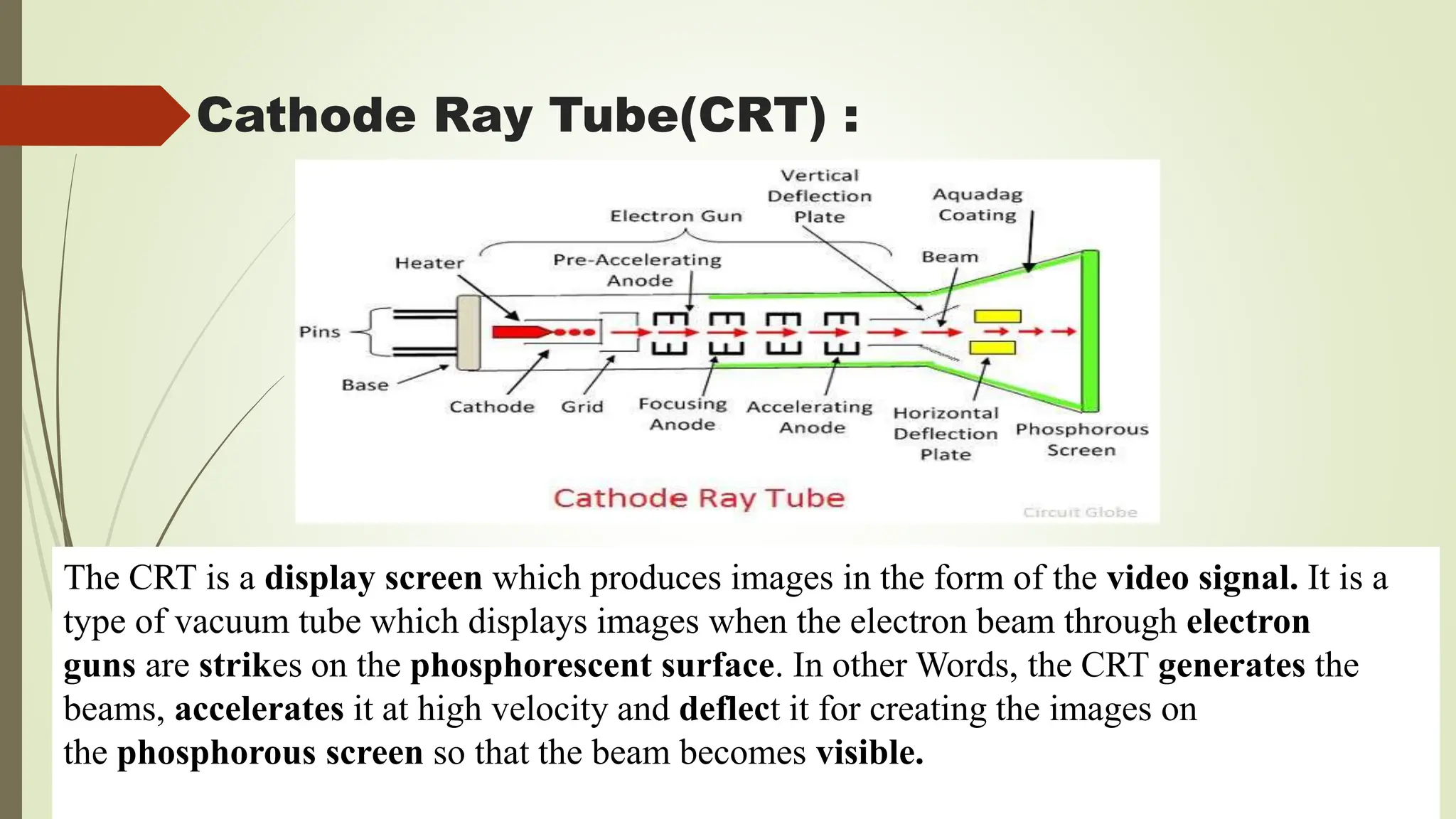
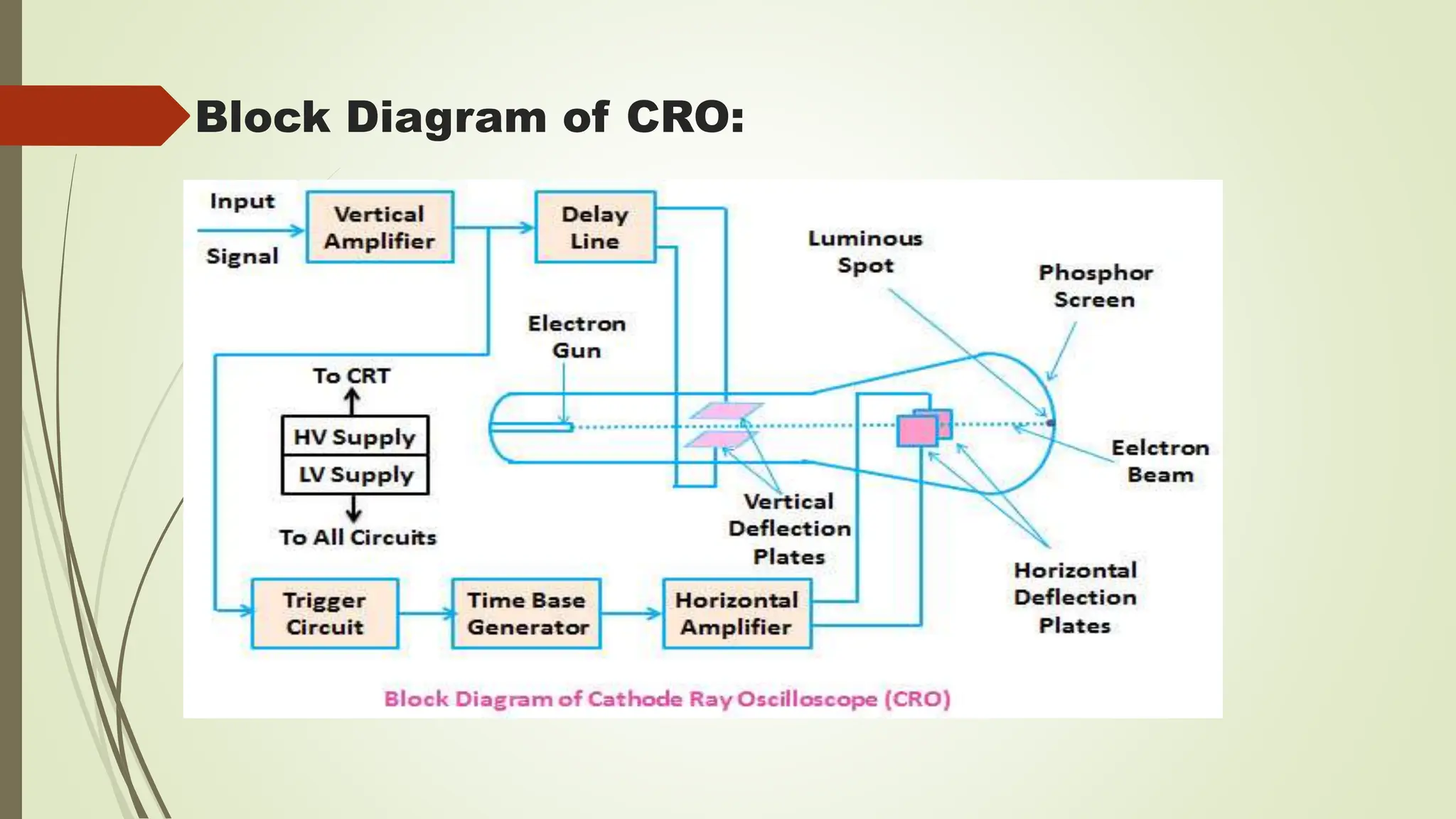
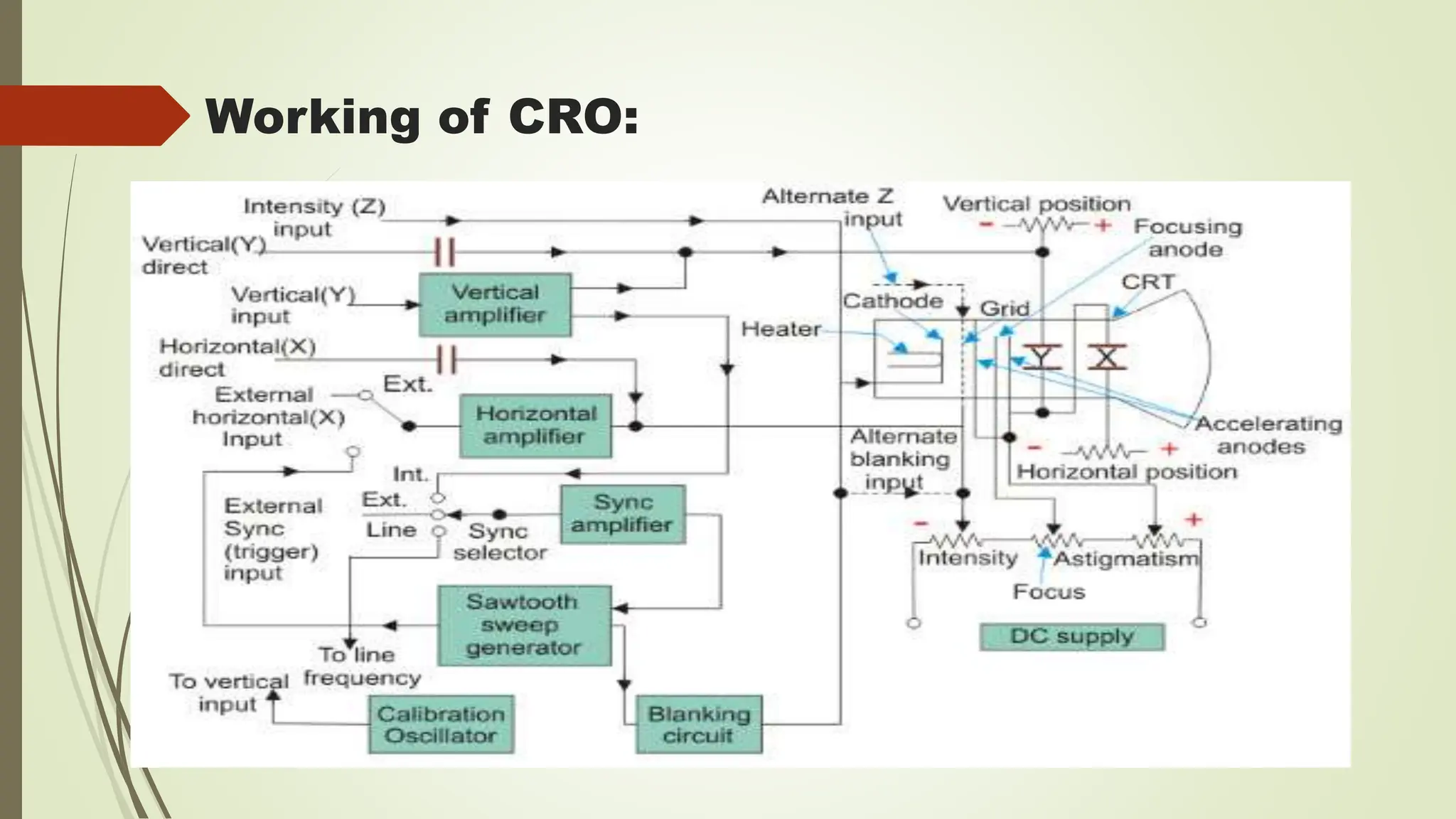
The document introduces the Cathode Ray Oscilloscope (CRO), explaining its structure, including display, vertical and horizontal controllers, and triggers, as well as the role of the cathode ray tube (CRT) in visualizing waveforms. It details the operation of the CRT, which generates images by directing an electron beam onto a phosphorescent screen, and outlines the functionality of the CRO's components, including the vertical and horizontal deflection systems. Finally, it highlights various applications of the CRO, such as voltage and current measurement, waveform analysis, and its use in laboratory settings.