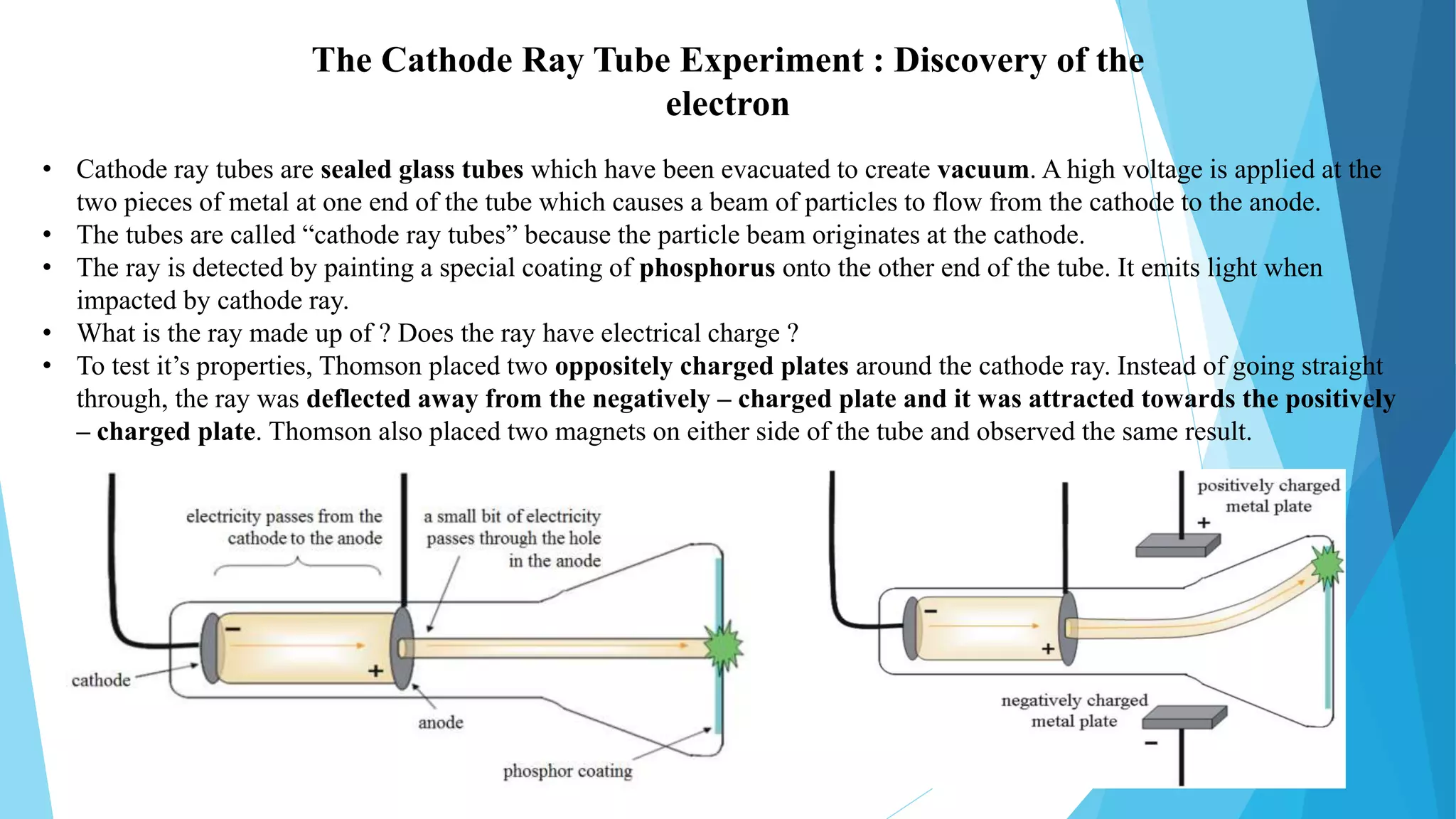
J.J. Thomson was a British physicist who won the 1906 Nobel Prize in Physics for his work on the conduction of electricity in gases. Some of his key accomplishments included discovering the electron in 1897 through experiments with cathode ray tubes, determining the mass-to-charge ratio of electrons, and proposing the "plum pudding" model of the atom. He had a long and distinguished career as a physicist, holding positions at Cambridge University and lecturing widely in the United States. Thomson made many contributions to the field and influenced several students and assistants who went on to also win Nobel Prizes.