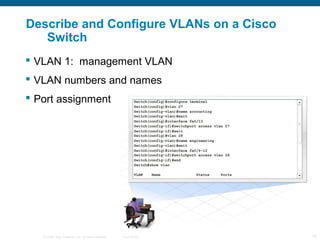
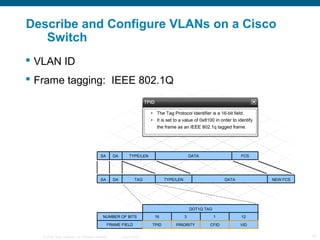
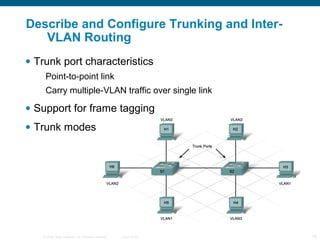
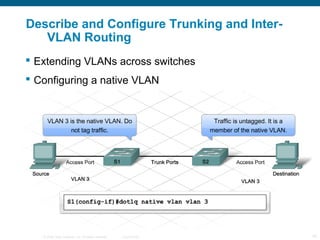
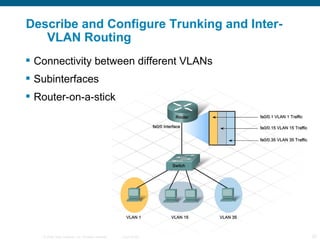
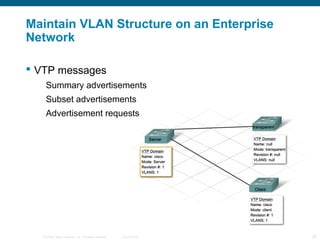
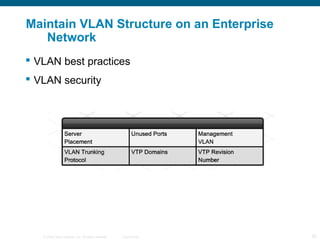
The document discusses switching in enterprise networks. It compares different types of switches used, including hardware-based layer 2 switches and software-based multilayer switches. It explains how spanning tree protocol prevents switching loops by blocking redundant links. It also describes how to configure and maintain VLANs on Cisco switches, including assigning ports, configuring trunking between switches, and using the VLAN Trunking Protocol to manage VLANs across the network. Inter-VLAN routing is enabled using a layer 3 device with subinterfaces.