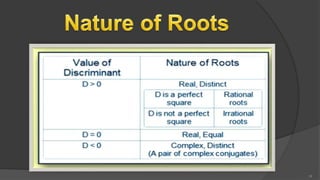
This document discusses quadratic equations. It defines a quadratic equation as having degree 2 in the standard form ax2 + bx + c = 0. It provides examples of quadratic equations and explains that the roots are the values that satisfy the equation. Methods for solving quadratic equations are outlined, including factorization, completing the square, and the quadratic formula. The quadratic formula is defined as x = (-b ± √(b2 - 4ac))/2a. Discriminant is also discussed, which is denoted by D and equals b2 - 4ac, and how it relates to the number of real roots.









![Example :- Find the roots of the
quadratic equation x2 + 4x – 5 = 0
Given quadratic equation is:
x2 + 4x – 5 = 0
Comparing the equation with the standard form,
b = 4, c = -5
(x + b/2)2 = -(c – b2/4)
So, [x + (4/2)]2 = -[-5 – (42/4)]
(x + 2)2 = 5 + 4 ⇒ (x + 2)2 = 9
⇒ (x + 2) = ±√9 ⇒ (x + 2) = ± 3
⇒ x + 2 = 3, x + 2 = -3 ⇒ x = 1 , -5
Therefore, the roots of the given equation are 1 and -5. 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mathspresentationofch4-230110100308-068840ff/85/MATHS-PRESENTATION-OF-CH-4-pptx-10-320.jpg)



![Question: Factorize x2 + 4x – 21 =0
using quadratic formula.
x2 + 4x – 21 = 0
Here, a = 1, b = 4, c = -21
b2 – 4ac = (4)2 – 4(1)(-21) = 16 + 84 = 100
Substituting these values in the quadratic formula, we get;
x = [-4 ± √ (4)2 – 4(1)(-21)]/ 2(1)
= (-4 ± 10)/2
x = (-4 + 10)/2 , x = (-4 – 10)/2
x = 6/2 , x = -14/2
x = 3 , x = -7
Therefore, the factors of quadratic equation are (x – 3) and (x + 7).
14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mathspresentationofch4-230110100308-068840ff/85/MATHS-PRESENTATION-OF-CH-4-pptx-14-320.jpg)