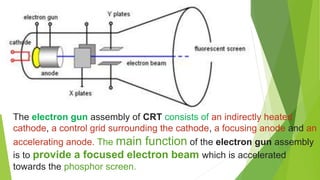
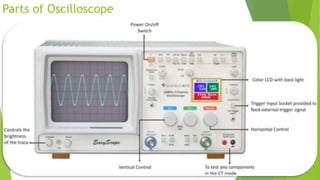
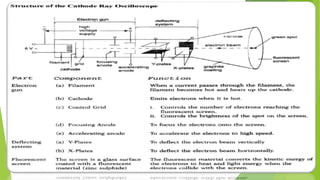
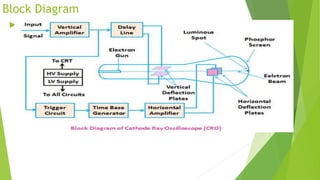
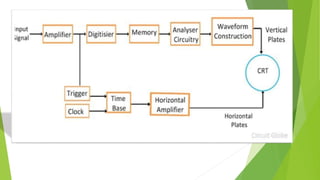
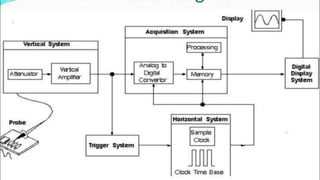
The document provides an overview of the cathode-ray oscilloscope (CRO), detailing its components, controls, and applications in measuring voltage and current signals. It explains the structure and function of the oscilloscope systems, including the vertical, horizontal, and trigger systems, and introduces the digital storage oscilloscope (DSO) which converts analog signals into digital records. The final sections cover the CRO's advantages, usage, and the working principles of digital oscilloscopes.