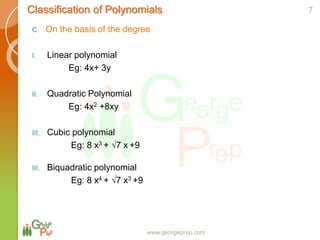
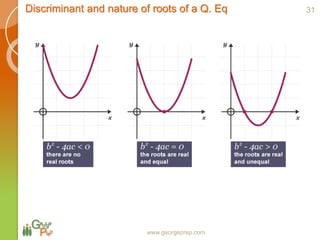
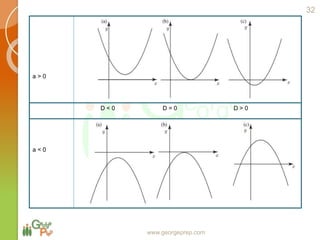
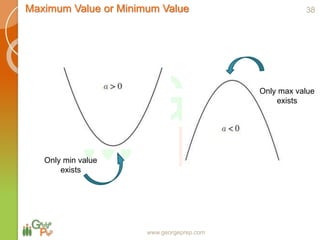
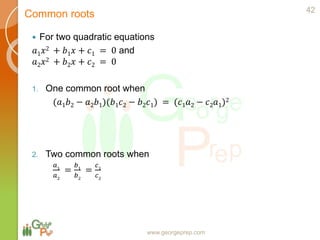
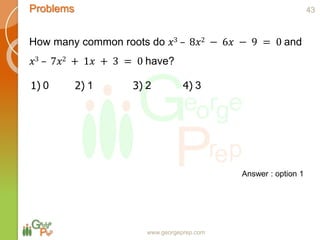
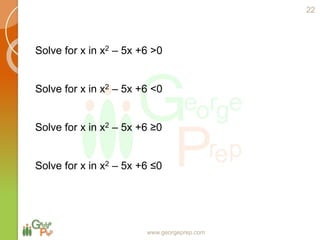This document discusses quadratic and higher order equations. It begins by introducing polynomials and classifying them based on coefficients and degree. Quadratic equations are then examined in more detail, including forming quadratic equations, finding roots using methods like the quadratic formula, and solving quadratic inequalities. The document also covers topics like the sum and product of roots, the discriminant and nature of roots, maximum/minimum values, common roots between equations, and relationships between coefficients and roots for higher order equations. Descartes' rule of signs is presented as a way to determine the number of positive and negative real roots of a polynomial equation.