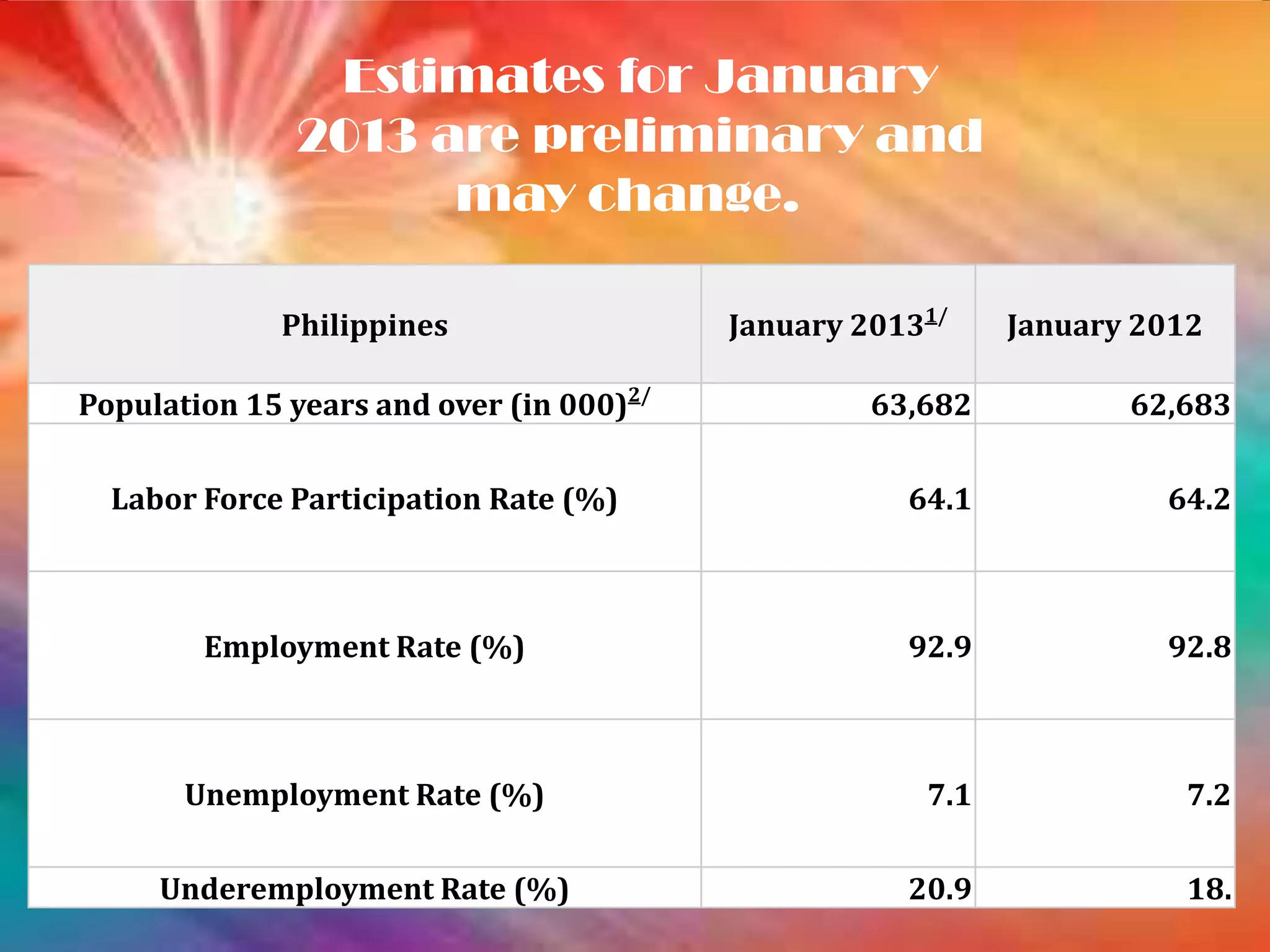
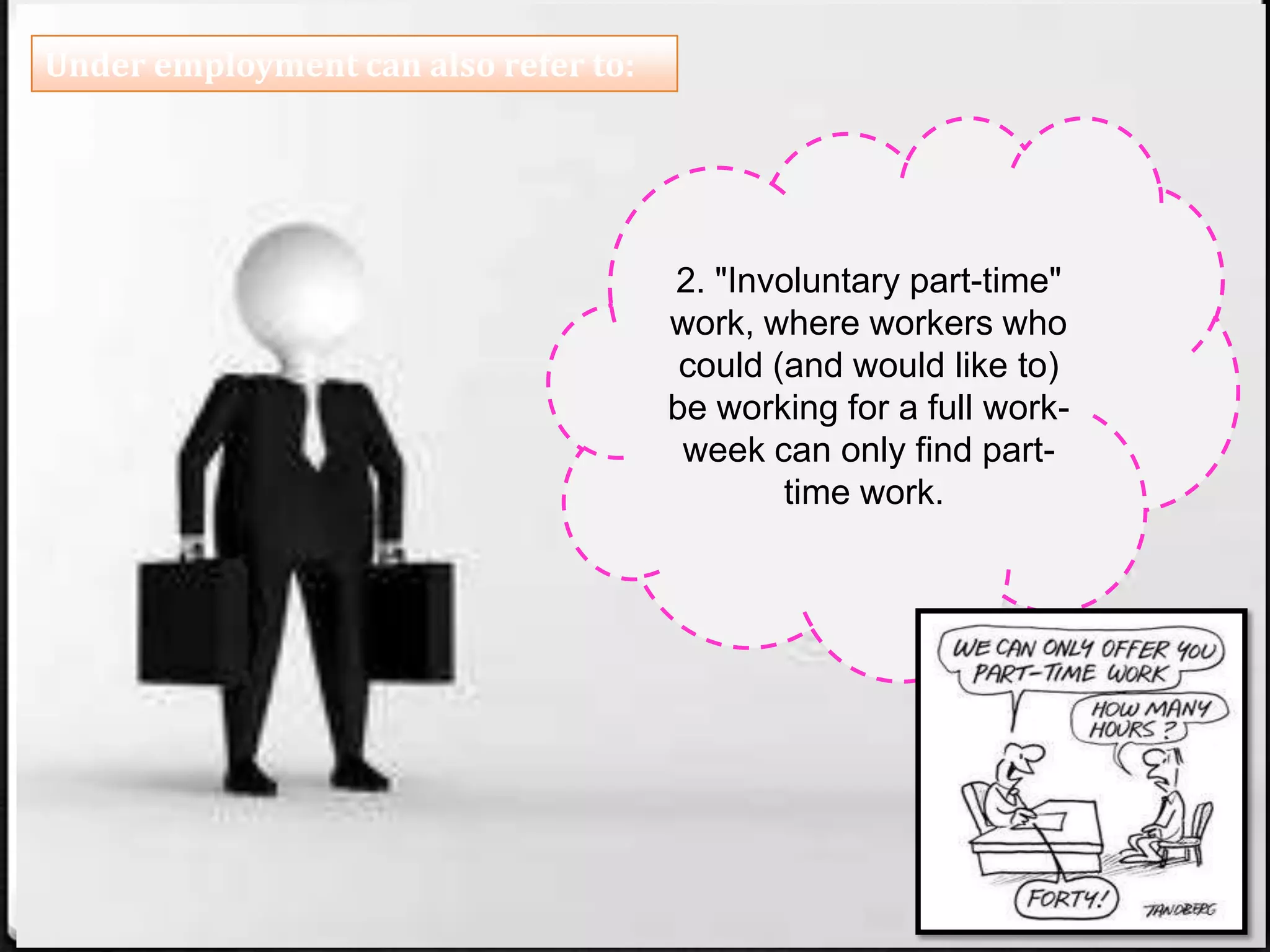
The document discusses unemployment and its causes, effects, and types. It notes that over 70% of the Philippines' labor force has low levels of education. Unemployment can cause mental health issues, loss of income, and loss of skills over time. The main types of unemployment mentioned are seasonal, cyclical, frictional, technical, and disguised unemployment. The document also discusses underemployment and argues that vocational training could help address mismatches between education and labor market needs. It notes vocational programs provide practical skills without the costs of more formal schooling.