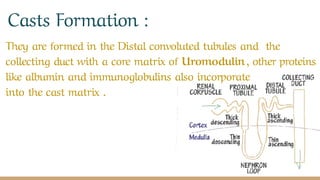
Casts are cylindrical particles found in urine that are formed in the kidney's distal convoluted tubules and collecting duct. They are composed of Tamm-Horsfall protein and other substances filtered from the blood. Casts come in various shapes and sizes depending on the tubule diameter and can be acellular (containing only protein) or cellular (containing cells and debris). The presence of casts provides information about kidney function and diseases, with hyaline casts being most common and fatty, red blood cell, or white blood cell casts indicating more serious conditions such as infection or kidney failure.