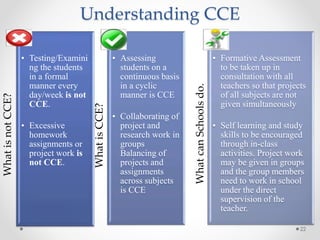
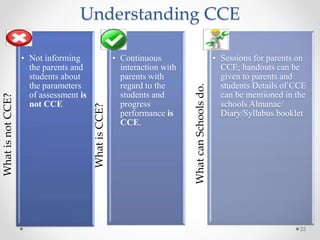
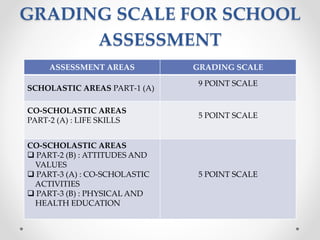
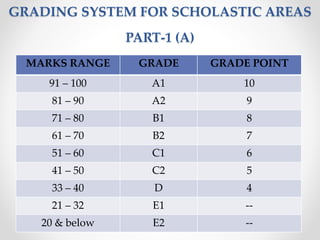
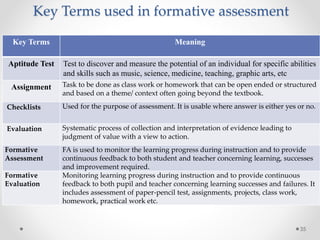
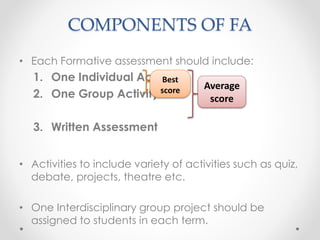
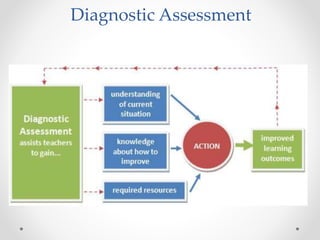
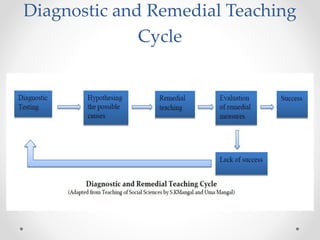
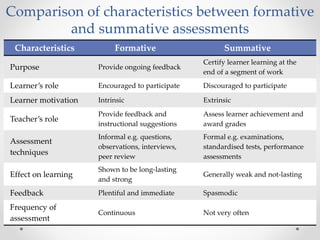
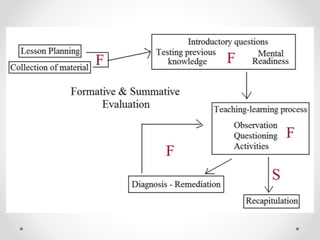
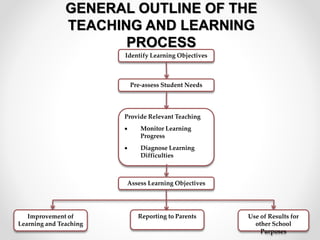
Continuous and comprehensive evaluation (CCE) involves assessing students regularly using multiple methods rather than only through annual exams. CCE aims to evaluate cognitive as well as non-cognitive aspects of learning, provide feedback to improve learning, and reduce student stress. It involves formative and summative assessments that are used to monitor student progress, diagnose learning needs, and improve teaching practices.